 عرض على TensorFlow.org عرض على TensorFlow.org |  تشغيل في Google Colab تشغيل في Google Colab |  عرض المصدر على جيثب عرض المصدر على جيثب |  تحميل دفتر تحميل دفتر |
ملخص
TFL ولم يضف الركام وظيفة النماذج هي طرق سريعة وسهلة لبناء TFL tf.keras.model الحالات للتعلم وظائف تجميع معقدة. يوضح هذا الدليل الخطوات اللازمة لإنشاء نموذج وظيفة تجميع TFL Premade وتدريبه / اختباره.
يثبت
تثبيت حزمة TF Lattice:
pip install -q tensorflow-lattice pydot
استيراد الحزم المطلوبة:
import tensorflow as tf
import collections
import logging
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import sys
import tensorflow_lattice as tfl
logging.disable(sys.maxsize)
تنزيل مجموعة بيانات Puzzles:
train_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/train.csv')
train_dataframe.head()
test_dataframe = pd.read_csv(
'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wbakst/puzzles_data/master/test.csv')
test_dataframe.head()
استخراج وتحويل الميزات والتسميات
# Features:
# - star_rating rating out of 5 stars (1-5)
# - word_count number of words in the review
# - is_amazon 1 = reviewed on amazon; 0 = reviewed on artifact website
# - includes_photo if the review includes a photo of the puzzle
# - num_helpful number of people that found this review helpful
# - num_reviews total number of reviews for this puzzle (we construct)
#
# This ordering of feature names will be the exact same order that we construct
# our model to expect.
feature_names = [
'star_rating', 'word_count', 'is_amazon', 'includes_photo', 'num_helpful',
'num_reviews'
]
def extract_features(dataframe, label_name):
# First we extract flattened features.
flattened_features = {
feature_name: dataframe[feature_name].values.astype(float)
for feature_name in feature_names[:-1]
}
# Construct mapping from puzzle name to feature.
star_rating = collections.defaultdict(list)
word_count = collections.defaultdict(list)
is_amazon = collections.defaultdict(list)
includes_photo = collections.defaultdict(list)
num_helpful = collections.defaultdict(list)
labels = {}
# Extract each review.
for i in range(len(dataframe)):
row = dataframe.iloc[i]
puzzle_name = row['puzzle_name']
star_rating[puzzle_name].append(float(row['star_rating']))
word_count[puzzle_name].append(float(row['word_count']))
is_amazon[puzzle_name].append(float(row['is_amazon']))
includes_photo[puzzle_name].append(float(row['includes_photo']))
num_helpful[puzzle_name].append(float(row['num_helpful']))
labels[puzzle_name] = float(row[label_name])
# Organize data into list of list of features.
names = list(star_rating.keys())
star_rating = [star_rating[name] for name in names]
word_count = [word_count[name] for name in names]
is_amazon = [is_amazon[name] for name in names]
includes_photo = [includes_photo[name] for name in names]
num_helpful = [num_helpful[name] for name in names]
num_reviews = [[len(ratings)] * len(ratings) for ratings in star_rating]
labels = [labels[name] for name in names]
# Flatten num_reviews
flattened_features['num_reviews'] = [len(reviews) for reviews in num_reviews]
# Convert data into ragged tensors.
star_rating = tf.ragged.constant(star_rating)
word_count = tf.ragged.constant(word_count)
is_amazon = tf.ragged.constant(is_amazon)
includes_photo = tf.ragged.constant(includes_photo)
num_helpful = tf.ragged.constant(num_helpful)
num_reviews = tf.ragged.constant(num_reviews)
labels = tf.constant(labels)
# Now we can return our extracted data.
return (star_rating, word_count, is_amazon, includes_photo, num_helpful,
num_reviews), labels, flattened_features
train_xs, train_ys, flattened_features = extract_features(train_dataframe, 'Sales12-18MonthsAgo')
test_xs, test_ys, _ = extract_features(test_dataframe, 'SalesLastSixMonths')
# Let's define our label minimum and maximum.
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
min_label, max_label = float(np.min(train_ys)), float(np.max(train_ys))
تحديد القيم الافتراضية المستخدمة للتدريب في هذا الدليل:
LEARNING_RATE = 0.1
BATCH_SIZE = 128
NUM_EPOCHS = 500
MIDDLE_DIM = 3
MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE = 2
MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS = 16
OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS = 8
ميزة Configs
يتم تعيين ميزة معايرة وتكوينات لكل ميزة استخدام tfl.configs.FeatureConfig . وتشمل تكوينات ميزة القيود الرتابه في الصوت، تنظيم لكل ميزة (انظر tfl.configs.RegularizerConfig )، والأحجام شعرية لنماذج شعرية.
