 TensorFlow.org에서 보기 TensorFlow.org에서 보기 |
 Google Colab에서 실행 Google Colab에서 실행 |
 GitHub에서보기 GitHub에서보기 |
 노트북 다운로드 노트북 다운로드 |
 TF Hub 모델 보기 TF Hub 모델 보기 |
이 튜토리얼은 사전 훈련된 비디오 분류 모델을 실행하여 주어진 비디오에서 활동(댄스, 수영, 자전거 타기 등)을 분류합니다.
이 튜토리얼에서 사용된 모델 아키텍처는 MoViNet(Mobile Video Networks)이라고 합니다. MoVieNets는 거대한 데이터세트(Kinetics 600)에서 훈련된 효율적인 비디오 분류 모델 집합입니다.
TF Hub에서 사용 가능한 i3d 모델과 달리 MoViNet은 스트리밍 비디오에서 프레임별 추론도 지원합니다.
사전 훈련된 모델은 TF Hub에서 사용할 수 있습니다. TF Hub 컬렉션에는 TFLite에 최적화된 양자화된 모델도 포함되어 있습니다.
이러한 모델의 소스는 TensorFlow Model Garden에서 얻을 수 있습니다. 여기에는 MoViNet 모델의 구축 및 미세 조정도 포함하는 이 튜토리얼의 상세 버전이 포함됩니다.

설정
더 작은 모델(A0-A2)에 대한 추론의 경우, 이 Colab에 대한 CPU가 충분합니다.
sudo apt install -y ffmpegpip install -q mediapy
pip uninstall -q -y opencv-python-headlesspip install -q "opencv-python-headless<4.3"
# Import libraries
import pathlib
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mediapy as media
import numpy as np
import PIL
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow_hub as hub
import tqdm
mpl.rcParams.update({
'font.size': 10,
})
2022-12-14 21:55:00.393078: W tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer.so.7'; dlerror: libnvinfer.so.7: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 2022-12-14 21:55:00.393186: W tensorflow/compiler/xla/stream_executor/platform/default/dso_loader.cc:64] Could not load dynamic library 'libnvinfer_plugin.so.7'; dlerror: libnvinfer_plugin.so.7: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory 2022-12-14 21:55:00.393197: W tensorflow/compiler/tf2tensorrt/utils/py_utils.cc:38] TF-TRT Warning: Cannot dlopen some TensorRT libraries. If you would like to use Nvidia GPU with TensorRT, please make sure the missing libraries mentioned above are installed properly.
kinetics 600 레이블 목록을 가져오고 처음 몇 개의 레이블을 인쇄합니다.
labels_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname='labels.txt',
origin='https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tensorflow/models/f8af2291cced43fc9f1d9b41ddbf772ae7b0d7d2/official/projects/movinet/files/kinetics_600_labels.txt'
)
labels_path = pathlib.Path(labels_path)
lines = labels_path.read_text().splitlines()
KINETICS_600_LABELS = np.array([line.strip() for line in lines])
KINETICS_600_LABELS[:20]
array(['background', 'tench', 'goldfish', 'great white shark',
'tiger shark', 'hammerhead', 'electric ray', 'stingray', 'cock',
'hen', 'ostrich', 'brambling', 'goldfinch', 'house finch', 'junco',
'indigo bunting', 'robin', 'bulbul', 'jay', 'magpie'], dtype='<U30')
분류를 위한 간단한 예제 비디오를 제공하기 위해 팔 벌려 뛰기를 수행 중인 짧은 gif를 로드할 수 있습니다.

저작자 표시: CC-BY 라이선스에 따라 Coach Bobby Bluford가 YouTube에서 공유한 영상입니다.
gif를 다운로드합니다.
jumpingjack_url = 'https://github.com/tensorflow/models/raw/f8af2291cced43fc9f1d9b41ddbf772ae7b0d7d2/official/projects/movinet/files/jumpingjack.gif'
jumpingjack_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file(
fname='jumpingjack.gif',
origin=jumpingjack_url,
cache_dir='.', cache_subdir='.',
)
Downloading data from https://github.com/tensorflow/models/raw/f8af2291cced43fc9f1d9b41ddbf772ae7b0d7d2/official/projects/movinet/files/jumpingjack.gif 783318/783318 [==============================] - 0s 0us/step
gif 파일을 tf.Tensor로 읽는 함수를 정의합니다.
