 TensorFlow.org'da görüntüleyin TensorFlow.org'da görüntüleyin |  Google Colab'da çalıştırın Google Colab'da çalıştırın |  Kaynağı GitHub'da görüntüleyin Kaynağı GitHub'da görüntüleyin |  Not defterini indir Not defterini indir |
genel bakış
TFL Premade Agrega Fonksiyon Modelleri TFL inşa etmek kolay ve hızlı yolu vardır tf.keras.model karmaşık toplama işlevlerini öğrenmek için örneklerini. Bu kılavuz, bir TFL Hazır Toplama Fonksiyon Modeli oluşturmak ve onu eğitmek/test etmek için gereken adımları özetlemektedir.
Kurmak
TF Kafes paketini yükleme:
pip install -q tensorflow-lattice pydot
Gerekli paketleri içe aktarma:
import tensorflow as tf
import collections
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
import tensorflow_lattice as tfl
logging.disable(sys.maxsize)
Bulmacalar veri setini indirme:
train_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/train.csv')
train_dataframe.head()
test_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/test.csv')
test_dataframe.head()
Özellikleri ve etiketleri ayıklayın ve dönüştürün
# Features:
# - star_rating rating out of 5 stars (1-5)
# - word_count number of words in the review
# - is_amazon 1 = reviewed on amazon; 0 = reviewed on artifact website
# - includes_photo if the review includes a photo of the puzzle
# - num_helpful number of people that found this review helpful
# - num_reviews total number of reviews for this puzzle (we construct)
#
# This ordering of feature names will be the exact same order that we construct
# our model to expect.
feature_names = [
'star_rating', 'word_count', 'is_amazon', 'includes_photo', 'num_helpful',
'num_reviews'
]
def extract_features(dataframe, label_name):
# First we extract flattened features.
flattened_features = {
feature_name: dataframe[feature_name].values.astype(float)
for feature_name in feature_names[:-1]
}
# Construct mapping from puzzle name to feature.
star_rating = collections.defaultdict(list)
word_count = collections.defaultdict(list)
is_amazon = collections.defaultdict(list)
includes_photo = collections.defaultdict(list)
num_helpful = collections.defaultdict(list)
labels = {}
# Extract each review.
for i in range(len(dataframe)):
row = dataframe.iloc[i]
puzzle_name = row['puzzle_name']
star_rating[puzzle_name].append(float(row['star_rating']))
word_count[puzzle_name].append(float(row['word_count']))
is_amazon[puzzle_name].append(float(row['is_amazon']))
includes_photo[puzzle_name].append(float(row['includes_photo']))
num_helpful[puzzle_name].append(float(row['num_helpful']))
labels[puzzle_name] = float(row[label_name])
# Organize data into list of list of features.
names = list(star_rating.keys())
star_rating = [star_rating[name] for name in names]
word_count = [word_count[name] for name in names]
is_amazon = [is_amazon[name] for name in names]
includes_photo = [includes_photo[name] for name in names]
num_helpful = [num_helpful[name] for name in names]
num_reviews = [[len(ratings)] * len(ratings) for ratings in star_rating]
labels = [labels[name] for name in names]
# Flatten num_reviews
flattened_features['num_reviews'] = [len(reviews) for reviews in num_reviews]
# Convert data into ragged tensors.
star_rating = tf.ragged.constant(star_rating)
word_count = tf.ragged.constant(word_count)
is_amazon = tf.ragged.constant(is_amazon)
includes_photo = tf.ragged.constant(includes_photo)
num_helpful = tf.ragged.constant(num_helpful)
num_reviews = tf.ragged.constant(num_reviews)
labels = tf.constant(labels)
# Now we can return our extracted data.
return (star_rating, word_count, is_amazon, includes_photo, num_helpful,
num_reviews), labels, flattened_features
train_xs, train_ys, flattened_features = extract_features(train_dataframe, 'Sales12-18MonthsAgo')
test_xs, test_ys, _ = extract_features(test_dataframe, 'SalesLastSixMonths')
