 הצג באתר TensorFlow.org הצג באתר TensorFlow.org |  הפעל בגוגל קולאב הפעל בגוגל קולאב |  צפה במקור ב-GitHub צפה במקור ב-GitHub |  הורד מחברת הורד מחברת |
סקירה כללית
מודלי פונקצית TFL Premade צבירת דרכים קלות ומהירות לבנות TFL tf.keras.model מקרים ללימוד פונקציות צבירה מורכבות. מדריך זה מתאר את השלבים הדרושים לבניית מודל תפקוד מצטבר של TFL Premade ולהכשיר/לבדוק אותו.
להכין
התקנת חבילת TF Lattice:
pip install -q tensorflow-lattice pydot
ייבוא חבילות נדרשות:
import tensorflow as tf
import collections
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
import tensorflow_lattice as tfl
logging.disable(sys.maxsize)
הורדת מערך הנתונים של פאזלים:
train_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/train.csv')
train_dataframe.head()
test_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/test.csv')
test_dataframe.head()
חלץ והמר תכונות ותוויות
# Features:
# - star_rating rating out of 5 stars (1-5)
# - word_count number of words in the review
# - is_amazon 1 = reviewed on amazon; 0 = reviewed on artifact website
# - includes_photo if the review includes a photo of the puzzle
# - num_helpful number of people that found this review helpful
# - num_reviews total number of reviews for this puzzle (we construct)
#
# This ordering of feature names will be the exact same order that we construct
# our model to expect.
feature_names = [
'star_rating', 'word_count', 'is_amazon', 'includes_photo', 'num_helpful',
'num_reviews'
]
def extract_features(dataframe, label_name):
# First we extract flattened features.
flattened_features = {
feature_name: dataframe[feature_name].values.astype(float)
for feature_name in feature_names[:-1]
}
# Construct mapping from puzzle name to feature.
star_rating = collections.defaultdict(list)
word_count = collections.defaultdict(list)
is_amazon = collections.defaultdict(list)
includes_photo = collections.defaultdict(list)
num_helpful = collections.defaultdict(list)
labels = {}
# Extract each review.
for i in range(len(dataframe)):
row = dataframe.iloc[i]
puzzle_name = row['puzzle_name']
star_rating[puzzle_name].append(float(row['star_rating']))
word_count[puzzle_name].append(float(row['word_count']))
is_amazon[puzzle_name].append(float(row['is_amazon']))
includes_photo[puzzle_name].append(float(row['includes_photo']))
num_helpful[puzzle_name].append(float(row['num_helpful']))
labels[puzzle_name] = float(row[label_name])
# Organize data into list of list of features.
names = list(star_rating.keys())
star_rating = [star_rating[name] for name in names]
word_count = [word_count[name] for name in names]
is_amazon = [is_amazon[name] for name in names]
includes_photo = [includes_photo[name] for name in names]
num_helpful = [num_helpful[name] for name in names]
num_reviews = [[len(ratings)] * len(ratings) for ratings in star_rating]
labels = [labels[name] for name in names]
# Flatten num_reviews
flattened_features['num_reviews'] = [len(reviews) for reviews in num_reviews]
# Convert data into ragged tensors.
star_rating = tf.ragged.constant(star_rating)
word_count = tf.ragged.constant(word_count)
is_amazon = tf.ragged.constant(is_amazon)
includes_photo = tf.ragged.constant(includes_photo)
num_helpful = tf.ragged.constant(num_helpful)
num_reviews = tf.ragged.constant(num_reviews)
labels = tf.constant(labels)
# Now we can return our extracted data.
return (star_rating, word_count, is_amazon, includes_photo, num_helpful,
num_reviews), labels, flattened_features
train_xs, train_ys, flattened_features = extract_features(train_dataframe, 'Sales12-18MonthsAgo')
test_xs, test_ys, _ = extract_features(test_dataframe, 'SalesLastSixMonths')
# Let's define our label minimum and maximum.
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
הגדרת ערכי ברירת המחדל המשמשים לאימון במדריך זה:
LEARNING_RATE = 0.1
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 500
MIDDLE_DIM = 3
MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE = 2
MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS = 16
OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS = 8
תצורות תכונה
כיול Feature ותצורות לכל תכונה נקבעים באמצעות tfl.configs.FeatureConfig . תצורות Feature כוללות מגבלות מונוטוניות, לכול תכונת הסדרה (ראה tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig ), וגדל סריג עבור דגמי סריג.
שים לב שעלינו לציין באופן מלא את תצורת התכונה עבור כל תכונה שאנו רוצים שהמודל שלנו יזהה. אחרת לא תהיה למודל שום דרך לדעת שקיימת תכונה כזו. עבור דגמי צבירה, תכונות אלה ייחשבו אוטומטית ויטופלו כראוי כמרופטים.
חשב קוונטילים
למרות הגדרת ברירת המחדל עבור pwl_calibration_input_keypoints ב tfl.configs.FeatureConfig היא "quantiles", עבור דגמים מוכנים מראש, אנחנו צריכים להגדיר את keypoints הקלט ידני. לשם כך, תחילה אנו מגדירים את פונקציית העזר שלנו לחישוב קוונטילים.
def compute_quantiles(features,
num_keypoints=10,
clip_min=None,
clip_max=None,
missing_value=None):
# Clip min and max if desired.
if clip_min is not None:
features = np.maximum(features, clip_min)
features = np.append(features, clip_min)
if clip_max is not None:
features = np.minimum(features, clip_max)
features = np.append(features, clip_max)
# Make features unique.
unique_features = np.unique(features)
# Remove missing values if specified.
if missing_value is not None:
unique_features = np.delete(unique_features,
np.where(unique_features == missing_value))
# Compute and return quantiles over unique non-missing feature values.
return np.quantile(
unique_features,
np.linspace(0., 1., num=num_keypoints),
interpolation='nearest').astype(float)
הגדרת תצורות התכונות שלנו
כעת, כשנוכל לחשב את הקוונטילים שלנו, אנו מגדירים תצורת תכונה עבור כל תכונה שאנו רוצים שהמודל שלנו ייקח כקלט.