# Read and process a video
def load_gif(file_path, image_size=(224, 224)):
"""Loads a gif file into a TF tensor.
Use images resized to match what's expected by your model.
The model pages say the "A2" models expect 224 x 224 images at 5 fps
Args:
file_path: path to the location of a gif file.
image_size: a tuple of target size.
Returns:
a video of the gif file
"""
# Load a gif file, convert it to a TF tensor
raw = tf.io.read_file(file_path)
video = tf.io.decode_gif(raw)
# Resize the video
video = tf.image.resize(video, image_size)
# change dtype to a float32
# Hub models always want images normalized to [0,1]
# ref: https://www.tensorflow.org/hub/common_signatures/images#input
video = tf.cast(video, tf.float32) / 255.
return video
비디오의 형상은 (frames, height, width, colors)입니다.
jumpingjack=load_gif(jumpingjack_path)
jumpingjack.shape
TensorShape([13, 224, 224, 3])
모델을 사용하는 방법
이 섹션에는 TensorFlow Hub의 모델을 사용하는 방법을 보여주는 연습이 포함되어 있습니다. 작동 중인 모델만 보고 싶다면 다음 섹션으로 건너뛰세요.
각 모델에는 base 및 streaming의 두 가지 버전이 있습니다.
base버전은 비디오를 입력으로 사용하고 프레임에 대한 평균 확률을 반환합니다.streaming버전은 비디오 프레임과 RNN 상태를 입력으로 사용하고 해당 프레임과 새 RNN 상태에 대한 예측을 반환합니다.
기본 모델
TensorFlow Hub에서 사전 훈련된 모델을 다운로드합니다.
%%time
id = 'a2'
mode = 'base'
version = '3'
hub_url = f'https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/movinet/{id}/{mode}/kinetics-600/classification/{version}'
model = hub.load(hub_url)
CPU times: user 14.9 s, sys: 760 ms, total: 15.7 s Wall time: 15.9 s
이 버전의 모델에는 하나의 signature가 있습니다. 형상이 (batch, frames, height, width, colors)인 tf.float32의 image 인수를 취합니다. 그리고 하나의 출력, 즉 형상이 (batch, classes)인 로짓의 tf.float32 텐서를 포함하는 사전을 반환합니다.
sig = model.signatures['serving_default']
print(sig.pretty_printed_signature())
signature_wrapper(*, image)
Args:
image: float32 Tensor, shape=(None, None, None, None, 3)
Returns:
{'classifier_head': <1>}
<1>: float32 Tensor, shape=(None, 600)
비디오에서 이 서명을 실행하려면 먼저 비디오에 외부 batch 차원을 추가해야 합니다.
#warmup
sig(image = jumpingjack[tf.newaxis, :1]);
%%time
logits = sig(image = jumpingjack[tf.newaxis, ...])
logits = logits['classifier_head'][0]
print(logits.shape)
print()
(600,) CPU times: user 4.13 s, sys: 50.3 ms, total: 4.18 s Wall time: 6.53 s
위의 출력 처리를 나중에 패키징하는 get_top_k 함수를 정의합니다.
# Get top_k labels and probabilities
def get_top_k(probs, k=5, label_map=KINETICS_600_LABELS):
"""Outputs the top k model labels and probabilities on the given video.
Args:
probs: probability tensor of shape (num_frames, num_classes) that represents
the probability of each class on each frame.
k: the number of top predictions to select.
label_map: a list of labels to map logit indices to label strings.
Returns:
a tuple of the top-k labels and probabilities.
"""
# Sort predictions to find top_k
top_predictions = tf.argsort(probs, axis=-1, direction='DESCENDING')[:k]
# collect the labels of top_k predictions
top_labels = tf.gather(label_map, top_predictions, axis=-1)
# decode lablels
top_labels = [label.decode('utf8') for label in top_labels.numpy()]
# top_k probabilities of the predictions
top_probs = tf.gather(probs, top_predictions, axis=-1).numpy()
return tuple(zip(top_labels, top_probs))
logits을 확률로 변환하고 비디오의 상위 5개 클래스를 찾습니다. 모델은 비디오가 jumping jacks일 가능성이 있음을 확인합니다.
probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=-1)
for label, p in get_top_k(probs):
print(f'{label:20s}: {p:.3f}')
EntleBucher : 0.834 home theater : 0.008 miniature poodle : 0.003 redshank : 0.003 spider monkey : 0.002
스트리밍 모델
이전 섹션에서는 전체 비디오를 실행하는 모델을 사용했습니다. 종종 비디오를 처리할 때 마지막에 하나의 예측을 원하지 않고 프레임별로 예측을 업데이트하고 싶을 수 있습니다. 모델의 stream 버전을 사용하면 가능합니다.
