 ดูบน TensorFlow.org ดูบน TensorFlow.org |  ทำงานใน Google Colab ทำงานใน Google Colab |  ดูบน GitHub ดูบน GitHub |  ดาวน์โหลดโน๊ตบุ๊ค ดาวน์โหลดโน๊ตบุ๊ค |
บทนำ
Decision Forests (DF) เป็นชุดอัลกอริธึมการเรียนรู้ของเครื่องขนาดใหญ่สำหรับการจำแนกประเภท การถดถอย และการจัดอันดับภายใต้การดูแล ตามชื่อที่แนะนำ DF ใช้แผนผังการตัดสินใจเป็นตัวสร้าง วันนี้ทั้งสองได้รับความนิยมมากที่สุดขั้นตอนวิธีการฝึกอบรม DF เป็น ป่าสุ่ม และ การไล่โทนสีต้นไม้การตัดสินใจเพิ่มขึ้น อัลกอริธึมทั้งสองเป็นเทคนิคทั้งมวลที่ใช้แผนผังการตัดสินใจหลายแบบ แต่ต่างกันที่วิธีการทำ
TensorFlow Decision Forests (TF-DF) เป็นห้องสมุดสำหรับการฝึกอบรม การประเมิน การตีความ และการอนุมานแบบจำลองการตัดสินใจ
ในบทช่วยสอนนี้ คุณจะได้เรียนรู้วิธี:
- ฝึกการจำแนกประเภทไบนารี Random Forest บนชุดข้อมูลที่มีคุณลักษณะที่เป็นตัวเลข จำแนกเป็นหมวดหมู่ และขาดหายไป
- ประเมินแบบจำลองในชุดข้อมูลทดสอบ
- เตรียมความพร้อมแบบจำลองสำหรับ TensorFlow การแสดง
- ตรวจสอบโครงสร้างโดยรวมของโมเดลและความสำคัญของแต่ละฟีเจอร์
- ฝึกโมเดลใหม่ด้วยอัลกอริธึมการเรียนรู้ที่แตกต่างกัน (Gradient Boosted Decision Trees)
- ใช้ชุดคุณสมบัติอินพุตอื่น
- เปลี่ยนไฮเปอร์พารามิเตอร์ของโมเดล
- ประมวลผลคุณสมบัติล่วงหน้า
- ฝึกแบบจำลองสำหรับการถดถอย
- ฝึกโมเดลสำหรับการจัดอันดับ
เอกสารรายละเอียดมีอยู่ใน คู่มือการใช้ ไดเรกทอรีตัวอย่างเช่น มีตัวอย่างแบบ end-to-end อื่น ๆ
การติดตั้ง TensorFlow Decision Forests
ติดตั้ง TF-DF โดยเรียกใช้เซลล์ต่อไปนี้
pip install tensorflow_decision_forests
ติดตั้ง Wurlitzer เพื่อแสดงรายละเอียดบันทึกการฝึกอบรม สิ่งนี้จำเป็นใน colab เท่านั้น
pip install wurlitzer
นำเข้าห้องสมุด
import tensorflow_decision_forests as tfdf
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
import math
try:
from wurlitzer import sys_pipes
except:
from colabtools.googlelog import CaptureLog as sys_pipes
from IPython.core.magic import register_line_magic
from IPython.display import Javascript
WARNING:root:Failure to load the custom c++ tensorflow ops. This error is likely caused the version of TensorFlow and TensorFlow Decision Forests are not compatible. WARNING:root:TF Parameter Server distributed training not available.
เซลล์โค้ดที่ซ่อนอยู่จะจำกัดความสูงของเอาต์พุตใน colab
# Some of the model training logs can cover the full
# screen if not compressed to a smaller viewport.
# This magic allows setting a max height for a cell.
@register_line_magic
def set_cell_height(size):
display(
Javascript("google.colab.output.setIframeHeight(0, true, {maxHeight: " +
str(size) + "})"))
# Check the version of TensorFlow Decision Forests
print("Found TensorFlow Decision Forests v" + tfdf.__version__)
Found TensorFlow Decision Forests v0.2.1
ฝึกโมเดลป่าสุ่ม
ในส่วนนี้เรารถไฟประเมินวิเคราะห์และการส่งออกการจัดหมวดหมู่ไบนารีสุ่มป่าได้รับการฝึกฝนใน พาลเมอร์เพนกวิน ชุด

โหลดชุดข้อมูลและแปลงเป็น tf.Dataset
ชุดข้อมูลนี้มีขนาดเล็กมาก (300 ตัวอย่าง) และจัดเก็บเป็นไฟล์ที่มีลักษณะคล้าย .csv ดังนั้นใช้ Pandas เพื่อโหลด
มาประกอบชุดข้อมูลเป็นไฟล์ csv (เช่น เพิ่มส่วนหัว) และโหลดมัน:
# Download the dataset
!wget -q https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/palmer_penguins/penguins.csv -O /tmp/penguins.csv
