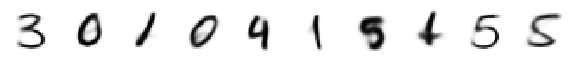Ver en TensorFlow.org Ver en TensorFlow.org |  Ejecutar en Google Colab Ejecutar en Google Colab |  Ver fuente en GitHub Ver fuente en GitHub |  Descargar cuaderno Descargar cuaderno |
En este ejemplo mostramos cómo ajustar un Autoencoder Variacional usando las "capas probabilísticas" de TFP.
Dependencias y requisitos previos
Importar
import numpy as np
import tensorflow.compat.v2 as tf
tf.enable_v2_behavior()
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
tfk = tf.keras
tfkl = tf.keras.layers
tfpl = tfp.layers
tfd = tfp.distributions
¡Haz las cosas rápido!
Antes de sumergirnos, asegurémonos de que estamos usando una GPU para esta demostración.
Para hacer esto, seleccione "Tiempo de ejecución" -> "Cambiar tipo de tiempo de ejecución" -> "Acelerador de hardware" -> "GPU".
El siguiente fragmento verificará que tenemos acceso a una GPU.
if tf.test.gpu_device_name() != '/device:GPU:0':
print('WARNING: GPU device not found.')
else:
print('SUCCESS: Found GPU: {}'.format(tf.test.gpu_device_name()))
SUCCESS: Found GPU: /device:GPU:0
Cargar conjunto de datos
datasets, datasets_info = tfds.load(name='mnist',
with_info=True,
as_supervised=False)
def _preprocess(sample):
image = tf.cast(sample['image'], tf.float32) / 255. # Scale to unit interval.
image = image < tf.random.uniform(tf.shape(image)) # Randomly binarize.
return image, image
train_dataset = (datasets['train']
.map(_preprocess)
.batch(256)
.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
.shuffle(int(10e3)))
eval_dataset = (datasets['test']
.map(_preprocess)
.batch(256)
.prefetch(tf.data.AUTOTUNE))
Tenga en cuenta que preproceso () devuelve por encima de image, image en lugar de sólo image porque Keras está configurado para modelos discriminativos con una (ejemplo, etiqueta) formato de entrada, es decir, \(p\theta(y|x)\). Dado que el objetivo de la VAE es recuperar las x de entrada de sí mismo (es decir, x \(p_\theta(x|x)\)), el par de datos es (ejemplo, ejemplo).
Código VAE Golf
Especificar modelo.
input_shape = datasets_info.features['image'].shape
encoded_size = 16
base_depth = 32
prior = tfd.Independent(tfd.Normal(loc=tf.zeros(encoded_size), scale=1),
reinterpreted_batch_ndims=1)
encoder = tfk.Sequential([
tfkl.InputLayer(input_shape=input_shape),
tfkl.Lambda(lambda x: tf.cast(x, tf.float32) - 0.5),
tfkl.Conv2D(base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(4 * encoded_size, 7, strides=1,
padding='valid', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Flatten(),
tfkl.Dense(tfpl.MultivariateNormalTriL.params_size(encoded_size),
activation=None),
tfpl.MultivariateNormalTriL(
encoded_size,
activity_regularizer=tfpl.KLDivergenceRegularizer(prior)),
])
WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/linalg/linear_operator_lower_triangular.py:158: calling LinearOperator.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.ops.linalg.linear_operator) with graph_parents is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Do not pass `graph_parents`. They will no longer be used. WARNING:tensorflow:From /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/ops/linalg/linear_operator_lower_triangular.py:158: calling LinearOperator.__init__ (from tensorflow.python.ops.linalg.linear_operator) with graph_parents is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: Do not pass `graph_parents`. They will no longer be used.
decoder = tfk.Sequential([
tfkl.InputLayer(input_shape=[encoded_size]),
tfkl.Reshape([1, 1, encoded_size]),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(2 * base_depth, 7, strides=1,
padding='valid', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(2 * base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(base_depth, 5, strides=2,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2DTranspose(base_depth, 5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=tf.nn.leaky_relu),
tfkl.Conv2D(filters=1, kernel_size=5, strides=1,
padding='same', activation=None),
tfkl.Flatten(),
tfpl.IndependentBernoulli(input_shape, tfd.Bernoulli.logits),
])
vae = tfk.Model(inputs=encoder.inputs,
outputs=decoder(encoder.outputs[0]))
Haz inferencia.
