 Xem trên TensorFlow.org Xem trên TensorFlow.org |  Chạy trong Google Colab Chạy trong Google Colab |  Xem nguồn trên GitHub Xem nguồn trên GitHub |  Tải xuống sổ ghi chép Tải xuống sổ ghi chép |
Hướng dẫn này giới thiệu bộ mã tự động với ba ví dụ: khái niệm cơ bản, làm giảm hình ảnh và phát hiện bất thường.
Autoencoder là một loại mạng thần kinh đặc biệt được huấn luyện để sao chép đầu vào của nó thành đầu ra của nó. Ví dụ: cho một hình ảnh của một chữ số viết tay, trước tiên, một bộ mã tự động mã hóa hình ảnh thành một biểu diễn tiềm ẩn có chiều thấp hơn, sau đó giải mã biểu diễn tiềm ẩn trở lại một hình ảnh. Trình mã tự động học cách nén dữ liệu trong khi giảm thiểu lỗi xây dựng lại.
Để tìm hiểu thêm về autoencoders, vui lòng đọc chương 14 từ Deep Learning của Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio và Aaron Courville.
Nhập TensorFlow và các thư viện khác
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score, recall_score
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.keras import layers, losses
from tensorflow.keras.datasets import fashion_mnist
from tensorflow.keras.models import Model
Tải tập dữ liệu
Để bắt đầu, bạn sẽ đào tạo trình mã tự động cơ bản bằng cách sử dụng bộ dữ liệu Fashion MNIST. Mỗi hình ảnh trong tập dữ liệu này có kích thước 28x28 pixel.
(x_train, _), (x_test, _) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
print (x_train.shape)
print (x_test.shape)
Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz 32768/29515 [=================================] - 0s 0us/step 40960/29515 [=========================================] - 0s 0us/step Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz 26427392/26421880 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step 26435584/26421880 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz 16384/5148 [===============================================================================================] - 0s 0us/step Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/tf-keras-datasets/t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz 4423680/4422102 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step 4431872/4422102 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step (60000, 28, 28) (10000, 28, 28)
Ví dụ đầu tiên: Trình mã tự động cơ bản
Xác định một bộ mã tự động có hai lớp Mật độ: một encoder nén hình ảnh thành một vectơ tiềm ẩn 64 chiều và một decoder , tái tạo lại hình ảnh ban đầu từ không gian tiềm ẩn.
Để xác định mô hình của bạn, hãy sử dụng API phân lớp mô hình Keras .
latent_dim = 64
class Autoencoder(Model):
def __init__(self, latent_dim):
super(Autoencoder, self).__init__()
self.latent_dim = latent_dim
self.encoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(latent_dim, activation='relu'),
])
self.decoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(784, activation='sigmoid'),
layers.Reshape((28, 28))
])
def call(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return decoded
autoencoder = Autoencoder(latent_dim)
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=losses.MeanSquaredError())
Đào tạo mô hình bằng cách sử dụng x_train làm đầu vào và mục tiêu. Bộ encoder sẽ học cách nén tập dữ liệu từ 784 kích thước vào không gian tiềm ẩn và decoder sẽ học cách tái tạo lại các hình ảnh ban đầu. .
