Uruchom w Google Colab Uruchom w Google Colab |  Zobacz źródło w GitHub Zobacz źródło w GitHub |
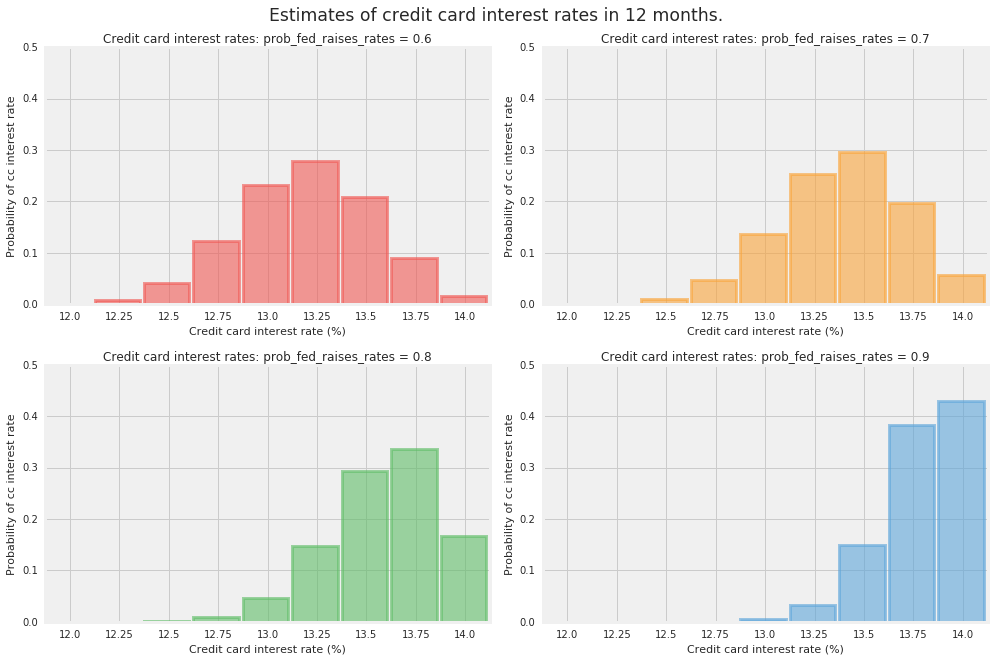
Wyobraźmy sobie, że chcesz oszacować oprocentowanie swojej karty kredytowej za rok. Załóżmy, że aktualna stawka główna wynosi 2%, a wystawca karty kredytowej pobiera opłatę w wysokości 10% plus prime. Biorąc pod uwagę siłę obecnej gospodarki, uważa Pan, że Rezerwa Federalna jest bardziej skłonna do podniesienia stóp procentowych niż do podniesienia stóp procentowych. Fed zbierze się osiem razy w ciągu najbliższych dwunastu miesięcy i albo podniesie stopę funduszy federalnych o 0,25%, albo pozostawi ją na dotychczasowym poziomie.
Do modelowania stopy procentowej Twojej karty kredytowej na koniec dwunastomiesięcznego okresu używamy rozkładu dwumianowego. W szczególności użyjemy klasy rozkładu dwumianu prawdopodobieństwa TensorFlow z następującymi parametrami: total_count = 8 (liczba prób lub spotkań), probs = {.6, .7, .8, .9} dla naszego zakresu szacunków dotyczących prawdopodobieństwo podniesienia przez Fed stopy funduszy federalnych o 0,25% na każdym posiedzeniu.
Zależności i wymagania wstępne
Ustawienia instalacji TensorFlow Prawdopodobieństwo
TFP_Installation = "Stable TFP"
if TFP_Installation == "Most Recent TFP":
!pip install -q tfp-nightly
print("Most recent TFP version installed")
elif TFP_Installation == "Stable TFP":
!pip install -q --upgrade tensorflow-probability
print("Up-to-date, stable TFP version installed")
elif TFP_Installation == "Stable TFP-GPU":
!pip install -q --upgrade tensorflow-probability-gpu
print("Up-to-date, stable TFP-GPU version installed")
print("(make sure GPU is properly configured)")
elif TFP_Installation == "Most Recent TFP-GPU":
!pip install -q tfp-nightly-gpu
print("Most recent TFP-GPU version installed")
print("(make sure GPU is properly configured)")
elif TFP_Installation == "TFP Already Installed":
print("TFP already installed in this environment")
pass
else:
print("Installation Error: Please select a viable TFP installation option.")
