सिंहावलोकन
TensorFlow मॉडल विश्लेषण (TFMA) पाइपलाइन को इस प्रकार दर्शाया गया है:
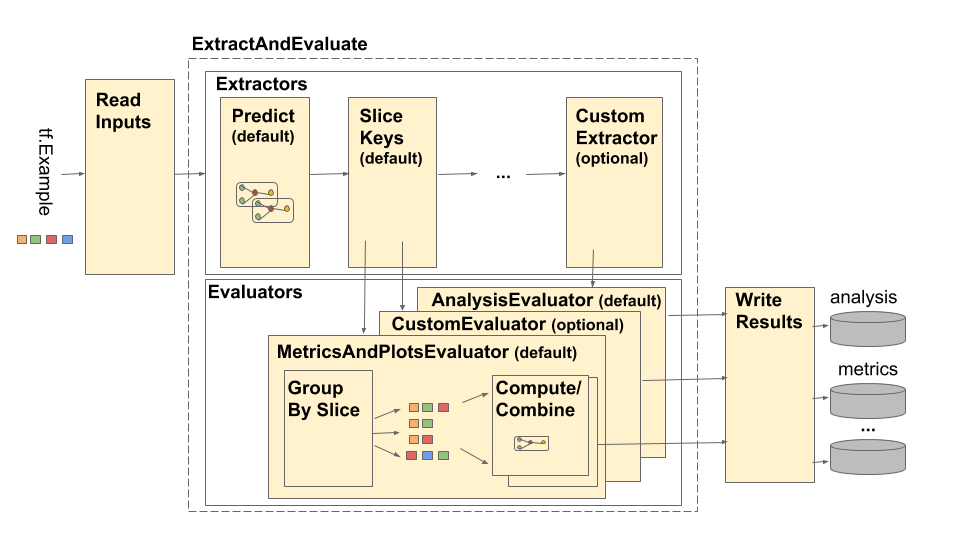
पाइपलाइन चार मुख्य घटकों से बनी है:
- इनपुट पढ़ें
- निष्कर्षण
- मूल्यांकन
- परिणाम लिखें
ये घटक दो प्राथमिक प्रकारों का उपयोग करते हैं: tfma.Extracts और tfma.evaluators.Evaluation । प्रकार tfma.Extracts उस डेटा का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है जो पाइपलाइन प्रसंस्करण के दौरान निकाला जाता है और मॉडल के लिए एक या अधिक उदाहरणों के अनुरूप हो सकता है। tfma.evaluators.Evaluation निष्कर्षण की प्रक्रिया के दौरान विभिन्न बिंदुओं पर अर्क के मूल्यांकन से प्राप्त आउटपुट का प्रतिनिधित्व करता है। एक लचीली एपीआई प्रदान करने के लिए, ये प्रकार केवल निर्देश हैं जहां विभिन्न कार्यान्वयन द्वारा कुंजियों को परिभाषित (उपयोग के लिए आरक्षित) किया जाता है। प्रकारों को इस प्रकार परिभाषित किया गया है:
# Extracts represent data extracted during pipeline processing.
# For example, the PredictExtractor stores the data for the
# features, labels, and predictions under the keys "features",
# "labels", and "predictions".
Extracts = Dict[Text, Any]