모델의 stream 버전을 로드합니다.
%%time
id = 'a2'
mode = 'stream'
version = '3'
hub_url = f'https://tfhub.dev/tensorflow/movinet/{id}/{mode}/kinetics-600/classification/{version}'
model = hub.load(hub_url)
CPU times: user 43.8 s, sys: 2.19 s, total: 46 s Wall time: 45.9 s
이 모델을 사용하는 것은 base 모델보다 약간 더 복잡합니다. 모델의 RNN에 대한 내부 상태를 추적해야 합니다.
list(model.signatures.keys())
['call', 'init_states']
init_states 서명은 비디오의 형상 (batch, frames, height, width, colors)를 입력으로 사용하고 초기 RNN 상태를 포함하는 텐서의 방대한 사전을 반환합니다.
lines = model.signatures['init_states'].pretty_printed_signature().splitlines()
lines = lines[:10]
lines.append(' ...')
print('.\n'.join(lines))
signature_wrapper(*, input_shape).
Args:.
input_shape: int32 Tensor, shape=(5,).
Returns:.
{'state/b0/l0/pool_buffer': <1>, 'state/b0/l0/pool_frame_count': <2>, 'state/b0/l1/pool_buffer': <3>, 'state/b0/l1/pool_frame_count': <4>, 'state/b0/l1/stream_buffer': <5>, 'state/b0/l2/pool_buffer': <6>, 'state/b0/l2/pool_frame_count': <7>, 'state/b0/l2/stream_buffer': <8>, 'state/b1/l0/pool_buffer': <9>, 'state/b1/l0/pool_frame_count': <10>, 'state/b1/l0/stream_buffer': <11>, 'state/b1/l1/pool_buffer': <12>, 'state/b1/l1/pool_frame_count': <13>, 'state/b1/l1/stream_buffer': <14>, 'state/b1/l2/pool_buffer': <15>, 'state/b1/l2/pool_frame_count': <16>, 'state/b1/l2/stream_buffer': <17>, 'state/b1/l3/pool_buffer': <18>, 'state/b1/l3/pool_frame_count': <19>, 'state/b1/l3/stream_buffer': <20>, 'state/b1/l4/pool_buffer': <21>, 'state/b1/l4/pool_frame_count': <22>, 'state/b1/l4/stream_buffer': <23>, 'state/b2/l0/pool_buffer': <24>, 'state/b2/l0/pool_frame_count': <25>, 'state/b2/l0/stream_buffer': <26>, 'state/b2/l1/pool_buffer': <27>, 'state/b2/l1/pool_frame_count': <28>, 'state/b2/l1/stream_buffer': <29>, 'state/b2/l2/pool_buffer': <30>, 'state/b2/l2/pool_frame_count': <31>, 'state/b2/l2/stream_buffer': <32>, 'state/b2/l3/pool_buffer': <33>, 'state/b2/l3/pool_frame_count': <34>, 'state/b2/l3/stream_buffer': <35>, 'state/b2/l4/pool_buffer': <36>, 'state/b2/l4/pool_frame_count': <37>, 'state/b2/l4/stream_buffer': <38>, 'state/b3/l0/pool_buffer': <39>, 'state/b3/l0/pool_frame_count': <40>, 'state/b3/l0/stream_buffer': <41>, 'state/b3/l1/pool_buffer': <42>, 'state/b3/l1/pool_frame_count': <43>, 'state/b3/l1/stream_buffer': <44>, 'state/b3/l2/pool_buffer': <45>, 'state/b3/l2/pool_frame_count': <46>, 'state/b3/l2/stream_buffer': <47>, 'state/b3/l3/pool_buffer': <48>, 'state/b3/l3/pool_frame_count': <49>, 'state/b3/l3/stream_buffer': <50>, 'state/b3/l4/pool_buffer': <51>, 'state/b3/l4/pool_frame_count': <52>, 'state/b3/l5/pool_buffer': <53>, 'state/b3/l5/pool_frame_count': <54>, 'state/b3/l5/stream_buffer': <55>, 'state/b4/l0/pool_buffer': <56>, 'state/b4/l0/pool_frame_count': <57>, 'state/b4/l0/stream_buffer': <58>, 'state/b4/l1/pool_buffer': <59>, 'state/b4/l1/pool_frame_count': <60>, 'state/b4/l2/pool_buffer': <61>, 'state/b4/l2/pool_frame_count': <62>, 'state/b4/l3/pool_buffer': <63>, 'state/b4/l3/pool_frame_count': <64>, 'state/b4/l4/pool_buffer': <65>, 'state/b4/l4/pool_frame_count': <66>, 'state/b4/l5/pool_buffer': <67>, 'state/b4/l5/pool_frame_count': <68>, 'state/b4/l5/stream_buffer': <69>, 'state/b4/l6/pool_buffer': <70>, 'state/b4/l6/pool_frame_count': <71>, 'state/head/pool_buffer': <72>, 'state/head/pool_frame_count': <73>}.