autoencoder.fit(x_train, x_train,
epochs=10,
shuffle=True,
validation_data=(x_test, x_test))
Epoch 1/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 4s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0243 - val_loss: 0.0140 Epoch 2/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0116 - val_loss: 0.0106 Epoch 3/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0100 - val_loss: 0.0098 Epoch 4/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0094 - val_loss: 0.0094 Epoch 5/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0092 - val_loss: 0.0092 Epoch 6/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0090 - val_loss: 0.0091 Epoch 7/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0090 - val_loss: 0.0090 Epoch 8/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0089 - val_loss: 0.0090 Epoch 9/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0088 - val_loss: 0.0089 Epoch 10/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 3s 2ms/step - loss: 0.0088 - val_loss: 0.0089 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7ff1d35df550>
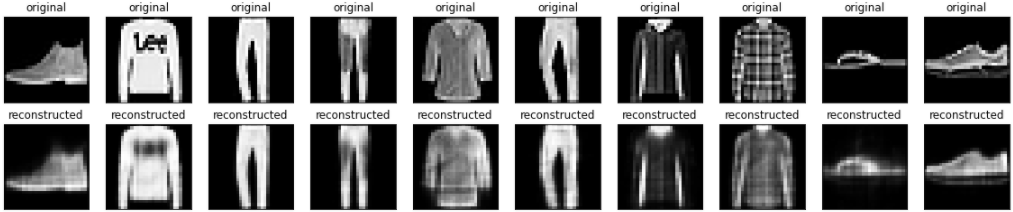
Bây giờ mô hình đã được huấn luyện, chúng ta hãy kiểm tra nó bằng cách mã hóa và giải mã hình ảnh từ bộ thử nghiệm.
encoded_imgs = autoencoder.encoder(x_test).numpy()
decoded_imgs = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_imgs).numpy()
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
# display original
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1)
plt.imshow(x_test[i])
plt.title("original")
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
# display reconstruction
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1 + n)
plt.imshow(decoded_imgs[i])
plt.title("reconstructed")
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()

Ví dụ thứ hai: Hình ảnh giảm giá trị
Một bộ mã tự động cũng có thể được đào tạo để loại bỏ nhiễu khỏi hình ảnh. Trong phần sau, bạn sẽ tạo một phiên bản nhiễu của tập dữ liệu Fashion MNIST bằng cách áp dụng nhiễu ngẫu nhiên cho mỗi hình ảnh. Sau đó, bạn sẽ đào tạo một bộ mã tự động sử dụng hình ảnh nhiễu làm đầu vào và hình ảnh gốc làm mục tiêu.
Hãy nhập lại tập dữ liệu để bỏ qua các sửa đổi đã thực hiện trước đó.
(x_train, _), (x_test, _) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') / 255.
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') / 255.
x_train = x_train[..., tf.newaxis]
x_test = x_test[..., tf.newaxis]
print(x_train.shape)
(60000, 28, 28, 1)
Thêm nhiễu ngẫu nhiên vào hình ảnh
noise_factor = 0.2
x_train_noisy = x_train + noise_factor * tf.random.normal(shape=x_train.shape)
x_test_noisy = x_test + noise_factor * tf.random.normal(shape=x_test.shape)
x_train_noisy = tf.clip_by_value(x_train_noisy, clip_value_min=0., clip_value_max=1.)
x_test_noisy = tf.clip_by_value(x_test_noisy, clip_value_min=0., clip_value_max=1.)
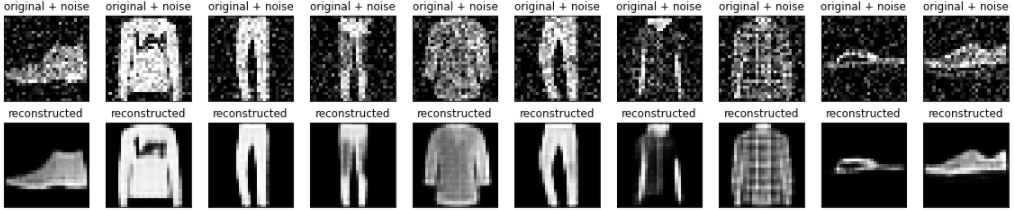
Vẽ các hình ảnh nhiễu.