# Let's define our label minimum and maximum.
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
Bu kılavuzda eğitim için kullanılan varsayılan değerlerin ayarlanması:
LEARNING_RATE = 0.1
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 500
MIDDLE_DIM = 3
MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE = 2
MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS = 16
OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS = 8
Özellik Yapılandırmaları
Özellik kalibrasyonu ve başına özelliği yapılandırmaları kullanılarak ayarlanır tfl.configs.FeatureConfig . Özellik konfigürasyonları monotonicity kısıtlamaları başına özelliği düzenlenişi, (bakınız; tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig ) ve örgü modelleri için kafes boyutları.
Modelimizin tanımasını istediğimiz herhangi bir özellik için özellik yapılandırmasını tam olarak belirtmemiz gerektiğini unutmayın. Aksi takdirde modelin böyle bir özelliğin varlığından haberi olmayacaktır. Toplama modelleri için bu özellikler otomatik olarak değerlendirilecek ve düzensiz olarak uygun şekilde işlenecektir.
Hesaplama Miktarları
İçin varsayılan ayar olsa pwl_calibration_input_keypoints içinde tfl.configs.FeatureConfig önceden yapılmış modeller için 'kantilleri', biz elle giriş keypoints tanımlamak zorunda. Bunu yapmak için önce nicelik hesaplamak için kendi yardımcı fonksiyonumuzu tanımlıyoruz.
def compute_quantiles(features,
num_keypoints=10,
clip_min=None,
clip_max=None,
missing_value=None):
# Clip min and max if desired.
if clip_min is not None:
features = np.maximum(features, clip_min)
features = np.append(features, clip_min)
if clip_max is not None:
features = np.minimum(features, clip_max)
features = np.append(features, clip_max)
# Make features unique.
unique_features = np.unique(features)
# Remove missing values if specified.
if missing_value is not None:
unique_features = np.delete(unique_features,
np.where(unique_features == missing_value))
# Compute and return quantiles over unique non-missing feature values.
return np.quantile(
unique_features,
np.linspace(0., 1., num=num_keypoints),
interpolation='nearest').astype(float)
Özellik Yapılandırmalarımızı Tanımlama
Artık niceliklerimizi hesaplayabildiğimize göre, modelimizin girdi olarak almasını istediğimiz her bir özellik için bir özellik konfigürasyonu tanımlıyoruz.
# Feature configs are used to specify how each feature is calibrated and used.
feature_configs = [
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='star_rating',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['star_rating'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='word_count',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['word_count'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='is_amazon',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='includes_photo',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_helpful',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_helpful'], num_keypoints=5),
# Larger num_helpful indicating more trust in star_rating.
reflects_trust_in=[
tfl.configs.TrustConfig(
feature_name="star_rating", trust_type="trapezoid"),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_reviews',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_reviews'], num_keypoints=5),
)
]
Toplama Fonksiyonu Modeli
Bir TFL önceden yapılmış bir model oluşturmak için, ilk olarak bir örnek konfigürasyonunu oluşturmak tfl.configs . Bir ortak işlev modeli kullanılarak inşa edilir tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig . Parçalı doğrusal ve kategorik kalibrasyonu uygular, ardından düzensiz girdinin her boyutunda bir kafes modeli izler. Daha sonra her boyut için çıktının üzerine bir toplama katmanı uygular. Bunu daha sonra isteğe bağlı bir çıktı parçalı doğrusal kalibrasyon izler.