# Load a dataset into a Pandas Dataframe.
dataset_df = pd.read_csv("/tmp/penguins.csv")
# Display the first 3 examples.
dataset_df.head(3)
ชุดข้อมูลที่มีส่วนผสมของตัวเลข (เช่น bill_depth_mm ) เด็ดขาด (เช่น island ) และคุณสมบัติที่ขาดหายไป TF-DF สนับสนุนทุกประเภทเหล่านี้คุณลักษณะกำเนิด (ที่แตกต่างกว่ารุ่น NN based) จึงมีความจำเป็นสำหรับ preprocessing ในรูปแบบของการเข้ารหัสร้อนฟื้นฟูพิเศษหรือไม่ is_present คุณลักษณะ
ป้ายกำกับแตกต่างกันเล็กน้อย: เมตริก Keras ต้องการจำนวนเต็ม ฉลาก ( species ) จะถูกเก็บไว้เป็นสตริงเพื่อให้แปลงเป็นจำนวนเต็ม
# Encode the categorical label into an integer.
#
# Details:
# This stage is necessary if your classification label is represented as a
# string. Note: Keras expected classification labels to be integers.
# Name of the label column.
label = "species"
classes = dataset_df[label].unique().tolist()
print(f"Label classes: {classes}")
dataset_df[label] = dataset_df[label].map(classes.index)
Label classes: ['Adelie', 'Gentoo', 'Chinstrap']
ถัดไปแบ่งชุดข้อมูลออกเป็นการฝึกอบรมและการทดสอบ:
# Split the dataset into a training and a testing dataset.
def split_dataset(dataset, test_ratio=0.30):
"""Splits a panda dataframe in two."""
test_indices = np.random.rand(len(dataset)) < test_ratio
return dataset[~test_indices], dataset[test_indices]
train_ds_pd, test_ds_pd = split_dataset(dataset_df)
print("{} examples in training, {} examples for testing.".format(
len(train_ds_pd), len(test_ds_pd)))
252 examples in training, 92 examples for testing.
และในที่สุดก็แปลงแพนด้า dataframe ( pd.Dataframe ) ลงในชุดข้อมูล tensorflow ( tf.data.Dataset ):
train_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_ds_pd, label=label)
test_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(test_ds_pd, label=label)
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow_decision_forests/keras/core.py:1612: FutureWarning: In a future version of pandas all arguments of DataFrame.drop except for the argument 'labels' will be keyword-only features_dataframe = dataframe.drop(label, 1)
หมายเหตุ: pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset จะได้แปลงฉลากเพื่อจำนวนเต็มสำหรับคุณ
และถ้าคุณต้องการที่จะสร้าง tf.data.Dataset ตัวเองมีสองสิ่งที่ต้องจำ:
- อัลกอริธึมการเรียนรู้ทำงานร่วมกับชุดข้อมูลยุคเดียวและไม่มีการสับเปลี่ยน
- ขนาดแบทช์ไม่ส่งผลต่ออัลกอริธึมการฝึกอบรม แต่ค่าเล็กน้อยอาจทำให้การอ่านชุดข้อมูลช้าลง
ฝึกโมเดล
%set_cell_height 300
# Specify the model.
model_1 = tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel()
# Optionally, add evaluation metrics.
model_1.compile(
metrics=["accuracy"])
# Train the model.
# "sys_pipes" is optional. It enables the display of the training logs.
with sys_pipes():
model_1.fit(x=train_ds)
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
1/4 [======>.......................] - ETA: 12s
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 8
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
0: "bill_depth_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:17.1936 min:13.2 max:21.5 sd:1.96763
1: "bill_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
2: "body_mass_g" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:4221 min:2700 max:6300 sd:811.125
3: "flipper_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:201.264 min:172 max:231 sd:14.0793
6: "year" NUMERICAL mean:2008.05 min:2007 max:2009 sd:0.817297
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
4: "island" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:4 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Biscoe" 126 (50%)
5: "sex" CATEGORICAL num-nas:7 (2.77778%) has-dict vocab-size:3 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"male" 124 (50.6122%)
7: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "RANDOM_FOREST"
features: "bill_depth_mm"
features: "bill_length_mm"
features: "body_mass_g"
features: "flipper_length_mm"
features: "island"
features: "sex"
features: "year"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.random_forest.proto.random_forest_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 16
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
winner_take_all_inference: true
compute_oob_performances: true
compute_oob_variable_importances: false
adapt_bootstrap_size_ratio_for_maximum_training_duration: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO random_forest.cc:315] Training random forest on 252 example(s) and 7 feature(s).