# Evaluation represents the output from evaluating extracts at
# particular point in the pipeline. The evaluation outputs are
# keyed by their associated output type. For example, the metric / plot
# dictionaries from evaluating metrics and plots will be stored under
# "metrics" and "plots" respectively.
Evaluation = Dict[Text, beam.pvalue.PCollection]
ध्यान दें कि tfma.Extracts कभी भी सीधे नहीं लिखे जाते हैं, उन्हें tfma.evaluators.Evaluation तैयार करने के लिए हमेशा एक मूल्यांकनकर्ता के माध्यम से जाना पड़ता है जिसे बाद में लिखा जाता है। यह भी ध्यान दें कि tfma.Extracts वे निर्देश हैं जो एक beam.pvalue.PCollection में संग्रहीत होते हैं (अर्थात् beam.PTransform एस इनपुट के रूप में लेता है beam.pvalue.PCollection[tfma.Extracts] ) जबकि एक tfma.evaluators.Evaluation एक निर्देश है जिसका मान beam.pvalue.PCollection एस हैं (यानी beam.PTransform एस निर्देश को beam.value.PCollection इनपुट के लिए तर्क के रूप में लेते हैं)। दूसरे शब्दों में, tfma.evaluators.Evaluation उपयोग पाइपलाइन निर्माण के समय किया जाता है, लेकिन tfma.Extracts उपयोग पाइपलाइन रनटाइम पर किया जाता है।
इनपुट पढ़ें
ReadInputs चरण एक ट्रांसफ़ॉर्म से बना है जो कच्चे इनपुट (tf.train.Example, CSV, ...) लेता है और उन्हें अर्क में परिवर्तित करता है। आज अर्क को tfma.INPUT_KEY के अंतर्गत संग्रहीत कच्चे इनपुट बाइट्स के रूप में दर्शाया जाता है, हालांकि अर्क किसी भी रूप में हो सकता है जो निष्कर्षण पाइपलाइन के साथ संगत है - जिसका अर्थ है कि यह आउटपुट के रूप में tfma.Extracts बनाता है, और वे अर्क डाउनस्ट्रीम के साथ संगत हैं निकालने वाले। यह विभिन्न निष्कर्षकों पर निर्भर है कि वे स्पष्ट रूप से दस्तावेजीकरण करें कि उन्हें क्या चाहिए।
निष्कर्षण
निष्कर्षण प्रक्रिया beam.PTransform की एक सूची है जो श्रृंखला में चलती है। एक्सट्रैक्टर्स tfma.Extracts इनपुट के रूप में लेते हैं और tfma.Extracts आउटपुट के रूप में लौटाते हैं। प्रोटो-टाइपिकल एक्सट्रैक्टर tfma.extractors.PredictExtractor है जो रीड इनपुट ट्रांसफॉर्म द्वारा उत्पादित इनपुट एक्सट्रैक्ट का उपयोग करता है और पूर्वानुमान एक्सट्रैक्ट का उत्पादन करने के लिए इसे एक मॉडल के माध्यम से चलाता है। कस्टमाइज़्ड एक्सट्रैक्टर्स को किसी भी बिंदु पर डाला जा सकता है, बशर्ते उनका ट्रांसफ़ॉर्म tfma.Extracts in और tfma.Extracts out API के अनुरूप हो। एक एक्सट्रैक्टर को इस प्रकार परिभाषित किया गया है:
# An Extractor is a PTransform that takes Extracts as input and returns
# Extracts as output. A typical example is a PredictExtractor that receives
# an 'input' placeholder for input and adds additional 'predictions' extracts.
Extractor = NamedTuple('Extractor', [
('stage_name', Text),
('ptransform', beam.PTransform)]) # Extracts -> Extracts
इनपुटएक्सट्रैक्टर
tfma.extractors.InputExtractor उपयोग मेट्रिक्स स्लाइसिंग और गणनाओं में उपयोग के लिए tf.train.Example रिकॉर्ड से कच्चे फीचर, कच्चे लेबल और कच्चे उदाहरण वजन निकालने के लिए किया जाता है। डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से मान क्रमशः एक्सट्रेक्ट कुंजियाँ features , labels और example_weights के अंतर्गत संग्रहीत किए जाते हैं। एकल-आउटपुट मॉडल लेबल और उदाहरण भार सीधे np.ndarray मान के रूप में संग्रहीत किए जाते हैं। मल्टी-आउटपुट मॉडल लेबल और उदाहरण भार को np.ndarray मानों (आउटपुट नाम द्वारा कुंजीबद्ध) के निर्देश के रूप में संग्रहीत किया जाता है। यदि बहु-मॉडल मूल्यांकन किया जाता है तो लेबल और उदाहरण भार को किसी अन्य निर्देश (मॉडल नाम से कुंजीबद्ध) के भीतर एम्बेड किया जाएगा।
