 View on TensorFlow.org View on TensorFlow.org
|
 Run in Google Colab Run in Google Colab
|
 View source on GitHub View source on GitHub
|
 Download notebook Download notebook
|
Overview
This tutorial focuses on streaming data from an Elasticsearch cluster into a tf.data.Dataset which is then used in conjunction with tf.keras for training and inference.
Elasticseach is primarily a distributed search engine which supports storing structured, unstructured, geospatial, numeric data etc. For the purpose of this tutorial, a dataset with structured records is utilized.
Setup packages
The elasticsearch package is utilized for preparing and storing the data within elasticsearch indices for demonstration purposes only. In real-world production clusters with numerous nodes, the cluster might be receiving the data from connectors like logstash etc.
Once the data is available in the elasticsearch cluster, only tensorflow-io is required to stream the data into the models.
Install the required tensorflow-io and elasticsearch packages
pip install tensorflow-iopip install elasticsearch
Import packages
import os
import time
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras.layers.experimental import preprocessing
import tensorflow_io as tfio
Validate tf and tfio imports
print("tensorflow-io version: {}".format(tfio.__version__))
print("tensorflow version: {}".format(tf.__version__))
tensorflow-io version: 0.16.0 tensorflow version: 2.3.0
Download and setup the Elasticsearch instance
For demo purposes, the open-source version of the elasticsearch package is used.
wget -q https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gzwget -q https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512tar -xzf elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gzsudo chown -R daemon:daemon elasticsearch-7.9.2/shasum -a 512 -c elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz.sha512
elasticsearch-oss-7.9.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz: OK
Run the instance as a daemon process
sudo -H -u daemon elasticsearch-7.9.2/bin/elasticsearch
Starting job # 0 in a separate thread.
# Sleep for few seconds to let the instance start.
time.sleep(20)
Once the instance has been started, grep for elasticsearch in the processes list to confirm the availability.
ps -ef | grep elasticsearch
root 144 142 0 21:24 ? 00:00:00 sudo -H -u daemon elasticsearch-7.9.2/bin/elasticsearch daemon 145 144 86 21:24 ? 00:00:17 /content/elasticsearch-7.9.2/jdk/bin/java -Xshare:auto -Des.networkaddress.cache.ttl=60 -Des.networkaddress.cache.negative.ttl=10 -XX:+AlwaysPreTouch -Xss1m -Djava.awt.headless=true -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -Djna.nosys=true -XX:-OmitStackTraceInFastThrow -XX:+ShowCodeDetailsInExceptionMessages -Dio.netty.noUnsafe=true -Dio.netty.noKeySetOptimization=true -Dio.netty.recycler.maxCapacityPerThread=0 -Dio.netty.allocator.numDirectArenas=0 -Dlog4j.shutdownHookEnabled=false -Dlog4j2.disable.jmx=true -Djava.locale.providers=SPI,COMPAT -Xms1g -Xmx1g -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:G1ReservePercent=25 -XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent=30 -Djava.io.tmpdir=/tmp/elasticsearch-16913031424109346409 -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=data -XX:ErrorFile=logs/hs_err_pid%p.log -Xlog:gc*,gc+age=trace,safepoint:file=logs/gc.log:utctime,pid,tags:filecount=32,filesize=64m -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=536870912 -Des.path.home=/content/elasticsearch-7.9.2 -Des.path.conf=/content/elasticsearch-7.9.2/config -Des.distribution.flavor=oss -Des.distribution.type=tar -Des.bundled_jdk=true -cp /content/elasticsearch-7.9.2/lib/* org.elasticsearch.bootstrap.Elasticsearch root 382 380 0 21:24 ? 00:00:00 grep elasticsearch
query the base endpoint to retrieve information about the cluster.
curl -sX GET "localhost:9200/"
{
"name" : "d1bc7d054c69",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "P8YXfKqYS-OS3k9CdMmlsw",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.9.2",
"build_flavor" : "oss",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "d34da0ea4a966c4e49417f2da2f244e3e97b4e6e",
"build_date" : "2020-09-23T00:45:33.626720Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.6.2",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
Explore the dataset
For the purpose of this tutorial, lets download the PetFinder dataset and feed the data into elasticsearch manually. The goal of this classification problem is predict if the pet will be adopted or not.
dataset_url = 'http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/petfinder-mini.zip'
csv_file = 'datasets/petfinder-mini/petfinder-mini.csv'
tf.keras.utils.get_file('petfinder_mini.zip', dataset_url,
extract=True, cache_dir='.')
pf_df = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
Downloading data from http://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/petfinder-mini.zip 1671168/1668792 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
pf_df.head()
For the purpose of the tutorial, modifications are made to the label column. 0 will indicate the pet was not adopted, and 1 will indicate that it was.