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 1/300 (tree index:0) done accuracy:0.922222 logloss:2.8034
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 11/300 (tree index:10) done accuracy:0.960159 logloss:0.355553
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 21/300 (tree index:17) done accuracy:0.960317 logloss:0.360011
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 31/300 (tree index:32) done accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.355906
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 41/300 (tree index:41) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.354263
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 51/300 (tree index:51) done accuracy:0.980159 logloss:0.355675
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 61/300 (tree index:60) done accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.354058
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 71/300 (tree index:70) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.355711
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 81/300 (tree index:82) done accuracy:0.980159 logloss:0.356747
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 91/300 (tree index:90) done accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.225018
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 101/300 (tree index:100) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.221976
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 111/300 (tree index:109) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.223525
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 121/300 (tree index:117) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.095911
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 131/300 (tree index:127) done accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.0970941
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 141/300 (tree index:140) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0962378
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 151/300 (tree index:151) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0952778
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 161/300 (tree index:161) done accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0953929
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 171/300 (tree index:172) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0966406
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 181/300 (tree index:180) done accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.096802
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 191/300 (tree index:189) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0952902
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 201/300 (tree index:200) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0926996
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 211/300 (tree index:210) done accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0923645
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 221/300 (tree index:221) done accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0928984
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 231/300 (tree index:230) done accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0938896
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 241/300 (tree index:240) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0947512
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 251/300 (tree index:250) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0952597
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 261/300 (tree index:260) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0948972
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 271/300 (tree index:270) done accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.096022
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 281/300 (tree index:280) done accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.0950604