भविष्यवाणी निकालने वाला
tfma.extractors.PredictExtractor मॉडल पूर्वानुमान चलाता है और उन्हें tfma.Extracts निर्देश में प्रमुख predictions अंतर्गत संग्रहीत करता है। एकल-आउटपुट मॉडल पूर्वानुमानों को सीधे अनुमानित आउटपुट मानों के रूप में संग्रहीत किया जाता है। मल्टी-आउटपुट मॉडल भविष्यवाणियों को आउटपुट मानों (आउटपुट नाम द्वारा कुंजीबद्ध) के रूप में संग्रहीत किया जाता है। यदि मल्टी-मॉडल मूल्यांकन किया जाता है तो भविष्यवाणी को किसी अन्य निर्देश (मॉडल नाम से कुंजीबद्ध) के भीतर एम्बेड किया जाएगा। उपयोग किया गया वास्तविक आउटपुट मान मॉडल पर निर्भर करता है (उदाहरण के लिए TF अनुमानक का रिटर्न आउटपुट एक निर्देश के रूप में होता है जबकि keras np.ndarray मान लौटाता है)।
स्लाइसकीएक्सट्रैक्टर
tfma.extractors.SliceKeyExtractor यह निर्धारित करने के लिए स्लाइसिंग स्पेक का उपयोग करता है कि निकाली गई विशेषताओं के आधार पर प्रत्येक उदाहरण इनपुट पर कौन से स्लाइस लागू होते हैं और मूल्यांकनकर्ताओं द्वारा बाद में उपयोग के लिए अर्क में संबंधित स्लाइसिंग मान जोड़ता है।
मूल्यांकन
मूल्यांकन एक उद्धरण लेने और उसका मूल्यांकन करने की प्रक्रिया है। हालांकि निष्कर्षण पाइपलाइन के अंत में मूल्यांकन करना आम बात है, ऐसे उपयोग-मामले भी हैं जिनके लिए निष्कर्षण प्रक्रिया में पहले मूल्यांकन की आवश्यकता होती है। चूँकि ऐसे मूल्यांकनकर्ता उन निष्कर्षकों से जुड़े होते हैं जिनके आउटपुट के विरुद्ध उनका मूल्यांकन किया जाना चाहिए। एक मूल्यांकनकर्ता को इस प्रकार परिभाषित किया गया है:
# An evaluator is a PTransform that takes Extracts as input and
# produces an Evaluation as output. A typical example of an evaluator
# is the MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator that takes the 'features', 'labels',
# and 'predictions' extracts from the PredictExtractor and evaluates
# them using post export metrics to produce metrics and plots dictionaries.
Evaluator = NamedTuple('Evaluator', [
('stage_name', Text),
('run_after', Text), # Extractor.stage_name
('ptransform', beam.PTransform)]) # Extracts -> Evaluation
ध्यान दें कि एक मूल्यांकनकर्ता एक beam.PTransform है जो tfma.Extracts इनपुट के रूप में लेता है। मूल्यांकन प्रक्रिया के हिस्से के रूप में कार्यान्वयन को अर्क पर अतिरिक्त परिवर्तन करने से कोई नहीं रोक सकता है। एक्सट्रैक्टर्स के विपरीत, जिन्हें एक tfma.Extracts डिक्ट लौटाना होता है, एक मूल्यांकनकर्ता द्वारा उत्पादित आउटपुट के प्रकारों पर कोई प्रतिबंध नहीं है, हालांकि अधिकांश मूल्यांकनकर्ता एक डिक्ट भी लौटाते हैं (उदाहरण के लिए मीट्रिक नाम और मान)।
मेट्रिक्सएंडप्लॉट्सइवैल्यूएटर
tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator इनपुट के रूप में features , labels और predictions लेता है, उन्हें स्लाइस द्वारा समूहीकृत करने के लिए tfma.slicer.FanoutSlices के माध्यम से चलाता है, और फिर मेट्रिक्स और प्लॉट गणना करता है। यह मेट्रिक्स और प्लॉट कुंजियों और मूल्यों के शब्दकोशों के रूप में आउटपुट तैयार करता है (इन्हें बाद में tfma.writers.MetricsAndPlotsWriter द्वारा आउटपुट के लिए क्रमबद्ध प्रोटोज़ में परिवर्तित किया जाता है)।
परिणाम लिखें
WriteResults चरण वह जगह है जहां मूल्यांकन आउटपुट डिस्क पर लिखा जाता है। WriteResults आउटपुट कुंजियों के आधार पर डेटा लिखने के लिए राइटर्स का उपयोग करता है। उदाहरण के लिए, tfma.evaluators.Evaluation में metrics और plots के लिए कुंजियाँ हो सकती हैं। फिर इन्हें 'मेट्रिक्स' और 'प्लॉट्स' नामक मेट्रिक्स और प्लॉट शब्दकोशों से जोड़ा जाएगा। लेखक निर्दिष्ट करते हैं कि प्रत्येक फ़ाइल को कैसे लिखना है:
