 TensorFlow.org で表示 TensorFlow.org で表示 |
 Google Colab で実行 Google Colab で実行 |
 GitHub でソースを表示 GitHub でソースを表示 |
 ノートブックをダウンロード ノートブックをダウンロード |
概要
TensorFlow の型昇格には 4 つのオプションがあります。
- デフォルトでは、混合型の演算に対し、TensorFlow は型を昇格する代わりにエラーを発します。
tf.numpy.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior()を実行すると、TensorFlow が NumPy 型の昇格ルールを使用するように切り替えられます。- このドキュメントでは、TensorFlow 2.15 で提供予定の新しい 2 つのオプションについて説明します(現在は、
tf-nightlyで提供されています)。
pip install -q tf_nightly注意: experimental_enable_numpy_behavior は、TensorFlow のすべての動作を変更します。
セットアップ
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import tensorflow.experimental.numpy as tnp
print("Using TensorFlow version %s" % tf.__version__)
Using TensorFlow version 2.16.0-dev20240110
新しい型昇格の有効化
JAX のような型昇格を TF-Numpy で使用するには、TensorFlow で NumPy の動作を有効にする際に、dtype 変換モードとして 'all' または 'safe' のいずれかを指定します。
この新しい組(dtype_conversion_mode="all" を使用)は結合的で可換であり、最終的にどのような幅の浮動小数になるかを制御するのが簡単になります(自動的により幅の広い float に変換しません)。ただし、オーバーフローと精度損失のリスクがいくらか導入されますが、dtype_conversion_mode="safe" によってそれらのケースの明示的な処理が強制されます。2 つのモードについては、次のセクションで詳しく説明されています。
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet.
2 つのモード: ALL モードと SAFE モード
新しい型昇格システムでは、ALL モードと SAFE モードの 2 つのモードが導入されています。SAFE モードは精度損失またはビット拡張となる「リスクのある」昇格の懸念を緩和するために使用されます。
Dtype
簡潔さの目的で、以下の略語を使用します。
bはtf.boolですu8はtf.uint8ですi16はtf.int16ですi32はtf.int32ですbf16はtf.bfloat16ですf32はtf.float32ですf64はtf.float64ですi32*は Python のintまたは弱く型付けされたi32ですf32*は Python のfloatまたは弱く型付けされたf32ですc128*は Python のcomplexまたは弱く型付けされたc128です
アスタリスク(*)は、対応する方が「弱い」ことを示します。そのような dtype は一時的にシステムによって推論されるため、他の dtype に従う可能性があります。この概念は、こちらでより詳しく説明されています。
精度を損失する演算の例
次の例では、i32 + f32 は ALL モードでは可能ですが、精度損失のリスクにより、SAFE モードでは行えません。
# i32 + f32 returns a f32 result in ALL mode.
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
a = tf.constant(10, dtype = tf.int32)
b = tf.constant(5.0, dtype = tf.float32)
a + b # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=15.0>
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet. <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=15.0>
# This promotion is not allowed in SAFE mode.
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="safe")
a = tf.constant(10, dtype = tf.int32)
b = tf.constant(5.0, dtype = tf.float32)
try:
a + b
except TypeError as e:
print(f'{type(e)}: {e}') # TypeError: explicitly specify the dtype or switch to ALL mode.
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet. <class 'TypeError'>: In promotion mode PromoMode.SAFE, implicit dtype promotion between (<dtype: 'int32'>, weak=False) and (<dtype: 'float32'>, weak=False) is disallowed. You need to explicitly specify the dtype in your op, or relax your dtype promotion rules (such as from SAFE mode to ALL mode).
ビット拡張の演算の例
次の例において、i8 + u32 は ALL モードでは可能ですが、入力のビットの数よりも多いビットを使用するビット拡張により、SAFE モードでは行えません。新しい型昇格セマンティクスでは必要なビット拡張のみが許可されることに注意してください。
# i8 + u32 returns an i64 result in ALL mode.
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
a = tf.constant(10, dtype = tf.int8)
b = tf.constant(5, dtype = tf.uint32)
a + b
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet. <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int64, numpy=15>
# This promotion is not allowed in SAFE mode.
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="safe")
a = tf.constant(10, dtype = tf.int8)
b = tf.constant(5, dtype = tf.uint32)
try:
a + b
except TypeError as e:
print(f'{type(e)}: {e}') # TypeError: explicitly specify the dtype or switch to ALL mode.