# Model config defines the model structure for the aggregate function model.
aggregate_function_model_config = tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
middle_dimension=MIDDLE_DIM,
middle_lattice_size=MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE,
middle_calibration=True,
middle_calibration_num_keypoints=MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS,
middle_monotonicity='increasing',
output_min=min_label,
output_max=max_label,
output_calibration=True,
output_calibration_num_keypoints=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS,
output_initialization=np.linspace(
min_label, max_label, num=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS))
# An AggregateFunction premade model constructed from the given model config.
aggregate_function_model = tfl.premade.AggregateFunction(
aggregate_function_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregate_function_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
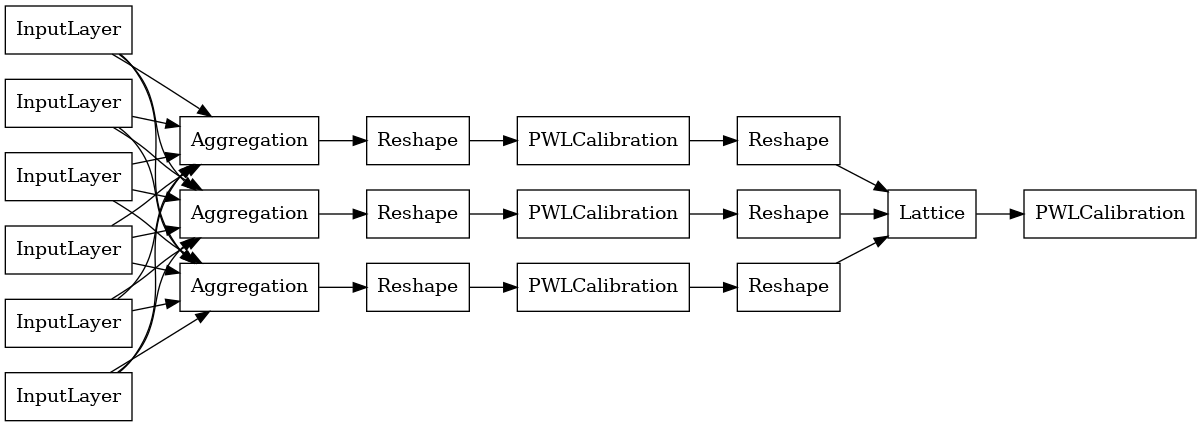
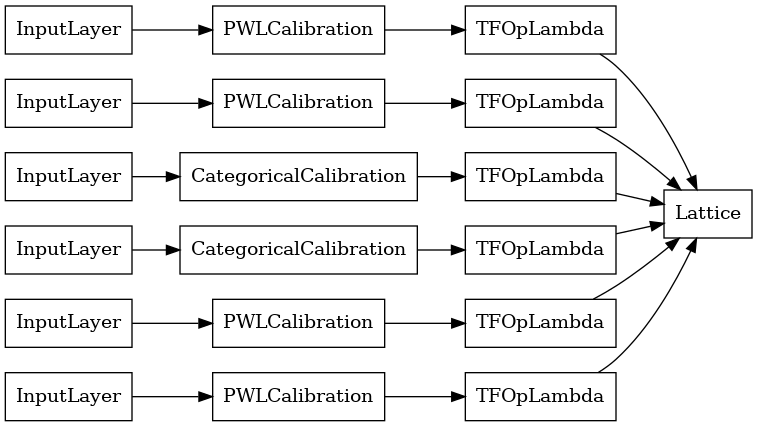
Her Toplama katmanının çıktısı, düzensiz girdiler üzerinden kalibre edilmiş bir kafesin ortalama çıktısıdır. İşte ilk Toplama katmanında kullanılan model:
aggregation_layers = [
layer for layer in aggregate_function_model.layers
if isinstance(layer, tfl.layers.Aggregation)
]
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregation_layers[0].model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
Şimdi, herhangi bir başka olduğu gibi tf.keras.Model , biz derlemek ve verilerimize modeli uygun.
aggregate_function_model.compile(
loss='mae',
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
aggregate_function_model.fit(
train_xs, train_ys, epochs=NUM_EPOCHS, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, verbose=False)
<tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fee7d3033c8>
Modelimizi eğittikten sonra test setimizde değerlendirebiliriz.
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(aggregate_function_model.evaluate(test_xs, test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 7/7 [==============================] - 2s 3ms/step - loss: 53.4633 53.4632682800293