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 2))
for i in range(n):
ax = plt.subplot(1, n, i + 1)
plt.title("original + noise")
plt.imshow(tf.squeeze(x_test_noisy[i]))
plt.gray()
plt.show()
Xác định một mã tự động mã hóa phức hợp
Trong ví dụ này, bạn sẽ đào tạo một bộ mã tự động tích hợp bằng cách sử dụng các lớp Conv2D trong encoder và các lớp Conv2DTranspose trong decoder .
class Denoise(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(Denoise, self).__init__()
self.encoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Input(shape=(28, 28, 1)),
layers.Conv2D(16, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', strides=2),
layers.Conv2D(8, (3, 3), activation='relu', padding='same', strides=2)])
self.decoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Conv2DTranspose(8, kernel_size=3, strides=2, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, activation='relu', padding='same'),
layers.Conv2D(1, kernel_size=(3, 3), activation='sigmoid', padding='same')])
def call(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return decoded
autoencoder = Denoise()
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=losses.MeanSquaredError())
autoencoder.fit(x_train_noisy, x_train,
epochs=10,
shuffle=True,
validation_data=(x_test_noisy, x_test))
Epoch 1/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 8s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0169 - val_loss: 0.0107 Epoch 2/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0095 - val_loss: 0.0086 Epoch 3/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0082 - val_loss: 0.0080 Epoch 4/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0078 - val_loss: 0.0077 Epoch 5/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0076 - val_loss: 0.0075 Epoch 6/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0074 - val_loss: 0.0074 Epoch 7/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0073 - val_loss: 0.0073 Epoch 8/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0072 - val_loss: 0.0072 Epoch 9/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0071 - val_loss: 0.0071 Epoch 10/10 1875/1875 [==============================] - 6s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0070 - val_loss: 0.0071 <keras.callbacks.History at 0x7ff1c45a31d0>
Hãy cùng xem tóm tắt về bộ mã hóa. Lưu ý cách hình ảnh được lấy mẫu từ 28x28 xuống 7x7.
autoencoder.encoder.summary()
Model: "sequential_2"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d (Conv2D) (None, 14, 14, 16) 160