# Feature configs are used to specify how each feature is calibrated and used.
feature_configs = [
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='star_rating',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['star_rating'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='word_count',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['word_count'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='is_amazon',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='includes_photo',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_helpful',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_helpful'], num_keypoints=5),
# Larger num_helpful indicating more trust in star_rating.
reflects_trust_in=[
tfl.configs.TrustConfig(
feature_name="star_rating", trust_type="trapezoid"),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_reviews',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_reviews'], num_keypoints=5),
)
]
מודל פונקציות מצטבר
כדי לבנות מודל premade TFL, ראשון לבנות תצורת מודל מ tfl.configs . מודל פונקציית צבירה בנוי באמצעות tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig . הוא מיישם כיול חלקי-ליניארי וקטגורי, ואחריו מודל סריג על כל מימד של הקלט המרופט. לאחר מכן הוא מחיל שכבת צבירה על הפלט עבור כל ממד. לאחר מכן, כיול פלט אופציונלי ליניארי חלקי.
# Model config defines the model structure for the aggregate function model.
aggregate_function_model_config = tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
middle_dimension=MIDDLE_DIM,
middle_lattice_size=MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE,
middle_calibration=True,
middle_calibration_num_keypoints=MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS,
middle_monotonicity='increasing',
output_min=min_label,
output_max=max_label,
output_calibration=True,
output_calibration_num_keypoints=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS,
output_initialization=np.linspace(
min_label, max_label, num=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS))
# An AggregateFunction premade model constructed from the given model config.
aggregate_function_model = tfl.premade.AggregateFunction(
aggregate_function_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregate_function_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
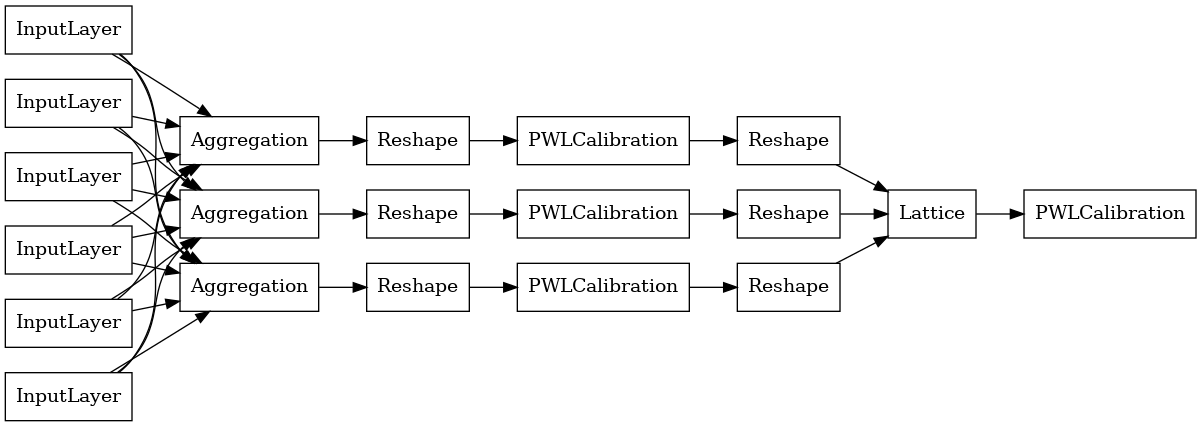
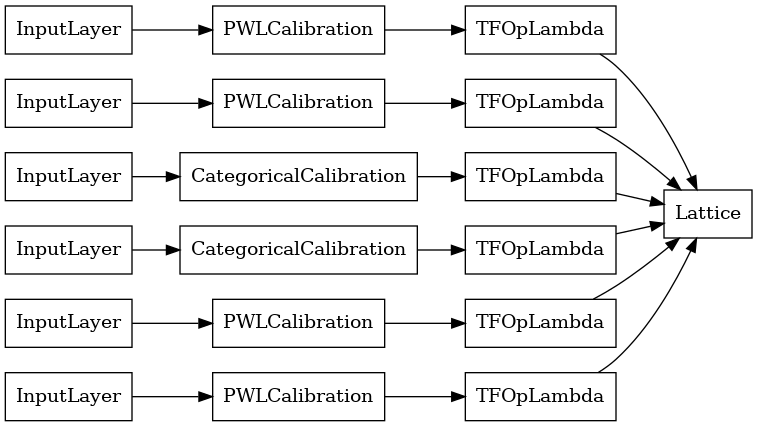
הפלט של כל שכבת Aggregation הוא הפלט הממוצע של סריג מכויל על פני הכניסות המרופדות. להלן המודל המשמש בשכבת הצבירה הראשונה:
aggregation_layers = [
layer for layer in aggregate_function_model.layers
if isinstance(layer, tfl.layers.Aggregation)
]
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregation_layers[0].model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
עכשיו, כמו כל האחרים tf.keras.Model , אנחנו לקמפל להתאים את המודל לנתונים שלנו.
aggregate_function_model.compile(
loss='mae',
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
aggregate_function_model.fit(
train_xs, train_ys, epochs=NUM_EPOCHS, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, verbose=False)
<tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fee7d3033c8>
לאחר אימון המודל שלנו, נוכל להעריך אותו במערך המבחנים שלנו.
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(aggregate_function_model.evaluate(test_xs, test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 7/7 [==============================] - 2s 3ms/step - loss: 53.4633 53.4632682800293