<1>: float32 Tensor, shape=(None, 1, 1, 1, 40).
<2>: int32 Tensor, shape=(1,).
<3>: float32 Tensor, shape=(None, 1, 1, 1, 40).
<4>: int32 Tensor, shape=(1,).
<5>: float32 Tensor, shape=(None, 2, None, None, 40).
...
initial_state = model.init_states(jumpingjack[tf.newaxis, ...].shape)
type(initial_state)
dict
list(sorted(initial_state.keys()))[:5]
['state/b0/l0/pool_buffer', 'state/b0/l0/pool_frame_count', 'state/b0/l1/pool_buffer', 'state/b0/l1/pool_frame_count', 'state/b0/l1/stream_buffer']
RNN의 초기 상태가 확보되면 상태와 비디오 프레임을 입력으로 전달할 수 있습니다(비디오 프레임의 (batch, frames, height, width, colors) 형상 유지). 모델은 (logits, state) 쌍을 반환합니다.
첫 번째 프레임을 본 후 모델은 비디오가 "팔 벌려 뛰기"인지 확신하지 못합니다.
inputs = initial_state.copy()
# Add the batch axis, take the first frme, but keep the frame-axis.
inputs['image'] = jumpingjack[tf.newaxis, 0:1, ...]
# warmup
model(inputs);
logits, new_state = model(inputs)
logits = logits[0]
probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=-1)
for label, p in get_top_k(probs):
print(f'{label:20s}: {p:.3f}')
print()
miniature schnauzer : 0.427 corkscrew : 0.134 miniature poodle : 0.056 church : 0.053 fly : 0.039
루프에서 모델을 실행하여 각 프레임과 함께 업데이트된 상태를 전달하면 모델이 올바른 결과로 빠르게 수렴됩니다.
%%time
state = initial_state.copy()
all_logits = []
for n in range(len(jumpingjack)):
inputs = state
inputs['image'] = jumpingjack[tf.newaxis, n:n+1, ...]
result, state = model(inputs)
all_logits.append(logits)
probabilities = tf.nn.softmax(all_logits, axis=-1)
CPU times: user 552 ms, sys: 17.7 ms, total: 570 ms Wall time: 509 ms
for label, p in get_top_k(probabilities[-1]):
print(f'{label:20s}: {p:.3f}')
miniature schnauzer : 0.427 corkscrew : 0.134 miniature poodle : 0.056 church : 0.053 fly : 0.039
id = tf.argmax(probabilities[-1])
plt.plot(probabilities[:, id])
plt.xlabel('Frame #')
plt.ylabel(f"p('{KINETICS_600_LABELS[id]}')");
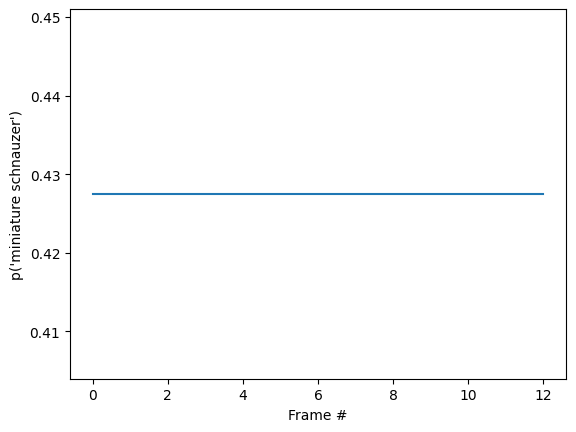
base 모델을 실행한 이전 섹션보다 최종 확률이 훨씬 더 확실하다는 것을 알 수 있습니다. base 모델은 전체 프레임에 대한 예측의 평균을 반환합니다.