Importy i zmienne globalne (upewnij się, że uruchomiłeś tę komórkę)
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function
warning_status = "ignore"
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(warning_status)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.filterwarnings(warning_status, category=DeprecationWarning)
warnings.filterwarnings(warning_status, category=UserWarning)
import numpy as np
import os
matplotlib_style = 'fivethirtyeight'
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt; plt.style.use(matplotlib_style)
import matplotlib.axes as axes;
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
%matplotlib inline
import seaborn as sns; sns.set_context('notebook')
notebook_screen_res = 'png'
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = notebook_screen_res
import tensorflow as tf
# Eager Execution
use_tf_eager = True
# Use try/except so we can easily re-execute the whole notebook.
if use_tf_eager:
try:
tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
except:
reset_session()
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
tfd = tfp.distributions
tfb = tfp.bijectors
def default_session_options(enable_gpu_ram_resizing=True,
enable_xla=False):
"""Creates default options for Graph-mode session."""
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.log_device_placement = True
if enable_gpu_ram_resizing:
# `allow_growth=True` makes it possible to connect multiple
# colabs to your GPU. Otherwise the colab malloc's all GPU ram.
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
if enable_xla:
# Enable on XLA. https://www.tensorflow.org/performance/xla/.
config.graph_options.optimizer_options.global_jit_level = (
tf.OptimizerOptions.ON_1)
return config
def reset_session(options=None):
"""Creates a new global, interactive session in Graph-mode."""
if tf.executing_eagerly():
return
global sess
try:
tf.reset_default_graph()
sess.close()
except:
pass
if options is None:
options = default_session_options()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession(config=options)
def evaluate(tensors):
"""Evaluates Tensor or EagerTensor to Numpy `ndarray`s.
Args:
tensors: Object of `Tensor` or EagerTensor`s; can be `list`, `tuple`,
`namedtuple` or combinations thereof.
Returns:
ndarrays: Object with same structure as `tensors` except with `Tensor` or
`EagerTensor`s replaced by Numpy `ndarray`s.
"""
if tf.executing_eagerly():
return tf.contrib.framework.nest.pack_sequence_as(
tensors,
[t.numpy() if tf.contrib.framework.is_tensor(t) else t
for t in tf.contrib.framework.nest.flatten(tensors)])
return sess.run(tensors)
class _TFColor(object):
"""Enum of colors used in TF docs."""
red = '#F15854'
blue = '#5DA5DA'
orange = '#FAA43A'
green = '#60BD68'
pink = '#F17CB0'
brown = '#B2912F'
purple = '#B276B2'
yellow = '#DECF3F'
gray = '#4D4D4D'
def __getitem__(self, i):
return [
self.red,
self.orange,
self.green,
self.blue,
self.pink,
self.brown,
self.purple,
self.yellow,
self.gray,
][i % 9]
TFColor = _TFColor()
Oblicz prawdopodobieństwa
Oblicz prawdopodobieństwo możliwych stóp procentowych karty kredytowej w ciągu 12 miesięcy.
# First we encode our assumptions.
num_times_fed_meets_per_year = 8.
possible_fed_increases = tf.range(
start=0.,
limit=num_times_fed_meets_per_year + 1)
possible_cc_interest_rates = 2. + 10. + 0.25 * possible_fed_increases
prob_fed_raises_rates = tf.constant([0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]) # Wild guesses.
# Now we use TFP to compute probabilities in a vectorized manner.
# Pad a dim so we broadcast fed probs against CC interest rates.
prob_fed_raises_rates = prob_fed_raises_rates[..., tf.newaxis]
prob_cc_interest_rate = tfd.Binomial(
total_count=num_times_fed_meets_per_year,
probs=prob_fed_raises_rates).prob(possible_fed_increases)
Wykonaj kod TF
# Convert from TF to numpy.
[
possible_cc_interest_rates_,
prob_cc_interest_rate_,
prob_fed_raises_rates_,
] = evaluate([
possible_cc_interest_rates,
prob_cc_interest_rate,
prob_fed_raises_rates,
])
Wizualizuj wyniki
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 9))
for i, pf in enumerate(prob_fed_raises_rates_):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)
plt.bar(possible_cc_interest_rates_,
prob_cc_interest_rate_[i],
color=TFColor[i],
width=0.23,
label="$p = {:.1f}$".format(pf[0]),
alpha=0.6,
edgecolor=TFColor[i],
lw="3")
plt.xticks(possible_cc_interest_rates_ + 0.125, possible_cc_interest_rates_)
plt.xlim(12, 14.25)
plt.ylim(0, 0.5)
plt.ylabel("Probability of cc interest rate")
plt.xlabel("Credit card interest rate (%)")
plt.title("Credit card interest rates: "
"prob_fed_raises_rates = {:.1f}".format(pf[0]));
plt.suptitle("Estimates of credit card interest rates in 12 months.",
fontsize="x-large",
y=1.02)
plt.tight_layout()