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 7, 7, 8) 1160
=================================================================
Total params: 1,320
Trainable params: 1,320
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
Bộ giải mã nâng cấp các hình ảnh từ 7x7 lên 28x28.
autoencoder.decoder.summary()
Model: "sequential_3"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d_transpose (Conv2DTra (None, 14, 14, 8) 584
nspose)
conv2d_transpose_1 (Conv2DT (None, 28, 28, 16) 1168
ranspose)
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 28, 28, 1) 145
=================================================================
Total params: 1,897
Trainable params: 1,897
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
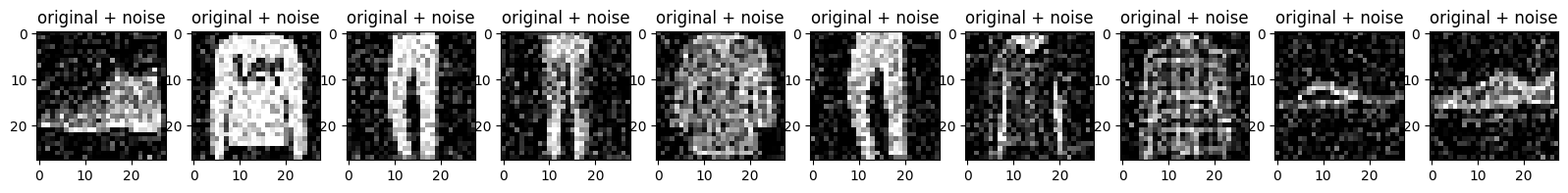
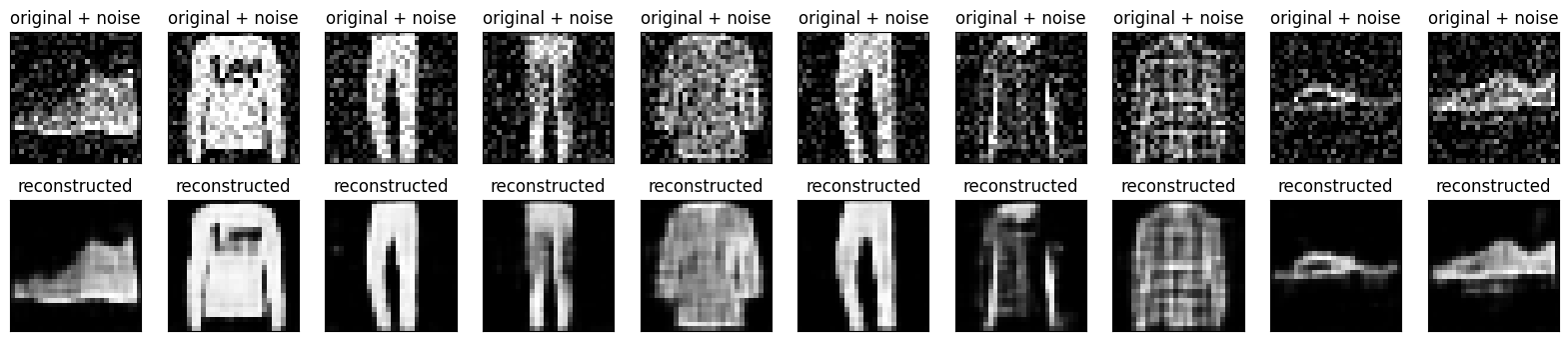
Vẽ cả hình ảnh nhiễu và hình ảnh bị nhiễu do bộ mã tự động tạo ra.
encoded_imgs = autoencoder.encoder(x_test).numpy()
decoded_imgs = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_imgs).numpy()
n = 10
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 4))
for i in range(n):
# display original + noise
ax = plt.subplot(2, n, i + 1)
plt.title("original + noise")
plt.imshow(tf.squeeze(x_test_noisy[i]))
plt.gray()
ax.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
# display reconstruction
bx = plt.subplot(2, n, i + n + 1)
plt.title("reconstructed")
plt.imshow(tf.squeeze(decoded_imgs[i]))
plt.gray()
bx.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
bx.get_yaxis().set_visible(False)
plt.show()
Ví dụ thứ ba: Phát hiện bất thường
Tổng quat
Trong ví dụ này, bạn sẽ đào tạo một bộ mã tự động để phát hiện các điểm bất thường trên tập dữ liệu ECG5000 . Bộ dữ liệu này chứa 5.000 điện tâm đồ , mỗi biểu đồ có 140 điểm dữ liệu. Bạn sẽ sử dụng phiên bản đơn giản hóa của tập dữ liệu, trong đó mỗi ví dụ được gắn nhãn 0 (tương ứng với nhịp điệu bất thường) hoặc 1 (tương ứng với nhịp điệu bình thường). Bạn quan tâm đến việc xác định các nhịp điệu bất thường.
Bạn sẽ làm cách nào để phát hiện những điểm bất thường bằng cách sử dụng một bộ mã tự động? Nhớ lại rằng một trình mã tự động được đào tạo để giảm thiểu lỗi xây dựng lại. Bạn sẽ đào tạo một tự động mã hóa chỉ theo nhịp điệu bình thường, sau đó sử dụng nó để tạo lại tất cả dữ liệu. Giả thuyết của chúng tôi là nhịp điệu bất thường sẽ có sai số tái tạo cao hơn. Sau đó, bạn sẽ phân loại nhịp điệu là dị thường nếu lỗi xây dựng lại vượt qua ngưỡng cố định.
Tải dữ liệu điện tâm đồ
Tập dữ liệu bạn sẽ sử dụng dựa trên tập dữ liệu từ timeseriesclassification.com .