for label, p in get_top_k(tf.reduce_mean(probabilities, axis=0)):
print(f'{label:20s}: {p:.3f}')
miniature schnauzer : 0.427 corkscrew : 0.134 miniature poodle : 0.056 church : 0.053 fly : 0.039
시간 경과에 따른 예측 애니메이션
이전 섹션에서는 이러한 모델을 사용하는 방법에 대해 자세히 설명했습니다. 이 섹션은 이를 바탕으로 멋진 추론 애니메이션을 생성합니다.
아래의 숨겨진 셀은 이 섹션에서 사용되는 도우미 함수를 정의합니다.
# Get top_k labels and probabilities predicted using MoViNets streaming model
def get_top_k_streaming_labels(probs, k=5, label_map=KINETICS_600_LABELS):
"""Returns the top-k labels over an entire video sequence.
Args:
probs: probability tensor of shape (num_frames, num_classes) that represents
the probability of each class on each frame.
k: the number of top predictions to select.
label_map: a list of labels to map logit indices to label strings.
Returns:
a tuple of the top-k probabilities, labels, and logit indices
"""
top_categories_last = tf.argsort(probs, -1, 'DESCENDING')[-1, :1]
# Sort predictions to find top_k
categories = tf.argsort(probs, -1, 'DESCENDING')[:, :k]
categories = tf.reshape(categories, [-1])
counts = sorted([
(i.numpy(), tf.reduce_sum(tf.cast(categories == i, tf.int32)).numpy())
for i in tf.unique(categories)[0]
], key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
top_probs_idx = tf.constant([i for i, _ in counts[:k]])
top_probs_idx = tf.concat([top_categories_last, top_probs_idx], 0)
# find unique indices of categories
top_probs_idx = tf.unique(top_probs_idx)[0][:k+1]
# top_k probabilities of the predictions
top_probs = tf.gather(probs, top_probs_idx, axis=-1)
top_probs = tf.transpose(top_probs, perm=(1, 0))
# collect the labels of top_k predictions
top_labels = tf.gather(label_map, top_probs_idx, axis=0)
# decode the top_k labels
top_labels = [label.decode('utf8') for label in top_labels.numpy()]
return top_probs, top_labels, top_probs_idx
# Plot top_k predictions at a given time step
def plot_streaming_top_preds_at_step(
top_probs,
top_labels,
step=None,
image=None,
legend_loc='lower left',
duration_seconds=10,
figure_height=500,
playhead_scale=0.8,
grid_alpha=0.3):
"""Generates a plot of the top video model predictions at a given time step.
Args:
top_probs: a tensor of shape (k, num_frames) representing the top-k
probabilities over all frames.
top_labels: a list of length k that represents the top-k label strings.
step: the current time step in the range [0, num_frames].
image: the image frame to display at the current time step.
legend_loc: the placement location of the legend.
duration_seconds: the total duration of the video.
figure_height: the output figure height.
playhead_scale: scale value for the playhead.
grid_alpha: alpha value for the gridlines.
Returns:
A tuple of the output numpy image, figure, and axes.