لاحظ أنه يجب علينا تحديد تكوين الميزة بالكامل لأي ميزة نريد أن يتعرف عليها نموذجنا. وإلا فلن يكون للنموذج أي طريقة لمعرفة وجود مثل هذه الميزة. بالنسبة لنماذج التجميع ، سيتم النظر تلقائيًا في هذه الميزات والتعامل معها بشكل صحيح باعتبارها خشنة.
حساب الكميات
على الرغم من أن الإعداد الافتراضي ل pwl_calibration_input_keypoints في tfl.configs.FeatureConfig هو 'quantiles، لنماذج ولم يضف لدينا لتحديد النقاط الرئيسية المدخلات يدويا. للقيام بذلك ، نحدد أولاً وظيفة المساعد الخاصة بنا لحساب الكميات.
def compute_quantiles(features,
num_keypoints=10,
clip_min=None,
clip_max=None,
missing_value=None):
# Clip min and max if desired.
if clip_min is not None:
features = np.maximum(features, clip_min)
features = np.append(features, clip_min)
if clip_max is not None:
features = np.minimum(features, clip_max)
features = np.append(features, clip_max)
# Make features unique.
unique_features = np.unique(features)
# Remove missing values if specified.
if missing_value is not None:
unique_features = np.delete(unique_features,
np.where(unique_features == missing_value))
# Compute and return quantiles over unique non-missing feature values.
return np.quantile(
unique_features,
np.linspace(0., 1., num=num_keypoints),
interpolation='nearest').astype(float)
تحديد الميزات الخاصة بنا
الآن بعد أن أصبح بإمكاننا حساب الكميات الخاصة بنا ، نحدد تكوين ميزة لكل ميزة نريد أن يتخذها نموذجنا كمدخلات.
# Feature configs are used to specify how each feature is calibrated and used.
feature_configs = [
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='star_rating',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['star_rating'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='word_count',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['word_count'], num_keypoints=5),
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='is_amazon',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='includes_photo',
lattice_size=2,
num_buckets=2,
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_helpful',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_helpful'], num_keypoints=5),
# Larger num_helpful indicating more trust in star_rating.
reflects_trust_in=[
tfl.configs.TrustConfig(
feature_name="star_rating", trust_type="trapezoid"),
],
),
tfl.configs.FeatureConfig(
name='num_reviews',
lattice_size=2,
monotonicity='increasing',
pwl_calibration_num_keypoints=5,
pwl_calibration_input_keypoints=compute_quantiles(
flattened_features['num_reviews'], num_keypoints=5),
)
]
نموذج الوظيفة التجميعية
لبناء نموذج ولم يضف TFL، أولا بناء تكوين نموذج من tfl.configs . يتم إنشاء نموذج وظيفة الكلي باستخدام tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig . وهي تطبق معايرة جزئية وخطية وفئوية ، متبوعة بنموذج شبكي على كل بُعد من أبعاد المدخلات الخشنة. ثم يطبق طبقة تجميع فوق الناتج لكل بُعد. ويتبع ذلك بعد ذلك معايرة اختيارية متعددة الخطوط للخرج.