# Download the dataset
dataframe = pd.read_csv('http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/ecg.csv', header=None)
raw_data = dataframe.values
dataframe.head()
# The last element contains the labels
labels = raw_data[:, -1]
# The other data points are the electrocadriogram data
data = raw_data[:, 0:-1]
train_data, test_data, train_labels, test_labels = train_test_split(
data, labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=21
)
Chuẩn hóa dữ liệu thành [0,1] .
min_val = tf.reduce_min(train_data)
max_val = tf.reduce_max(train_data)
train_data = (train_data - min_val) / (max_val - min_val)
test_data = (test_data - min_val) / (max_val - min_val)
train_data = tf.cast(train_data, tf.float32)
test_data = tf.cast(test_data, tf.float32)
Bạn sẽ đào tạo trình mã tự động chỉ sử dụng các nhịp điệu bình thường, được gắn nhãn trong tập dữ liệu này là 1 . Tách các nhịp điệu bình thường khỏi các nhịp điệu bất thường.
train_labels = train_labels.astype(bool)
test_labels = test_labels.astype(bool)
normal_train_data = train_data[train_labels]
normal_test_data = test_data[test_labels]
anomalous_train_data = train_data[~train_labels]
anomalous_test_data = test_data[~test_labels]
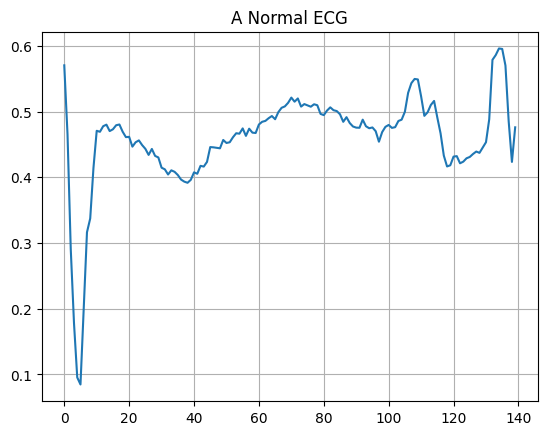
Vẽ một điện tâm đồ bình thường.
plt.grid()
plt.plot(np.arange(140), normal_train_data[0])
plt.title("A Normal ECG")
plt.show()
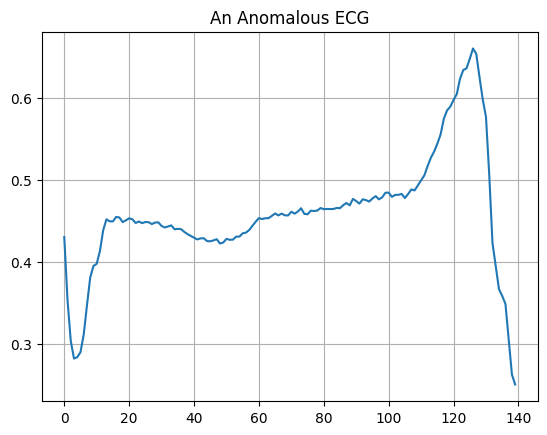
Vẽ một ECG bất thường.
plt.grid()
plt.plot(np.arange(140), anomalous_train_data[0])
plt.title("An Anomalous ECG")
plt.show()
Xây dựng mô hình
class AnomalyDetector(Model):
def __init__(self):
super(AnomalyDetector, self).__init__()
self.encoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(32, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(16, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(8, activation="relu")])
self.decoder = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(16, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(32, activation="relu"),
layers.Dense(140, activation="sigmoid")])
def call(self, x):
encoded = self.encoder(x)
decoded = self.decoder(encoded)
return decoded
autoencoder = AnomalyDetector()
autoencoder.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mae')
Lưu ý rằng bộ mã tự động chỉ được đào tạo bằng cách sử dụng ECG thông thường, nhưng được đánh giá bằng cách sử dụng bộ thử nghiệm đầy đủ.