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet. <class 'TypeError'>: In promotion mode PromoMode.SAFE, implicit dtype promotion between (<dtype: 'int8'>, weak=False) and (<dtype: 'uint32'>, weak=False) is disallowed. You need to explicitly specify the dtype in your op, or relax your dtype promotion rules (such as from SAFE mode to ALL mode).
格子に基づくシステム
型昇格格子
新しい型昇格の動作は、次の型昇格の格子を通じて決定されます。
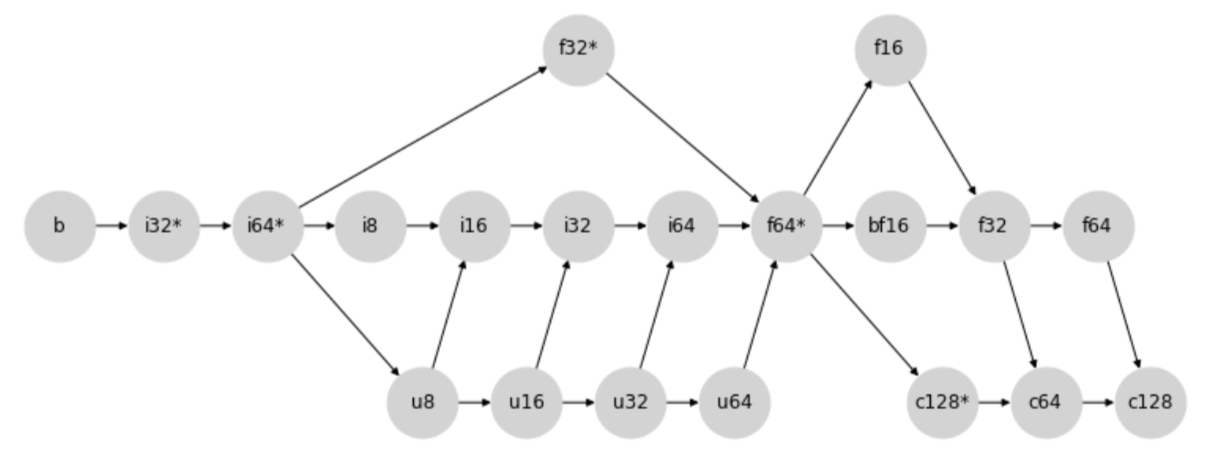
より具体的には、2 つの型の間の昇格は、2 つのノード(ノード事態を含む)の最初の共通の子を見つけて決定されます。
たとえば、上のダイアグラムの場合、i8 と i32 の最初の共通の子は i32 です。この 2 つのノードは矢印の方向に進む際に最初に i32 で交差するためです。
もう 1 つの例とも同様に、u64 と f16 の間の昇格の結果の方は f16 となります。
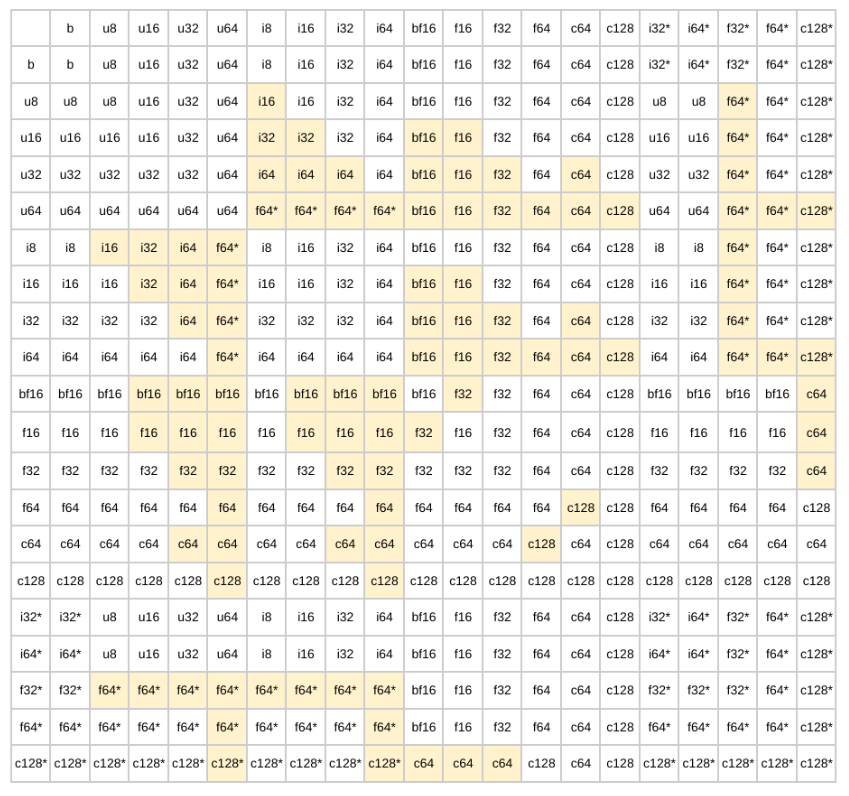
型昇格テーブル
格子に従うと、以下のバイナリ昇格テーブルが生成されます。
注意: SAFE モードでは、ハイライトされたセルは許可されません。ALL モードではすべてのケースが許可されます。
新しい型昇格のメリット
新しい型昇格には、以下のメリットのある JAX のような格子ベースのシステムを採用します。
格子ベースのシステムのメリット
まず、格子ベースのシステムを使用することで、3 つの非常に重要な特性が確保されます。
- 存在: あらゆる型の組み合わせに固有の結果昇格型があります。
- 可換性:
a + b = b + a - 結合性:
a + (b + c) = (a + b) + c
これらの 3 つの特性は、一貫性と予測可能性を備えた型昇格セマンティクスを構築する上で重要な特性です。
JAX のような格子系のメリット
JAX のような格子系のもう 1 つの重大なメリットは、符号なしの int の外側では、必要以上に広範なプロモーションをすべて回避することです。つまり、64 ビットの入力なしに 64 ビットの結果を取得することはできません。これは以前の型昇格で頻繁であった不要な 64 ビット値を回避するため、特にアクセラレータで処理する際に大きなメリットがあります。
ただし、これにはトレードオフがあります。float/integer が混合する昇格には精度損失の非常に強い傾向があることです。たとえば、下の例では i64 + f16 は i64 を f16 に昇格してしまいます。
# The first input is promoted to f16 in ALL mode.
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
