در Google Colab اجرا شود در Google Colab اجرا شود |  مشاهده منبع در GitHub مشاهده منبع در GitHub |
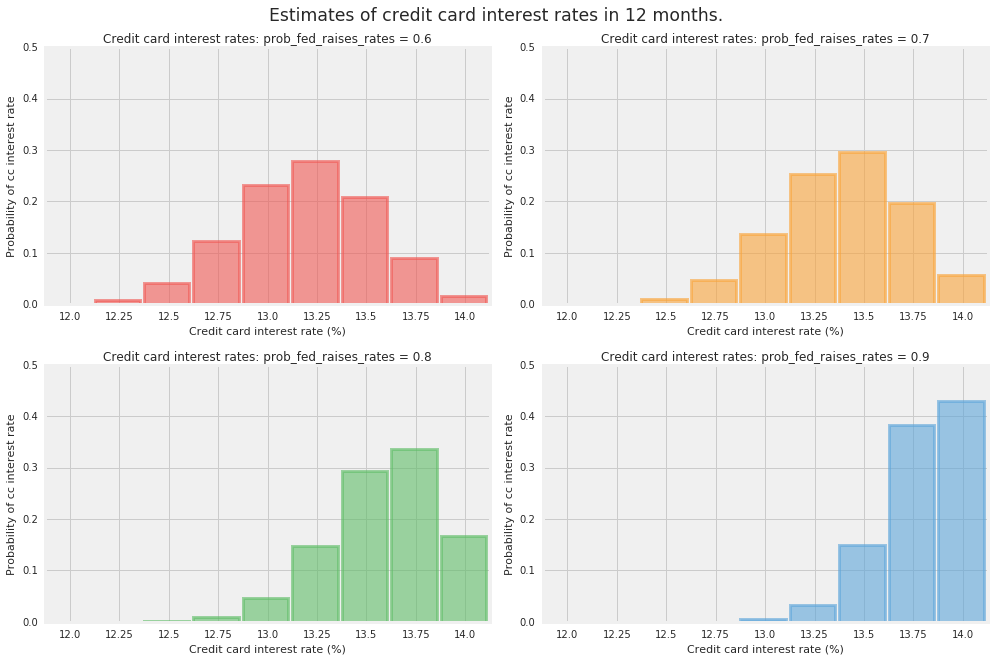
بیایید تصور کنیم که می خواهید نرخ بهره کارت اعتباری خود را یک سال بعد تخمین بزنید. فرض کنید نرخ اولیه فعلی 2٪ است و شرکت کارت اعتباری شما 10٪ به علاوه پرایم را از شما دریافت می کند. با توجه به قدرت اقتصاد کنونی، شما بر این باورید که فدرال رزرو بیشتر احتمال دارد که نرخ بهره را افزایش دهد. فدرال رزرو در دوازده ماه آینده هشت بار تشکیل جلسه می دهد و یا نرخ وجوه فدرال را 0.25 درصد افزایش می دهد یا آن را در سطح قبلی باقی می گذارد.
ما از توزیع دو جمله ای برای مدل سازی نرخ بهره کارت اعتباری شما در پایان دوره دوازده ماهه استفاده می کنیم. به طور خاص، ما از کلاس توزیع دوجملهای احتمال TensorFlow با پارامترهای زیر استفاده میکنیم: total_count = 8 (تعداد آزمایشها یا جلسات)، probs = {.6، 0.7، 0.8، 0.9}، برای محدوده تخمینهای خود در مورد احتمال افزایش نرخ وجوه فدرال توسط فدرال رزرو در هر جلسه 0.25٪.
وابستگی ها و پیش نیازها
تنظیمات نصب TensorFlow Probability
TFP_Installation = "Stable TFP"
if TFP_Installation == "Most Recent TFP":
!pip install -q tfp-nightly
print("Most recent TFP version installed")
elif TFP_Installation == "Stable TFP":
!pip install -q --upgrade tensorflow-probability
print("Up-to-date, stable TFP version installed")
elif TFP_Installation == "Stable TFP-GPU":
!pip install -q --upgrade tensorflow-probability-gpu
print("Up-to-date, stable TFP-GPU version installed")
print("(make sure GPU is properly configured)")
elif TFP_Installation == "Most Recent TFP-GPU":
!pip install -q tfp-nightly-gpu
print("Most recent TFP-GPU version installed")
print("(make sure GPU is properly configured)")
elif TFP_Installation == "TFP Already Installed":
print("TFP already installed in this environment")
pass
else:
print("Installation Error: Please select a viable TFP installation option.")