history = autoencoder.fit(normal_train_data, normal_train_data,
epochs=20,
batch_size=512,
validation_data=(test_data, test_data),
shuffle=True)
Epoch 1/20 5/5 [==============================] - 1s 33ms/step - loss: 0.0576 - val_loss: 0.0531 Epoch 2/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0552 - val_loss: 0.0514 Epoch 3/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0519 - val_loss: 0.0499 Epoch 4/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0483 - val_loss: 0.0475 Epoch 5/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0445 - val_loss: 0.0451 Epoch 6/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0409 - val_loss: 0.0432 Epoch 7/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0377 - val_loss: 0.0415 Epoch 8/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0348 - val_loss: 0.0401 Epoch 9/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0319 - val_loss: 0.0388 Epoch 10/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0293 - val_loss: 0.0378 Epoch 11/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0273 - val_loss: 0.0369 Epoch 12/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0259 - val_loss: 0.0361 Epoch 13/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0249 - val_loss: 0.0354 Epoch 14/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0239 - val_loss: 0.0346 Epoch 15/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0230 - val_loss: 0.0340 Epoch 16/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0222 - val_loss: 0.0335 Epoch 17/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0215 - val_loss: 0.0331 Epoch 18/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 9ms/step - loss: 0.0211 - val_loss: 0.0331 Epoch 19/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0208 - val_loss: 0.0329 Epoch 20/20 5/5 [==============================] - 0s 8ms/step - loss: 0.0206 - val_loss: 0.0327
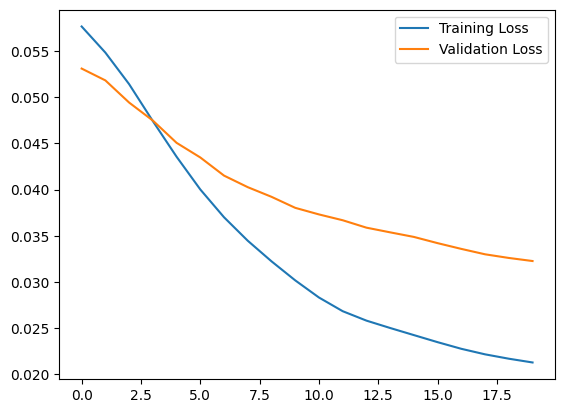
plt.plot(history.history["loss"], label="Training Loss")
plt.plot(history.history["val_loss"], label="Validation Loss")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7ff1d339b790>
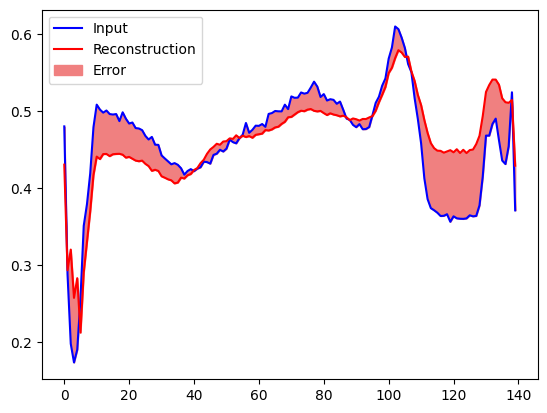
Bạn sẽ sớm phân loại ECG là dị thường nếu sai số xây dựng lại lớn hơn một độ lệch chuẩn so với các ví dụ huấn luyện thông thường. Đầu tiên, hãy vẽ một ECG bình thường từ tập huấn luyện, quá trình tái tạo sau khi nó được mã hóa và giải mã bởi bộ tự động mã hóa và lỗi xây dựng lại.
encoded_data = autoencoder.encoder(normal_test_data).numpy()
decoded_data = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_data).numpy()
plt.plot(normal_test_data[0], 'b')
plt.plot(decoded_data[0], 'r')
plt.fill_between(np.arange(140), decoded_data[0], normal_test_data[0], color='lightcoral')
plt.legend(labels=["Input", "Reconstruction", "Error"])
plt.show()
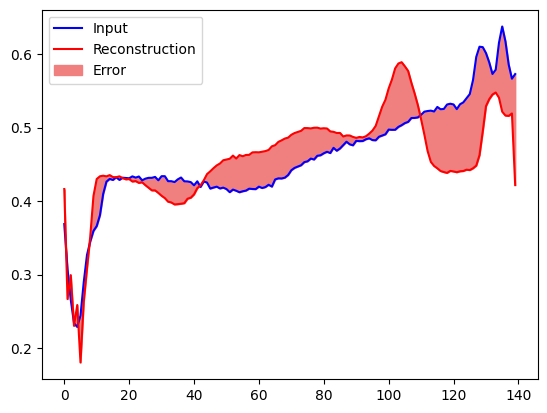
Tạo một âm mưu tương tự, lần này cho một ví dụ kiểm tra dị thường.