tf.constant(1, tf.int64) + tf.constant(3.2, tf.float16) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=4.2>
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet. <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=4.2>
このような懸念を緩和するために、こういった「リスクのある」昇格を許可しない SAFE モードを導入しました。
注意: 格子系の構築における設計上の考慮点については、JAX の型昇格セマンティクスの設計をご覧ください。
WeakTensor
概要
弱いテンソルとは、JAX における概念に似た「弱く型付けされた」テンソルです。
WeakTensor の dtype は一時的にシステムによって推論され、他の dtype に従う可能性があります。この概念は、TF 値と、Python のスカラーリテラルのように明示的にユーザーが指定した型がない値の間で行われるバイナリ演算内で不要な型昇格が行われないようにするために、新しい型昇格に導入されています。
たとえば下の例では、tf.constant(1.2) には特定の dtype がないため、「弱い」と見なされます。したがって、tf.constant(1.2) は tf.constant(3.1, tf.float16) の型に従い、f16 の出力結果が得られます。
tf.constant(1.2) + tf.constant(3.1, tf.float16) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=4.3>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=4.3>
WeakTensor の構造
WeakTensor は、dtype を指定せずにテンソルを作成した場合に作成され、その結果として WeakTensor となります。テンソルが「弱い」かどうかは、テンソルの文字列表現の最後にある weak 属性をチェックすることでわかります。
最初のケース: tf.constant が、ユーザー指定の dtype のない入力で呼び出された場合。
tf.constant(5) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=5, weak=True>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=5, weak=True>
tf.constant([5.0, 10.0, 3]) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(3,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([ 5., 10., 3.], dtype=float32), weak=True>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(3,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([ 5., 10., 3.], dtype=float32), weak=True>