# In the original dataset "4" indicates the pet was not adopted.
pf_df['target'] = np.where(pf_df['AdoptionSpeed']==4, 0, 1)
# Drop un-used columns.
pf_df = pf_df.drop(columns=['AdoptionSpeed', 'Description'])
# Number of datapoints and columns
len(pf_df), len(pf_df.columns)
(11537, 14)
Split the dataset
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(pf_df, test_size=0.3, shuffle=True)
print("Number of training samples: ",len(train_df))
print("Number of testing sample: ",len(test_df))
Number of training samples: 8075 Number of testing sample: 3462
Store the train and test data in elasticsearch indices
Storing the data in the local elasticsearch cluster simulates an environment for continuous remote data retrieval for training and inference purposes.
ES_NODES = "http://localhost:9200"
def prepare_es_data(index, doc_type, df):
records = df.to_dict(orient="records")
es_data = []
for idx, record in enumerate(records):
meta_dict = {
"index": {
"_index": index,
"_type": doc_type,
"_id": idx
}
}
es_data.append(meta_dict)
es_data.append(record)
return es_data
def index_es_data(index, es_data):
es_client = Elasticsearch(hosts = [ES_NODES])
if es_client.indices.exists(index):
print("deleting the '{}' index.".format(index))
res = es_client.indices.delete(index=index)
print("Response from server: {}".format(res))
print("creating the '{}' index.".format(index))
res = es_client.indices.create(index=index)
print("Response from server: {}".format(res))
print("bulk index the data")
res = es_client.bulk(index=index, body=es_data, refresh = True)
print("Errors: {}, Num of records indexed: {}".format(res["errors"], len(res["items"])))
train_es_data = prepare_es_data(index="train", doc_type="pet", df=train_df)
test_es_data = prepare_es_data(index="test", doc_type="pet", df=test_df)
index_es_data(index="train", es_data=train_es_data)
time.sleep(3)
index_es_data(index="test", es_data=test_es_data)
creating the 'train' index.
Response from server: {'acknowledged': True, 'shards_acknowledged': True, 'index': 'train'}
bulk index the data
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/elasticsearch/connection/base.py:190: ElasticsearchDeprecationWarning: [types removal] Specifying types in bulk requests is deprecated.
warnings.warn(message, category=ElasticsearchDeprecationWarning)
Errors: False, Num of records indexed: 8075
creating the 'test' index.
Response from server: {'acknowledged': True, 'shards_acknowledged': True, 'index': 'test'}
bulk index the data
Errors: False, Num of records indexed: 3462
Prepare tfio datasets
Once the data is available in the cluster, only tensorflow-io is required to stream the data from the indices. The elasticsearch.ElasticsearchIODataset class is utilized for this purpose. The class inherits from tf.data.Dataset and thus exposes all the useful functionalities of tf.data.Dataset out of the box.
Training dataset
BATCH_SIZE=32
HEADERS = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
train_ds = tfio.experimental.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchIODataset(
nodes=[ES_NODES],
index="train",
doc_type="pet",
headers=HEADERS
)
# Prepare a tuple of (features, label)
train_ds = train_ds.map(lambda v: (v, v.pop("target")))
train_ds = train_ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
Connection successful: http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health
Testing dataset
test_ds = tfio.experimental.elasticsearch.ElasticsearchIODataset(
nodes=[ES_NODES],
index="test",
doc_type="pet",
headers=HEADERS
)
# Prepare a tuple of (features, label)
test_ds = test_ds.map(lambda v: (v, v.pop("target")))
test_ds = test_ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
Connection successful: http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health
Define the keras preprocessing layers
As per the structured data tutorial, it is recommended to use the Keras Preprocessing Layers as they are more intuitive, and can be easily integrated with the models. However, the standard feature_columns can also be used.
For a better understanding of the preprocessing_layers in classifying structured data, please refer to the structured data tutorial
def get_normalization_layer(name, dataset):
# Create a Normalization layer for our feature.
normalizer = preprocessing.Normalization()
# Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature.
feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name])
# Learn the statistics of the data.
normalizer.adapt(feature_ds)
return normalizer
def get_category_encoding_layer(name, dataset, dtype, max_tokens=None):
# Create a StringLookup layer which will turn strings into integer indices
if dtype == 'string':
index = preprocessing.StringLookup(max_tokens=max_tokens)
else:
index = preprocessing.IntegerLookup(max_values=max_tokens)
# Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature
feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name])
# Learn the set of possible values and assign them a fixed integer index.
index.adapt(feature_ds)
# Create a Discretization for our integer indices.
encoder = preprocessing.CategoryEncoding(max_tokens=index.vocab_size())
# Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature.
feature_ds = feature_ds.map(index)
# Learn the space of possible indices.
encoder.adapt(feature_ds)
# Apply one-hot encoding to our indices. The lambda function captures the
# layer so you can use them, or include them in the functional model later.
return lambda feature: encoder(index(feature))
Fetch a batch and observe the features of a sample record. This will help in defining the keras preprocessing layers for training the tf.keras model.
ds_iter = iter(train_ds)
features, label = next(ds_iter)
{key: value.numpy()[0] for key,value in features.items()}
{'Age': 2,
'Breed1': b'Tabby',
'Color1': b'Black',
'Color2': b'Cream',
'Fee': 0,
'FurLength': b'Short',
'Gender': b'Male',
'Health': b'Healthy',
'MaturitySize': b'Small',
'PhotoAmt': 4,
'Sterilized': b'No',
'Type': b'Cat',
'Vaccinated': b'No'}
Choose a subset of features.
all_inputs = []
encoded_features = []
# Numeric features.
for header in ['PhotoAmt', 'Fee']:
numeric_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header)
normalization_layer = get_normalization_layer(header, train_ds)
encoded_numeric_col = normalization_layer(numeric_col)
all_inputs.append(numeric_col)
encoded_features.append(encoded_numeric_col)
# Categorical features encoded as string.
categorical_cols = ['Type', 'Color1', 'Color2', 'Gender', 'MaturitySize',
'FurLength', 'Vaccinated', 'Sterilized', 'Health', 'Breed1']
for header in categorical_cols:
categorical_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header, dtype='string')
encoding_layer = get_category_encoding_layer(header, train_ds, dtype='string',
max_tokens=5)
encoded_categorical_col = encoding_layer(categorical_col)
all_inputs.append(categorical_col)
encoded_features.append(encoded_categorical_col)
Build, compile and train the model
# Set the parameters
OPTIMIZER="adam"
LOSS=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
METRICS=['accuracy']
EPOCHS=10
# Convert the feature columns into a tf.keras layer
all_features = tf.keras.layers.concatenate(encoded_features)
# design/build the model
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation="relu")(all_features)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation="relu")(x)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(x)
output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(all_inputs, output)
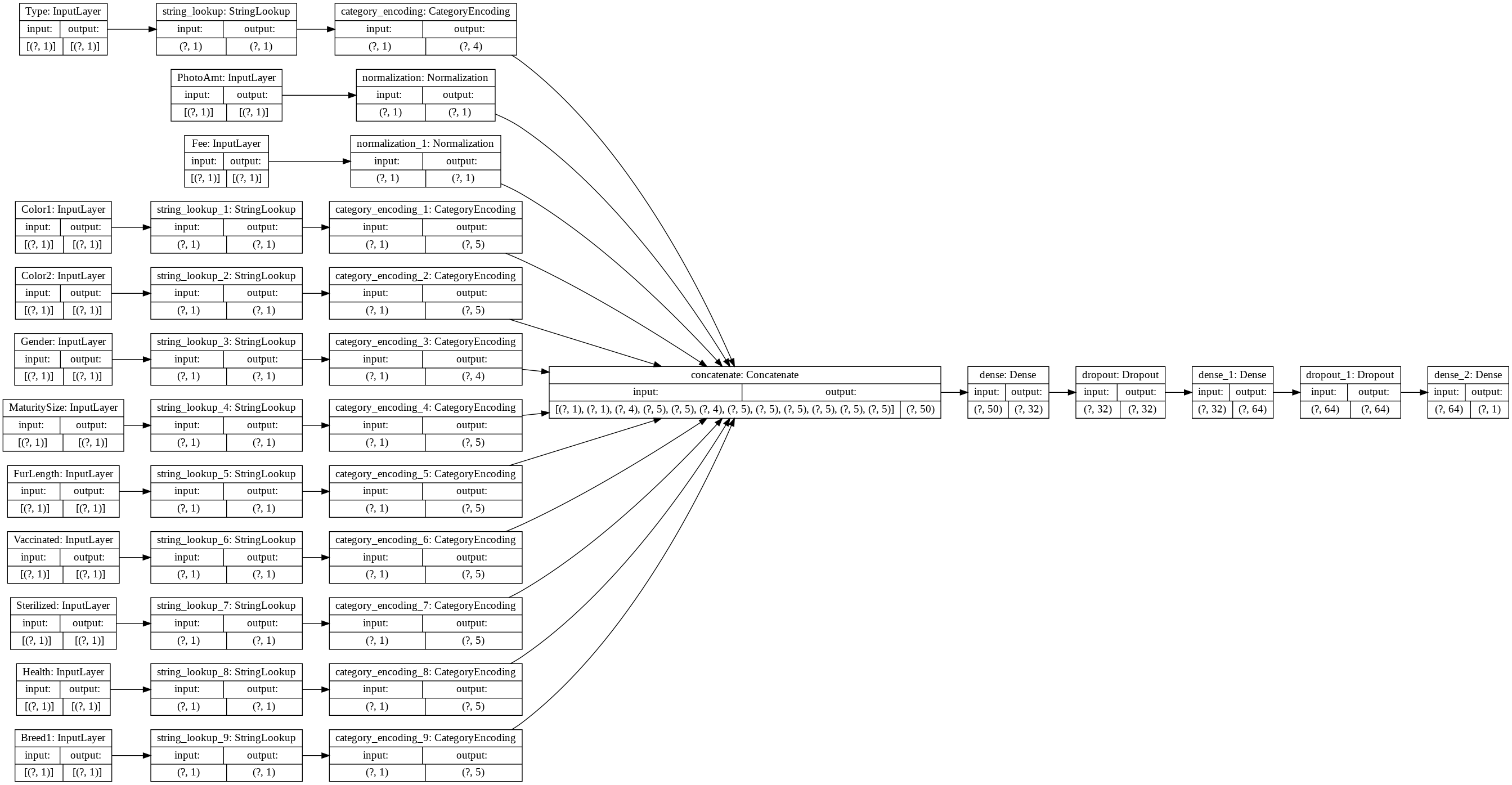
tf.keras.utils.plot_model(model, rankdir='LR', show_shapes=True)
# compile the model
model.compile(optimizer=OPTIMIZER, loss=LOSS, metrics=METRICS)
# fit the model
model.fit(train_ds, epochs=EPOCHS)
Epoch 1/10 /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/keras/engine/functional.py:543: UserWarning: Input dict contained keys ['Age'] which did not match any model input. They will be ignored by the model. [n for n in tensors.keys() if n not in ref_input_names]) 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.6169 - accuracy: 0.6042 Epoch 2/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.5634 - accuracy: 0.6937 Epoch 3/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5573 - accuracy: 0.6981 Epoch 4/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5528 - accuracy: 0.7087 Epoch 5/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.5512 - accuracy: 0.7173 Epoch 6/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5456 - accuracy: 0.7219 Epoch 7/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5397 - accuracy: 0.7283 Epoch 8/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 14ms/step - loss: 0.5385 - accuracy: 0.7331 Epoch 9/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5355 - accuracy: 0.7326 Epoch 10/10 253/253 [==============================] - 4s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5412 - accuracy: 0.7321 <tensorflow.python.keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f5c235112e8>
Infer on the test data
res = model.evaluate(test_ds)
print("test loss, test acc:", res)
/usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages/tensorflow/python/keras/engine/functional.py:543: UserWarning: Input dict contained keys ['Age'] which did not match any model input. They will be ignored by the model. [n for n in tensors.keys() if n not in ref_input_names]) 109/109 [==============================] - 2s 15ms/step - loss: 0.5344 - accuracy: 0.7421 test loss, test acc: [0.534355640411377, 0.7420566082000732]