# A writer is a PTransform that takes evaluation output as input and
# serializes the associated PCollections of data to a sink.
Writer = NamedTuple('Writer', [
('stage_name', Text),
('ptransform', beam.PTransform)]) # Evaluation -> PDone
मेट्रिक्सएंडप्लॉट्सराइटर
हम एक tfma.writers.MetricsAndPlotsWriter प्रदान करते हैं जो मेट्रिक्स और प्लॉट शब्दकोशों को क्रमबद्ध प्रोटोज़ में परिवर्तित करता है और उन्हें डिस्क पर लिखता है।
यदि आप एक अलग क्रमबद्धता प्रारूप का उपयोग करना चाहते हैं, तो आप एक कस्टम लेखक बना सकते हैं और इसके बजाय उसका उपयोग कर सकते हैं। चूँकि लेखकों को दिए गए tfma.evaluators.Evaluation में सभी मूल्यांकनकर्ताओं के संयुक्त आउटपुट शामिल होते हैं, एक tfma.writers.Write सहायक परिवर्तन प्रदान किया जाता है, जिसका उपयोग लेखक अपने ptransform कार्यान्वयन में उपयुक्त beam.PCollection चयन करने के लिए कर सकते हैं।PCollection s एक पर आधारित है आउटपुट कुंजी (उदाहरण के लिए नीचे देखें)।
अनुकूलन
tfma.run_model_analysis विधि पाइपलाइन द्वारा उपयोग किए जाने वाले extractors , evaluators और लेखकों को अनुकूलित करने के लिए एक्सट्रैक्टर्स, मूल्यांकनकर्ताओं और writers तर्क लेती है। यदि कोई तर्क प्रदान नहीं किया गया है तो tfma.default_extractors , tfma.default_evaluators , और tfma.default_writers डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से उपयोग किए जाते हैं।
कस्टम एक्सट्रैक्टर्स
एक कस्टम एक्सट्रैक्टर बनाने के लिए, एक tfma.extractors.Extractor प्रकार बनाएं जो एक beam.PTransform लपेटता है। इनपुट के रूप में tfma.Extracts लेकर ट्रांसफ़ॉर्म करता है और आउटपुट के रूप में tfma.Extracts लौटाता है। एक्सट्रैक्टर्स के उदाहरण tfma.extractors के अंतर्गत उपलब्ध हैं।
कस्टम मूल्यांकनकर्ता
एक कस्टम मूल्यांकनकर्ता बनाने के लिए, एक tfma.evaluators.Evaluator प्रकार बनाएं जो कि एक beam.PTransform tfma.Extracts है tfma.evaluators.Evaluation एक बहुत ही बुनियादी मूल्यांकनकर्ता आने वाले tfma.Extracts ले सकता है और उन्हें एक तालिका में संग्रहीत करने के लिए आउटपुट कर सकता है। यह बिल्कुल वही है जो tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator TableEvaluator करता है। एक अधिक जटिल मूल्यांकनकर्ता अतिरिक्त प्रसंस्करण और डेटा एकत्रीकरण कर सकता है। उदाहरण के तौर पर tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator देखें।
ध्यान दें कि tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator कस्टम मेट्रिक्स का समर्थन करने के लिए अनुकूलित किया जा सकता है (अधिक विवरण के लिए मेट्रिक्स देखें)।
कस्टम लेखक
एक कस्टम राइटर बनाने के लिए, एक tfma.writers.Writer प्रकार बनाएं जो एक beam.PTransform beam.pvalue.PDone है tfma.evaluators.Evaluation मेट्रिक्स वाले TFRecords को लिखने के लिए लेखक का एक बुनियादी उदाहरण निम्नलिखित है:
tfma.writers.Writer(
stage_name='WriteTFRecord(%s)' % tfma.METRICS_KEY,
ptransform=tfma.writers.Write(
key=tfma.METRICS_KEY,
ptransform=beam.io.WriteToTFRecord(file_path_prefix=output_file))