# A normal Tensor is created when dtype arg is specified.
tf.constant(5, tf.int32) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=5>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=5>
2 つ目のケース: ユーザー指定の dtype のない入力が WeakTensor をサポートする API に渡された場合。
tf.math.abs([100.0, 4.0]) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([100., 4.], dtype=float32), weak=True>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2,), dtype=float32, numpy=array([100., 4.], dtype=float32), weak=True>
新しい型昇格をオンにした効果
以下は、新しい型昇格をオンにしたことによる変更の部分リストです。
- より一貫性のある予測可能な昇格結果。
- ビット拡張のリスクの軽減。
tf.Tensorの数学的ダンダーメソッドでは、新しい型の昇格が使用されます。tf.constantはWeakTensorを戻せます。tf.constantは、dtype引数とは異なる dtype を持つテンソル入力が渡された場合に、暗黙的な変換を行えます。tf.Variableインプレース演算(assign、assign-add、assign-sub)で暗黙の変換が可能です。tnp.array(1)とtnp.array(1.0)は 32 ビット WeakTensor を返します。WeakTensorが作成され、WeakTensor がサポートする単項およびバイナリ API に使用されます。
より一貫性のある予測可能な昇格結果
格子ベースのシステムを使用することで、新しい型昇格により、一貫性のある予測可能な型昇格結果を生成することができます。
以前の型昇格
以前の型昇格を使用すると、演算の順序の変更によって結果にばらつきが生じます。
# Setup
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="legacy")
a = np.array(1, dtype=np.int8)
b = tf.constant(1)
c = np.array(1, dtype=np.float16)
# (a + b) + c throws an InvalidArgumentError.
try:
tf.add(tf.add(a, b), c)
except tf.errors.InvalidArgumentError as e:
print(f'{type(e)}: {e}') # InvalidArgumentError
<class 'tensorflow.python.framework.errors_impl.InvalidArgumentError'>: cannot compute AddV2 as input #1(zero-based) was expected to be a int8 tensor but is a int32 tensor [Op:AddV2] name:
# (b + a) + c returns an i32 result.
tf.add(tf.add(b, a), c) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=3>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=3>
新しい型昇格
新しい型昇格では、順序に関係なく一貫した結果を得られます。
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
a = np.array(1, dtype=np.int8)
b = tf.constant(1)
c = np.array(1, dtype=np.float16)
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet.
# (a + b) + c returns a f16 result.
tf.add(tf.add(a, b), c) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=3.0>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=3.0>
# (b + a) + c also returns a f16 result.
tf.add(tf.add(b, a), c) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=3.0>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=3.0>
ビット拡張のリスクの軽減
以前の型昇格
以前の型昇格では、64 ビットの結果が生成されることがありました。
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="legacy")
np.array(3.2, np.float16) + tf.constant(1, tf.int8) + tf.constant(50) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=54.19921875>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float64, numpy=54.19921875>
新しい型昇格
新しい型昇格では、必要最小限のビット数で結果が返されます。
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet.