"""
# find number of top_k labels and frames in the video
num_labels, num_frames = top_probs.shape
if step is None:
step = num_frames
# Visualize frames and top_k probabilities of streaming video
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(6.5, 7), dpi=300)
gs = mpl.gridspec.GridSpec(8, 1)
ax2 = plt.subplot(gs[:-3, :])
ax = plt.subplot(gs[-3:, :])
# display the frame
if image is not None:
ax2.imshow(image, interpolation='nearest')
ax2.axis('off')
# x-axis (frame number)
preview_line_x = tf.linspace(0., duration_seconds, num_frames)
# y-axis (top_k probabilities)
preview_line_y = top_probs
line_x = preview_line_x[:step+1]
line_y = preview_line_y[:, :step+1]
for i in range(num_labels):
ax.plot(preview_line_x, preview_line_y[i], label=None, linewidth='1.5',
linestyle=':', color='gray')
ax.plot(line_x, line_y[i], label=top_labels[i], linewidth='2.0')
ax.grid(which='major', linestyle=':', linewidth='1.0', alpha=grid_alpha)
ax.grid(which='minor', linestyle=':', linewidth='0.5', alpha=grid_alpha)
min_height = tf.reduce_min(top_probs) * playhead_scale
max_height = tf.reduce_max(top_probs)
ax.vlines(preview_line_x[step], min_height, max_height, colors='red')
ax.scatter(preview_line_x[step], max_height, color='red')
ax.legend(loc=legend_loc)
plt.xlim(0, duration_seconds)
plt.ylabel('Probability')
plt.xlabel('Time (s)')
plt.yscale('log')
fig.tight_layout()
fig.canvas.draw()
data = np.frombuffer(fig.canvas.tostring_rgb(), dtype=np.uint8)
data = data.reshape(fig.canvas.get_width_height()[::-1] + (3,))
plt.close()
figure_width = int(figure_height * data.shape[1] / data.shape[0])
image = PIL.Image.fromarray(data).resize([figure_width, figure_height])
image = np.array(image)
return image
# Plotting top_k predictions from MoViNets streaming model
def plot_streaming_top_preds(
probs,
video,
top_k=5,
video_fps=25.,
figure_height=500,
use_progbar=True):
"""Generates a video plot of the top video model predictions.
Args:
probs: probability tensor of shape (num_frames, num_classes) that represents
the probability of each class on each frame.
video: the video to display in the plot.
top_k: the number of top predictions to select.
video_fps: the input video fps.
figure_fps: the output video fps.
figure_height: the height of the output video.
use_progbar: display a progress bar.
Returns:
A numpy array representing the output video.
"""
# select number of frames per second
video_fps = 8.
# select height of the image
figure_height = 500
# number of time steps of the given video
steps = video.shape[0]
# estimate duration of the video (in seconds)
duration = steps / video_fps
# estiamte top_k probabilities and corresponding labels
top_probs, top_labels, _ = get_top_k_streaming_labels(probs, k=top_k)
images = []
step_generator = tqdm.trange(steps) if use_progbar else range(steps)
for i in step_generator:
image = plot_streaming_top_preds_at_step(
top_probs=top_probs,
top_labels=top_labels,
step=i,
image=video[i],
duration_seconds=duration,
figure_height=figure_height,
)
images.append(image)
return np.array(images)
비디오 프레임에서 스트리밍 모델을 실행하고 로짓을 수집하여 시작합니다.
init_states = model.init_states(jumpingjack[tf.newaxis].shape)
# Insert your video clip here
video = jumpingjack
images = tf.split(video[tf.newaxis], video.shape[0], axis=1)
all_logits = []
# To run on a video, pass in one frame at a time
states = init_states
for image in tqdm.tqdm(images):
# predictions for each frame
logits, states = model({**states, 'image': image})
all_logits.append(logits)
# concatinating all the logits
logits = tf.concat(all_logits, 0)
# estimating probabilities
probs = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=-1)
100%|██████████| 13/13 [00:00<00:00, 25.79it/s]
final_probs = probs[-1]
print('Top_k predictions and their probablities\n')
for label, p in get_top_k(final_probs):
print(f'{label:20s}: {p:.3f}')
Top_k predictions and their probablities EntleBucher : 0.999 home theater : 0.000 redshank : 0.000 spoonbill : 0.000 candle : 0.000
확률 시퀀스를 비디오로 변환합니다.
# Generate a plot and output to a video tensor
plot_video = plot_streaming_top_preds(probs, video, video_fps=8.)
100%|██████████| 13/13 [00:07<00:00, 1.64it/s]
# For gif format, set codec='gif'
media.show_video(plot_video, fps=3)
리소스
사전 훈련된 모델은 TF Hub에서 사용할 수 있습니다. TF Hub 컬렉션에는 TFLite에 최적화된 양자화된 모델도 포함되어 있습니다.
이러한 모델의 소스는 TensorFlow Model Garden에서 제공합니다. 여기에는 MoViNet 모델 구축 및 미세 조정에 대한 내용도 담긴 이 튜토리얼의 상세 버전이 포함됩니다.