# Model config defines the model structure for the aggregate function model.
aggregate_function_model_config = tfl.configs.AggregateFunctionConfig(
feature_configs=feature_configs,
middle_dimension=MIDDLE_DIM,
middle_lattice_size=MIDDLE_LATTICE_SIZE,
middle_calibration=True,
middle_calibration_num_keypoints=MIDDLE_KEYPOINTS,
middle_monotonicity='increasing',
output_min=min_label,
output_max=max_label,
output_calibration=True,
output_calibration_num_keypoints=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS,
output_initialization=np.linspace(
min_label, max_label, num=OUTPUT_KEYPOINTS))
# An AggregateFunction premade model constructed from the given model config.
aggregate_function_model = tfl.premade.AggregateFunction(
aggregate_function_model_config)
# Let's plot our model.
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregate_function_model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
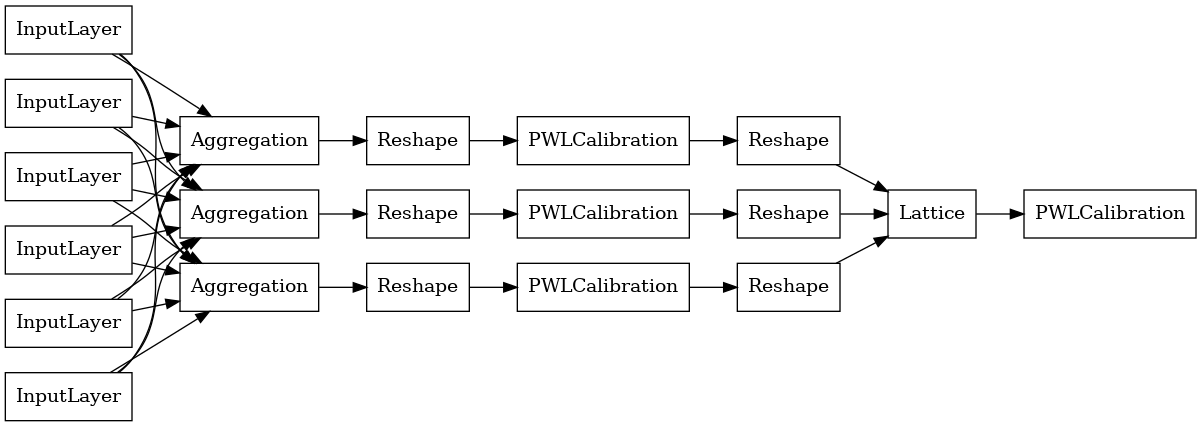
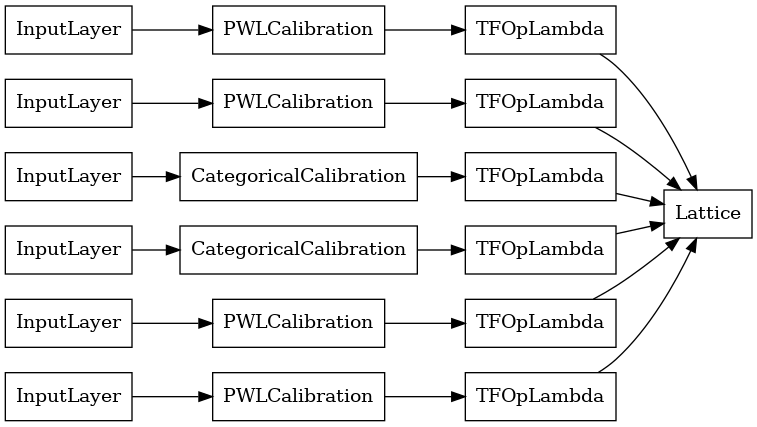
ناتج كل طبقة تجميع هو الناتج المتوسط لشبكة معايرة فوق المدخلات الخشنة. هذا هو النموذج المستخدم داخل طبقة التجميع الأولى:
aggregation_layers = [
layer for layer in aggregate_function_model.layers
if isinstance(layer, tfl.layers.Aggregation)
]
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(
aggregation_layers[0].model, show_layer_names=False, rankdir='LR')
الآن، كما هو الحال مع أي دولة أخرى tf.keras.Model ، نحن تجميع وتناسب نموذج لمعلوماتنا.
aggregate_function_model.compile(
loss='mae',
optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(LEARNING_RATE))
aggregate_function_model.fit(
train_xs, train_ys, epochs=NUM_EPOCHS, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, verbose=False)
<tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7fee7d3033c8>
بعد تدريب نموذجنا ، يمكننا تقييمه على مجموعة الاختبار الخاصة بنا.
print('Test Set Evaluation...')
print(aggregate_function_model.evaluate(test_xs, test_ys))
Test Set Evaluation... 7/7 [==============================] - 2s 3ms/step - loss: 53.4633 53.4632682800293