np.array(3.2, np.float16) + tf.constant(1, tf.int8) + tf.constant(50) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=54.2>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float16, numpy=54.2>
tf.Tensor の数学的ダンダーメソッド
すべての tf.Tensor 数学的ダンダーメソッドは、新しい型昇格に従います。
-tf.constant(5) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=-5, weak=True>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=-5, weak=True>
tf.constant(5, tf.int16) - tf.constant(1, tf.float32) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=4.0>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=4.0>
tf.Variable インプレース演算
tf.Variable インプレース演算では、暗黙的変換が可能です。
注意: 変数の元の dtype とは異なる dtype を生成する昇格は許可されません。これは、tf.Variable がその dtype を変更できないためです。
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
a = tf.Variable(10, tf.int32)
a.assign_add(tf.constant(5, tf.int16)) # <tf.Variable shape=() dtype=int32, numpy=15>
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet. <tf.Variable 'UnreadVariable' shape=() dtype=int32, numpy=15>
tf.constant の暗黙的変換
以前の型昇格の場合、tf.constant では、入力テンソルに dtype 引数と同じ dtype が使用されている必要がありましたが、新しい型昇格では、テンソルが指定された dtype に暗黙的に変換されます。
tnp.experimental_enable_numpy_behavior(dtype_conversion_mode="all")
a = tf.constant(10, tf.int16)
tf.constant(a, tf.float32) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=10.0>
WARNING:tensorflow:UserWarning: enabling the new type promotion must happen at the beginning of the program. Please ensure no TF APIs have been used yet. <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=10.0>
TF-NumPy の配列
新しい型昇格では、Python の tnp.array はデフォルトで i32* と f32* になります。
tnp.array(1) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1, weak=True>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1, weak=True>
tnp.array(1.0) # <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1, weak=True>
<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.0, weak=True>
入力の型推論
新しい型昇格では、異なる入力の型は以下のようにして推論されます。
tf.Tensor:tf.Tensorには dtype プロパティがあるため、それ以上の推論は行われません。- NumPy 型: これには
np.array(1)、np.int16(1)、np.floatなどの型が含まれます。NumPy 型入力にも dtype プロパティが含まれているため、その dtype プロパティが結果の推論型として使用されます。NumPy はデフォルトでi64とf64になることに注意してください。 - Python スカラー/ネスト型: これには
1、[1, 2, 3]、(1.0, 2.0)などの型が含まれます。- Python
intはi32*として推論されます。 - Python
floatはf32*として推論されます。 - Python
complexはc128*として推論されます。
- Python
- 入力が上記のいずれのカテゴリにも当てはまらない場合でも dtype プロパティがある場合には、その dtype プロパティが結果の推論型として使用されます。
その他の資料
新しい型昇格は JAC-NumPy の型昇格に非常によく似ています。新しい型昇格とその設計上の選択についての詳細は、以下のリソースをご覧ください。
参考資料
WeakTensor をサポートしている API
以下は、WeakTensor をサポートしている API のリストです。
単項演算については、ユーザー指定の型がない入力が渡されると、WeakTensor を返します。
バイナリ演算については、こちらの昇格テーブルに従います。2 つの入力の昇格結果に応じて、WeakTensor が返される場合とそうでない場合があります。
注意: すべての数学的演算(+、-、* など)がサポートされています。
tf.bitwise.inverttf.clip_by_valuetf.debugging.check_numericstf.expand_dimstf.identitytf.image.adjust_brightnesstf.image.adjust_gammatf.image.extract_patchestf.image.random_brightnesstf.image.stateless_random_brightnesstf.linalg.diagtf.linalg.diag_parttf.linalg.matmultf.linalg.matrix_transposetf.linalg.tensor_diag_parttf.linalg.tracetf.math.abstf.math.acostf.math.acoshtf.math.addtf.math.angletf.math.asintf.math.asinhtf.math.atantf.math.atanhtf.math.ceiltf.math.conjtf.math.costf.math.coshtf.math.digammatf.math.divide_no_nantf.math.dividetf.math.erftf.math.erfctf.math.erfcinvtf.math.erfinvtf.math.exptf.math.expm1tf.math.floortf.math.floordivtf.math.floormodtf.math.imagtf.math.lgammatf.math.log1ptf.math.log_sigmoidtf.math.logtf.math.multiply_no_nantf.math.multiplytf.math.ndtritf.math.negativetf.math.powtf.math.realtf.math.realtf.math.reciprocal_no_nantf.math.reciprocaltf.math.reduce_euclidean_normtf.math.reduce_logsumexptf.math.reduce_maxtf.math.reduce_meantf.math.reduce_mintf.math.reduce_prodtf.math.reduce_stdtf.math.reduce_sumtf.math.reduce_variancetf.math.rinttf.math.roundtf.math.rsqrttf.math.scalar_multf.math.sigmoidtf.math.signtf.math.sintf.math.sinhtf.math.softplustf.math.special.bessel_i0tf.math.special.bessel_i0etf.math.special.bessel_i1tf.math.special.bessel_i1etf.math.special.bessel_j0tf.math.special.bessel_j1tf.math.special.bessel_k0tf.math.special.bessel_k0etf.math.special.bessel_k1tf.math.special.bessel_k1etf.math.special.bessel_y0tf.math.special.bessel_y1tf.math.special.dawsntf.math.special.expinttf.math.special.fresnel_costf.math.special.fresnel_sintf.math.special.spencetf.math.sqrttf.math.squaretf.math.subtracttf.math.tantf.math.tanhtf.nn.depth_to_spacetf.nn.elutf.nn.gelutf.nn.leaky_relutf.nn.log_softmaxtf.nn.relu6tf.nn.relutf.nn.selutf.nn.softsigntf.nn.space_to_depthtf.nn.swishtf.ones_liketf.realdivtf.reshapetf.squeezetf.stop_gradienttf.transposetf.truncatedivtf.truncatemodtf.zeros_liketf.experimental.numpy.abstf.experimental.numpy.absolutetf.experimental.numpy.amaxtf.experimental.numpy.amintf.experimental.numpy.angletf.experimental.numpy.arangetf.experimental.numpy.arccostf.experimental.numpy.arccoshtf.experimental.numpy.arcsintf.experimental.numpy.arcsinhtf.experimental.numpy.arctantf.experimental.numpy.arctanhtf.experimental.numpy.aroundtf.experimental.numpy.arraytf.experimental.numpy.asanyarraytf.experimental.numpy.asarraytf.experimental.numpy.ascontiguousarraytf.experimental.numpy.averagetf.experimental.numpy.bitwise_nottf.experimental.numpy.cbrttf.experimental.numpy.ceiltf.experimental.numpy.conjtf.experimental.numpy.conjugatetf.experimental.numpy.copytf.experimental.numpy.costf.experimental.numpy.coshtf.experimental.numpy.cumprodtf.experimental.numpy.cumsumtf.experimental.numpy.deg2radtf.experimental.numpy.diagtf.experimental.numpy.diagflattf.experimental.numpy.diagonaltf.experimental.numpy.difftf.experimental.numpy.empty_liketf.experimental.numpy.exp2tf.experimental.numpy.exptf.experimental.numpy.expand_dimstf.experimental.numpy.expm1tf.experimental.numpy.fabstf.experimental.numpy.fixtf.experimental.numpy.flattentf.experimental.numpy.fliptf.experimental.numpy.fliplrtf.experimental.numpy.flipudtf.experimental.numpy.floortf.experimental.numpy.full_liketf.experimental.numpy.imagtf.experimental.numpy.log10tf.experimental.numpy.log1ptf.experimental.numpy.log2tf.experimental.numpy.logtf.experimental.numpy.maxtf.experimental.numpy.meantf.experimental.numpy.mintf.experimental.numpy.moveaxistf.experimental.numpy.nanmeantf.experimental.numpy.negativetf.experimental.numpy.ones_liketf.experimental.numpy.positivetf.experimental.numpy.prodtf.experimental.numpy.rad2degtf.experimental.numpy.raveltf.experimental.numpy.realtf.experimental.numpy.reciprocaltf.experimental.numpy.repeattf.experimental.numpy.reshapetf.experimental.numpy.rot90tf.experimental.numpy.roundtf.experimental.numpy.signbittf.experimental.numpy.sintf.experimental.numpy.sinctf.experimental.numpy.sinhtf.experimental.numpy.sorttf.experimental.numpy.sqrttf.experimental.numpy.squaretf.experimental.numpy.squeezetf.experimental.numpy.stdtf.experimental.numpy.sumtf.experimental.numpy.swapaxestf.experimental.numpy.tantf.experimental.numpy.tanhtf.experimental.numpy.tracetf.experimental.numpy.transposetf.experimental.numpy.triutf.experimental.numpy.vandertf.experimental.numpy.vartf.experimental.numpy.zeros_like