एक लेखक का इनपुट संबंधित मूल्यांकनकर्ता के आउटपुट पर निर्भर करता है। उपरोक्त उदाहरण के लिए, आउटपुट tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator द्वारा निर्मित एक क्रमबद्ध प्रोटो है। tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator के लिए एक लेखक tfma.Extracts का एक beam.pvalue.PCollection .pvalue.PCollection लिखने के लिए जिम्मेदार होगा।
ध्यान दें कि एक लेखक उपयोग की गई आउटपुट कुंजी (उदाहरण के लिए tfma.METRICS_KEY , tfma.ANALYSIS_KEY , आदि) के माध्यम से एक मूल्यांकनकर्ता के आउटपुट से जुड़ा होता है।
चरण दर चरण उदाहरण
निम्नलिखित निष्कर्षण और मूल्यांकन पाइपलाइन में शामिल चरणों का एक उदाहरण है जब tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator और tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator दोनों का उपयोग किया जाता है:
run_model_analysis(
...
extractors=[
tfma.extractors.InputExtractor(...),
tfma.extractors.PredictExtractor(...),
tfma.extractors.SliceKeyExtrator(...)
],
evaluators=[
tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator(...),
tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator(...)
])
ReadInputs
# Out
Extracts {
'input': bytes # CSV, Proto, ...
}
ExtractAndEvaluate
# In: ReadInputs Extracts
# Out:
Extracts {
'input': bytes # CSV, Proto, ...
'features': tensor_like # Raw features
'labels': tensor_like # Labels
'example_weights': tensor_like # Example weights
}
# In: InputExtractor Extracts
# Out:
Extracts {
'input': bytes # CSV, Proto, ...
'features': tensor_like # Raw features
'labels': tensor_like # Labels
'example_weights': tensor_like # Example weights
'predictions': tensor_like # Predictions
}
# In: PredictExtractor Extracts
# Out:
Extracts {
'features': tensor_like # Raw features
'labels': tensor_like # Labels
'example_weights': tensor_like # Example weights
'predictions': tensor_like # Predictions
'slice_key': Tuple[bytes...] # Slice
}
tfma.evaluators.MetricsAndPlotsEvaluator(रन_आफ्टर:SLICE_KEY_EXTRACTOR_STAGE_NAME)
# In: SliceKeyExtractor Extracts
# Out:
Evaluation {
'metrics': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from metric key to metric values)
'plots': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from plot key to plot values)
}
tfma.evaluators.AnalysisTableEvaluator(रन_आफ्टर:LAST_EXTRACTOR_STAGE_NAME)
# In: SliceKeyExtractor Extracts
# Out:
Evaluation {
'analysis': PCollection[Extracts] # Final Extracts
}
WriteResults
# In:
Evaluation {
'metrics': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from metric key to metric values)
'plots': PCollection[Tuple[slicer.SliceKeyType, Dict[Text, Any]]] # Tuples of (slice key, dictionary from plot key to plot values)
'analysis': PCollection[Extracts] # Final Extracts
}
# Out: metrics, plots, and analysis files