واردات و متغیرهای جهانی (حتما این سلول را اجرا کنید)
from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function
warning_status = "ignore"
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings(warning_status)
with warnings.catch_warnings():
warnings.filterwarnings(warning_status, category=DeprecationWarning)
warnings.filterwarnings(warning_status, category=UserWarning)
import numpy as np
import os
matplotlib_style = 'fivethirtyeight'
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt; plt.style.use(matplotlib_style)
import matplotlib.axes as axes;
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
%matplotlib inline
import seaborn as sns; sns.set_context('notebook')
notebook_screen_res = 'png'
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = notebook_screen_res
import tensorflow as tf
# Eager Execution
use_tf_eager = True
# Use try/except so we can easily re-execute the whole notebook.
if use_tf_eager:
try:
tf.compat.v1.enable_eager_execution()
except:
reset_session()
import tensorflow_probability as tfp
tfd = tfp.distributions
tfb = tfp.bijectors
def default_session_options(enable_gpu_ram_resizing=True,
enable_xla=False):
"""Creates default options for Graph-mode session."""
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.log_device_placement = True
if enable_gpu_ram_resizing:
# `allow_growth=True` makes it possible to connect multiple
# colabs to your GPU. Otherwise the colab malloc's all GPU ram.
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
if enable_xla:
# Enable on XLA. https://www.tensorflow.org/performance/xla/.
config.graph_options.optimizer_options.global_jit_level = (
tf.OptimizerOptions.ON_1)
return config
def reset_session(options=None):
"""Creates a new global, interactive session in Graph-mode."""
if tf.executing_eagerly():
return
global sess
try:
tf.reset_default_graph()
sess.close()
except:
pass
if options is None:
options = default_session_options()
sess = tf.InteractiveSession(config=options)
def evaluate(tensors):
"""Evaluates Tensor or EagerTensor to Numpy `ndarray`s.
Args:
tensors: Object of `Tensor` or EagerTensor`s; can be `list`, `tuple`,
`namedtuple` or combinations thereof.
Returns:
ndarrays: Object with same structure as `tensors` except with `Tensor` or
`EagerTensor`s replaced by Numpy `ndarray`s.
"""
if tf.executing_eagerly():
return tf.contrib.framework.nest.pack_sequence_as(
tensors,
[t.numpy() if tf.contrib.framework.is_tensor(t) else t
for t in tf.contrib.framework.nest.flatten(tensors)])
return sess.run(tensors)
class _TFColor(object):
"""Enum of colors used in TF docs."""
red = '#F15854'
blue = '#5DA5DA'
orange = '#FAA43A'
green = '#60BD68'
pink = '#F17CB0'
brown = '#B2912F'
purple = '#B276B2'
yellow = '#DECF3F'
gray = '#4D4D4D'
def __getitem__(self, i):
return [
self.red,
self.orange,
self.green,
self.blue,
self.pink,
self.brown,
self.purple,
self.yellow,
self.gray,
][i % 9]
TFColor = _TFColor()
محاسبه احتمالات
احتمالات احتمالی نرخ بهره کارت اعتباری را در 12 ماه محاسبه کنید.
# First we encode our assumptions.
num_times_fed_meets_per_year = 8.
possible_fed_increases = tf.range(
start=0.,
limit=num_times_fed_meets_per_year + 1)
possible_cc_interest_rates = 2. + 10. + 0.25 * possible_fed_increases
prob_fed_raises_rates = tf.constant([0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9]) # Wild guesses.
# Now we use TFP to compute probabilities in a vectorized manner.
# Pad a dim so we broadcast fed probs against CC interest rates.
prob_fed_raises_rates = prob_fed_raises_rates[..., tf.newaxis]
prob_cc_interest_rate = tfd.Binomial(
total_count=num_times_fed_meets_per_year,
probs=prob_fed_raises_rates).prob(possible_fed_increases)
کد TF را اجرا کنید
# Convert from TF to numpy.
[
possible_cc_interest_rates_,
prob_cc_interest_rate_,
prob_fed_raises_rates_,
] = evaluate([
possible_cc_interest_rates,
prob_cc_interest_rate,
prob_fed_raises_rates,
])
تجسم نتایج
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 9))
for i, pf in enumerate(prob_fed_raises_rates_):
plt.subplot(2, 2, i+1)
plt.bar(possible_cc_interest_rates_,
prob_cc_interest_rate_[i],
color=TFColor[i],
width=0.23,
label="$p = {:.1f}$".format(pf[0]),
alpha=0.6,
edgecolor=TFColor[i],
lw="3")
plt.xticks(possible_cc_interest_rates_ + 0.125, possible_cc_interest_rates_)
plt.xlim(12, 14.25)
plt.ylim(0, 0.5)
plt.ylabel("Probability of cc interest rate")
plt.xlabel("Credit card interest rate (%)")
plt.title("Credit card interest rates: "
"prob_fed_raises_rates = {:.1f}".format(pf[0]));
plt.suptitle("Estimates of credit card interest rates in 12 months.",
fontsize="x-large",
y=1.02)
plt.tight_layout()