encoded_data = autoencoder.encoder(anomalous_test_data).numpy()
decoded_data = autoencoder.decoder(encoded_data).numpy()
plt.plot(anomalous_test_data[0], 'b')
plt.plot(decoded_data[0], 'r')
plt.fill_between(np.arange(140), decoded_data[0], anomalous_test_data[0], color='lightcoral')
plt.legend(labels=["Input", "Reconstruction", "Error"])
plt.show()
Phát hiện bất thường
Phát hiện sự bất thường bằng cách tính toán xem tổn thất xây dựng lại có lớn hơn ngưỡng cố định hay không. Trong hướng dẫn này, bạn sẽ tính toán sai số trung bình cộng cho các ví dụ bình thường từ tập huấn luyện, sau đó phân loại các ví dụ trong tương lai là dị thường nếu lỗi xây dựng lại cao hơn một độ lệch chuẩn so với tập huấn luyện.
Vẽ đồ thị lỗi xây dựng lại trên điện tâm đồ bình thường từ tập huấn luyện
reconstructions = autoencoder.predict(normal_train_data)
train_loss = tf.keras.losses.mae(reconstructions, normal_train_data)
plt.hist(train_loss[None,:], bins=50)
plt.xlabel("Train loss")
plt.ylabel("No of examples")
plt.show()

Chọn một giá trị ngưỡng cao hơn một độ lệch chuẩn so với giá trị trung bình.
threshold = np.mean(train_loss) + np.std(train_loss)
print("Threshold: ", threshold)
Threshold: 0.03241627
Nếu bạn kiểm tra lỗi xây dựng lại cho các ví dụ bất thường trong bộ kiểm tra, bạn sẽ nhận thấy hầu hết đều có lỗi xây dựng lại lớn hơn ngưỡng. Bằng cách thay đổi ngưỡng, bạn có thể điều chỉnh độ chính xác và thu hồi bộ phân loại của mình.
reconstructions = autoencoder.predict(anomalous_test_data)
test_loss = tf.keras.losses.mae(reconstructions, anomalous_test_data)
plt.hist(test_loss[None, :], bins=50)
plt.xlabel("Test loss")
plt.ylabel("No of examples")
plt.show()

Phân loại điện tâm đồ là dị thường nếu sai số xây dựng lại lớn hơn ngưỡng.
def predict(model, data, threshold):
reconstructions = model(data)
loss = tf.keras.losses.mae(reconstructions, data)
return tf.math.less(loss, threshold)
def print_stats(predictions, labels):
print("Accuracy = {}".format(accuracy_score(labels, predictions)))
print("Precision = {}".format(precision_score(labels, predictions)))
print("Recall = {}".format(recall_score(labels, predictions)))
preds = predict(autoencoder, test_data, threshold)
print_stats(preds, test_labels)
Accuracy = 0.944 Precision = 0.9921875 Recall = 0.9071428571428571
Bước tiếp theo
Để tìm hiểu thêm về cách phát hiện bất thường với tự động mã hóa, hãy xem ví dụ tương tác tuyệt vời này được xây dựng bằng TensorFlow.js của Victor Dibia. Đối với trường hợp sử dụng trong thế giới thực, bạn có thể tìm hiểu cách Airbus phát hiện các điểm bất thường trong dữ liệu đo từ xa của ISS bằng cách sử dụng TensorFlow. Để tìm hiểu thêm về những điều cơ bản, hãy cân nhắc đọc bài đăng trên blog này của François Chollet. Để biết thêm chi tiết, hãy xem chương 14 từ Học sâu của Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio và Aaron Courville.