negloglik = lambda x, rv_x: -rv_x.log_prob(x)
vae.compile(optimizer=tf.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=1e-3),
loss=negloglik)
_ = vae.fit(train_dataset,
epochs=15,
validation_data=eval_dataset)
Epoch 1/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 61ms/step - loss: 206.5541 - val_loss: 163.1924 Epoch 2/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 59ms/step - loss: 151.1891 - val_loss: 143.6748 Epoch 3/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 141.3275 - val_loss: 137.9188 Epoch 4/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 136.7453 - val_loss: 133.2726 Epoch 5/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 132.3803 - val_loss: 131.8343 Epoch 6/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 129.2451 - val_loss: 127.1935 Epoch 7/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 59ms/step - loss: 126.0975 - val_loss: 123.6789 Epoch 8/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 124.0565 - val_loss: 122.5058 Epoch 9/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 122.9974 - val_loss: 121.9544 Epoch 10/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 121.7349 - val_loss: 120.8735 Epoch 11/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 121.0856 - val_loss: 120.1340 Epoch 12/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 120.2232 - val_loss: 121.3554 Epoch 13/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 119.8123 - val_loss: 119.2351 Epoch 14/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 58ms/step - loss: 119.2685 - val_loss: 118.2133 Epoch 15/15 235/235 [==============================] - 14s 59ms/step - loss: 118.8895 - val_loss: 119.4771
Mira mamá, no Manos ¡Tensores!
# We'll just examine ten random digits.
x = next(iter(eval_dataset))[0][:10]
xhat = vae(x)
assert isinstance(xhat, tfd.Distribution)
Imagen Plot Util
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def display_imgs(x, y=None):
if not isinstance(x, (np.ndarray, np.generic)):
x = np.array(x)
plt.ioff()
n = x.shape[0]
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, n, figsize=(n, 1))
if y is not None:
fig.suptitle(np.argmax(y, axis=1))
for i in range(n):
axs.flat[i].imshow(x[i].squeeze(), interpolation='none', cmap='gray')
axs.flat[i].axis('off')
plt.show()
plt.close()
plt.ion()
print('Originals:')
display_imgs(x)
print('Decoded Random Samples:')
display_imgs(xhat.sample())
print('Decoded Modes:')
display_imgs(xhat.mode())
print('Decoded Means:')
display_imgs(xhat.mean())
Originals:
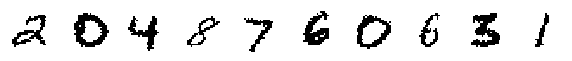
Decoded Random Samples:

Decoded Modes:
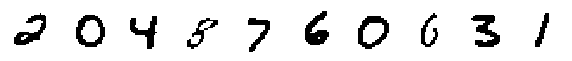
Decoded Means:
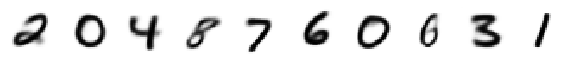
# Now, let's generate ten never-before-seen digits.
z = prior.sample(10)
xtilde = decoder(z)
assert isinstance(xtilde, tfd.Distribution)
print('Randomly Generated Samples:')
display_imgs(xtilde.sample())
print('Randomly Generated Modes:')
display_imgs(xtilde.mode())
print('Randomly Generated Means:')
display_imgs(xtilde.mean())
Randomly Generated Samples:
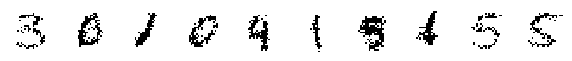
Randomly Generated Modes:
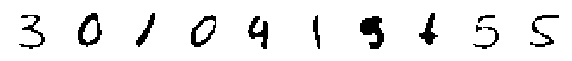
Randomly Generated Means: