 Ver no TensorFlow.org Ver no TensorFlow.org |  Executar no Google Colab Executar no Google Colab |  Ver no GitHub Ver no GitHub |  Baixar caderno Baixar caderno |  Veja o modelo TF Hub Veja o modelo TF Hub |
Este Colab ilustra como usar o Universal Sentence Encoder-Lite para a tarefa de similaridade de frases. Este módulo é muito semelhante à Universal Sentença Encoder com a única diferença de que você precisa para executar SentencePiece processamento em suas frases de entrada.
O Codificador de Sentença Universal torna a obtenção de embeddings em nível de frase tão fácil quanto tem sido historicamente procurar embeddings de palavras individuais. Os embeddings de frase podem então ser usados trivialmente para computar similaridade de significado de nível de frase, bem como para permitir um melhor desempenho em tarefas de classificação downstream usando menos dados de treinamento supervisionados.
Começando
Configurar
# Install seaborn for pretty visualizationspip3 install --quiet seaborn# Install SentencePiece package# SentencePiece package is needed for Universal Sentence Encoder Lite. We'll# use it for all the text processing and sentence feature ID lookup.pip3 install --quiet sentencepiece
from absl import logging
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import sentencepiece as spm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
import pandas as pd
import re
import seaborn as sns
WARNING:tensorflow:From /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow/python/compat/v2_compat.py:111: disable_resource_variables (from tensorflow.python.ops.variable_scope) is deprecated and will be removed in a future version. Instructions for updating: non-resource variables are not supported in the long term
Carregue o módulo do TF-Hub
module = hub.Module("https://tfhub.dev/google/universal-sentence-encoder-lite/2")
input_placeholder = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=[None, None])
encodings = module(
inputs=dict(
values=input_placeholder.values,
indices=input_placeholder.indices,
dense_shape=input_placeholder.dense_shape))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
Carregar o modelo SentencePiece do módulo TF-Hub
O modelo SentencePiece é convenientemente armazenado dentro dos ativos do módulo. Ele precisa ser carregado para inicializar o processador.
with tf.Session() as sess:
spm_path = sess.run(module(signature="spm_path"))
sp = spm.SentencePieceProcessor()
with tf.io.gfile.GFile(spm_path, mode="rb") as f:
sp.LoadFromSerializedProto(f.read())
print("SentencePiece model loaded at {}.".format(spm_path))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore SentencePiece model loaded at b'/tmp/tfhub_modules/539544f0a997d91c327c23285ea00c37588d92cc/assets/universal_encoder_8k_spm.model'.
def process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, sentences):
# An utility method that processes sentences with the sentence piece processor
# 'sp' and returns the results in tf.SparseTensor-similar format:
# (values, indices, dense_shape)
ids = [sp.EncodeAsIds(x) for x in sentences]
max_len = max(len(x) for x in ids)
dense_shape=(len(ids), max_len)
values=[item for sublist in ids for item in sublist]
indices=[[row,col] for row in range(len(ids)) for col in range(len(ids[row]))]
return (values, indices, dense_shape)
Teste o módulo com alguns exemplos
# Compute a representation for each message, showing various lengths supported.
word = "Elephant"
sentence = "I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding."
paragraph = (
"Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. "
"There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer "
"the more 'diluted' the embedding will be.")
messages = [word, sentence, paragraph]
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, messages)
# Reduce logging output.
logging.set_verbosity(logging.ERROR)
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run([tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.tables_initializer()])
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
for i, message_embedding in enumerate(np.array(message_embeddings).tolist()):
print("Message: {}".format(messages[i]))
print("Embedding size: {}".format(len(message_embedding)))
message_embedding_snippet = ", ".join(
(str(x) for x in message_embedding[:3]))
print("Embedding: [{}, ...]\n".format(message_embedding_snippet))
Message: Elephant Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.053387489169836044, 0.053194381296634674, -0.052356015890836716, ...] Message: I am a sentence for which I would like to get its embedding. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [0.03533298149704933, -0.04714975506067276, 0.012305550277233124, ...] Message: Universal Sentence Encoder embeddings also support short paragraphs. There is no hard limit on how long the paragraph is. Roughly, the longer the more 'diluted' the embedding will be. Embedding size: 512 Embedding: [-0.004081667400896549, -0.08954868465662003, 0.03737196698784828, ...]
Exemplo de tarefa de semelhança textual semântica (STS)
Os embeddings produzidos pelo Codificador de Sentença Universal são aproximadamente normalizados. A semelhança semântica de duas sentenças pode ser trivialmente calculada como o produto interno das codificações.
def plot_similarity(labels, features, rotation):
corr = np.inner(features, features)
sns.set(font_scale=1.2)
g = sns.heatmap(
corr,
xticklabels=labels,
yticklabels=labels,
vmin=0,
vmax=1,
cmap="YlOrRd")
g.set_xticklabels(labels, rotation=rotation)
g.set_title("Semantic Textual Similarity")
def run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages):
values, indices, dense_shape = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp,messages)
message_embeddings = session.run(
encodings,
feed_dict={input_placeholder.values: values,
input_placeholder.indices: indices,
input_placeholder.dense_shape: dense_shape})
plot_similarity(messages, message_embeddings, 90)
Semelhança visualizada
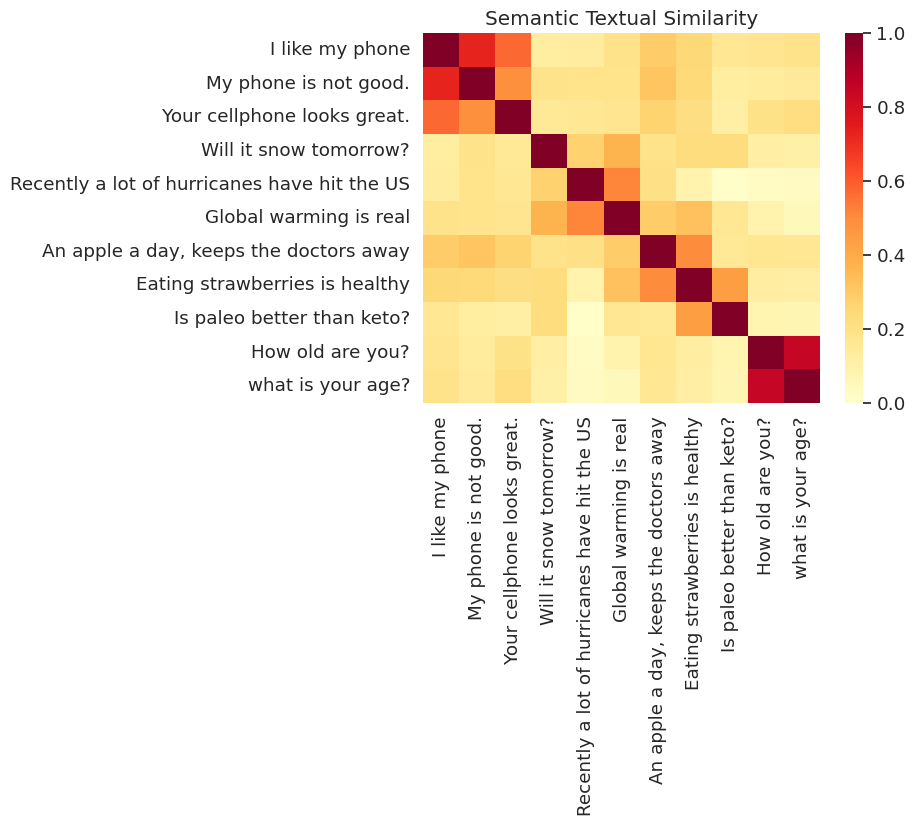
Aqui, mostramos a semelhança em um mapa de calor. O gráfico final é uma matriz de 9x9, onde cada entrada [i, j] é colorida com base no produto interno das codificações para frase i e j .
messages = [
# Smartphones
"I like my phone",
"My phone is not good.",
"Your cellphone looks great.",
# Weather
"Will it snow tomorrow?",
"Recently a lot of hurricanes have hit the US",
"Global warming is real",
# Food and health
"An apple a day, keeps the doctors away",
"Eating strawberries is healthy",
"Is paleo better than keto?",
# Asking about age
"How old are you?",
"what is your age?",
]
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
run_and_plot(session, input_placeholder, messages)
Avaliação: Referência STS (Semântica Textual Similarity)
O benchmark STS fornece uma avaliação intristic do grau em que a pontuação de similaridade calculada usando frase embeddings alinhar com julgamentos humanos. O benchmark requer que os sistemas retornem pontuações de similaridade para uma seleção diversa de pares de frases. De correlação de Pearson é então utilizado para avaliar a qualidade das pontuações de semelhança máquina contra julgamentos humanos.
Baixar dados
import pandas
import scipy
import math
def load_sts_dataset(filename):
# Loads a subset of the STS dataset into a DataFrame. In particular both
# sentences and their human rated similarity score.
sent_pairs = []
with tf.gfile.GFile(filename, "r") as f:
for line in f:
ts = line.strip().split("\t")
# (sent_1, sent_2, similarity_score)
sent_pairs.append((ts[5], ts[6], float(ts[4])))
return pandas.DataFrame(sent_pairs, columns=["sent_1", "sent_2", "sim"])
def download_and_load_sts_data():
sts_dataset = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname="Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
origin="http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz",
extract=True)
sts_dev = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-dev.csv"))
sts_test = load_sts_dataset(
os.path.join(
os.path.dirname(sts_dataset), "stsbenchmark", "sts-test.csv"))
return sts_dev, sts_test
sts_dev, sts_test = download_and_load_sts_data()
Downloading data from http://ixa2.si.ehu.es/stswiki/images/4/48/Stsbenchmark.tar.gz 417792/409630 [==============================] - 2s 5us/step 425984/409630 [===============================] - 2s 5us/step
Construir gráfico de avaliação
sts_input1 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
sts_input2 = tf.sparse_placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(None, None))
# For evaluation we use exactly normalized rather than
# approximately normalized.
sts_encode1 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input1.values,
indices=sts_input1.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input1.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sts_encode2 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(
module(
inputs=dict(values=sts_input2.values,
indices=sts_input2.indices,
dense_shape=sts_input2.dense_shape)),
axis=1)
sim_scores = -tf.acos(tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(sts_encode1, sts_encode2), axis=1))
INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore INFO:tensorflow:Saver not created because there are no variables in the graph to restore
Avalie as incorporações de frases
Escolha o conjunto de dados para referência
dataset = sts_dev
values1, indices1, dense_shape1 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_1'].tolist())
values2, indices2, dense_shape2 = process_to_IDs_in_sparse_format(sp, dataset['sent_2'].tolist())
similarity_scores = dataset['sim'].tolist()
def run_sts_benchmark(session):
"""Returns the similarity scores"""
scores = session.run(
sim_scores,
feed_dict={
sts_input1.values: values1,
sts_input1.indices: indices1,
sts_input1.dense_shape: dense_shape1,
sts_input2.values: values2,
sts_input2.indices: indices2,
sts_input2.dense_shape: dense_shape2,
})
return scores
with tf.Session() as session:
session.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
session.run(tf.tables_initializer())
scores = run_sts_benchmark(session)
pearson_correlation = scipy.stats.pearsonr(scores, similarity_scores)
print('Pearson correlation coefficient = {0}\np-value = {1}'.format(
pearson_correlation[0], pearson_correlation[1]))
Pearson correlation coefficient = 0.7856484874001958 p-value = 1.065794746e-314