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 291/300 (tree index:290) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0962781
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 300/300 (tree index:298) done accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0967387
[INFO random_forest.cc:696] Final OOB metrics: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0967387
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmpdqbqx3ck
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 300 root(s), 4558 node(s), and 7 input feature(s).
[INFO abstract_model.cc:993] Engine "RandomForestGeneric" built
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
4/4 [==============================] - 4s 19ms/step
หมายเหตุ
- ไม่ได้ระบุคุณสมบัติอินพุต ดังนั้น คอลัมน์ทั้งหมดจะถูกใช้เป็นคุณสมบัติอินพุต ยกเว้นป้ายกำกับ คุณลักษณะที่ใช้โดยรูปแบบจะแสดงในบันทึกการฝึกอบรมและใน
model.summary() - DF ใช้คุณลักษณะที่เป็นตัวเลข เชิงหมวดหมู่ ชุดตามหมวดหมู่ และค่าที่ขาดหายไป คุณสมบัติเชิงตัวเลขไม่จำเป็นต้องถูกทำให้เป็นมาตรฐาน ค่าสตริงตามหมวดหมู่ไม่จำเป็นต้องเข้ารหัสในพจนานุกรม
- ไม่ได้ระบุพารามิเตอร์ไฮเปอร์การฝึกอบรม ดังนั้น พารามิเตอร์ไฮเปอร์เริ่มต้นจะถูกใช้ พารามิเตอร์ไฮเปอร์เริ่มต้นให้ผลลัพธ์ที่สมเหตุสมผลในสถานการณ์ส่วนใหญ่
- โทร
compileในรูปแบบก่อนที่จะfitเป็นตัวเลือก คอมไพล์สามารถใช้เพื่อให้เมตริกการประเมินเพิ่มเติม - อัลกอริทึมการฝึกอบรมไม่จำเป็นต้องมีชุดข้อมูลการตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง หากมีการระบุชุดข้อมูลการตรวจสอบ จะใช้เพื่อแสดงเมตริกเท่านั้น
ประเมินแบบจำลอง
มาประเมินแบบจำลองของเราในชุดข้อมูลทดสอบกัน
evaluation = model_1.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True)
print()
for name, value in evaluation.items():
print(f"{name}: {value:.4f}")
2/2 [==============================] - 0s 4ms/step - loss: 0.0000e+00 - accuracy: 1.0000 loss: 0.0000 accuracy: 1.0000
หมายเหตุ: ความถูกต้องทดสอบ (0.86514) อยู่ใกล้กับความถูกต้องออกจากถุง (0.8672) แสดงให้เห็นว่าในบันทึกการฝึกอบรม
ดูส่วนรูปแบบการประเมินตนเองด้านล่างสำหรับวิธีการประเมินผลเพิ่มเติม
เตรียมโมเดลนี้สำหรับ TensorFlow Serving
การส่งออกรูปแบบไปเป็นรูปแบบ SavedModel ในภายหลังอีกครั้งการใช้งานเช่น การให้บริการ TensorFlow
model_1.save("/tmp/my_saved_model")
2021-11-08 12:10:07.057561: W tensorflow/python/util/util.cc:368] Sets are not currently considered sequences, but this may change in the future, so consider avoiding using them. INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/my_saved_model/assets INFO:tensorflow:Assets written to: /tmp/my_saved_model/assets
พล็อตโมเดล
การวางแผนแผนผังต้นไม้การตัดสินใจและการทำตามกิ่งแรกจะช่วยให้เรียนรู้เกี่ยวกับป่าการตัดสินใจ ในบางกรณี การพล็อตโมเดลสามารถใช้สำหรับการดีบั๊กได้
เนื่องจากความแตกต่างในวิธีการฝึกอบรม บางรุ่นจึงน่าสนใจในการวางแผนมากกว่ารุ่นอื่นๆ เนื่องจากเสียงที่แทรกเข้ามาระหว่างการฝึกและความลึกของต้นไม้ การวางแผนพล็อตป่าสุ่มจึงให้ข้อมูลน้อยกว่าการวางแผนรถเข็นหรือต้นไม้ต้นแรกของต้นไม้ที่มีการไล่ระดับการไล่ระดับสี
ไม่น้อยไปกว่านั้น เรามาพล็อตต้นไม้ต้นแรกของแบบจำลอง Random Forest ของเรากัน:
tfdf.model_plotter.plot_model_in_colab(model_1, tree_idx=0, max_depth=3)
โหนดรากด้านซ้ายมีเงื่อนไขแรก ( bill_depth_mm >= 16.55 ) จำนวนตัวอย่าง (240) และการจัดจำหน่ายฉลาก (แถบสีแดงสีฟ้าสีเขียว)
ตัวอย่างที่ประเมินจริงเพื่อ bill_depth_mm >= 16.55 จะแยกไปยังเส้นทางสีเขียว อื่น ๆ จะแตกแขนงไปตามเส้นทางสีแดง
ลึกโหนดที่มากกว่าที่ pure พวกเขากลายเป็นเช่นกระจายฉลากเอนเอียงไปทางส่วนหนึ่งของการเรียน
โครงสร้างแบบจำลองและความสำคัญของคุณลักษณะ
โครงสร้างโดยรวมของรูปแบบคือการแสดงที่มี .summary() แล้วคุณจะได้เห็น:
- ประเภท: ขั้นตอนวิธีการเรียนรู้ที่ใช้ในการฝึกอบรมรุ่น (
Random Forestในกรณีของเรา) - ภารกิจ: แก้ปัญหาโดยรูปแบบ (คน
Classificationในกรณีของเรา) - ป้อนข้อมูลคุณสมบัติ: ใส่ให้บริการของรูปแบบ
- ความสำคัญการศึกษา: มาตรการที่แตกต่างกันถึงความสำคัญของแต่ละคุณลักษณะสำหรับรูปแบบ
- ออกจากถุงประเมินผล: การประเมินผลออกจากกระเป๋าของรูปแบบ นี่เป็นทางเลือกที่ประหยัดและมีประสิทธิภาพสำหรับการตรวจสอบข้าม
- จำนวน {ต้นไม้โหนด} และตัวชี้วัดอื่น ๆ : สถิติเกี่ยวกับโครงสร้างของป่าการตัดสินใจ
หมายเหตุ: เนื้อหาสรุปขึ้นอยู่กับขั้นตอนวิธีการเรียนรู้ (เช่นออกจากถุงจะใช้ได้เฉพาะสุ่มป่า) และ Hyper-พารามิเตอร์ (เช่นตัวแปรสำคัญค่าเฉลี่ยลดลงในความถูกต้องสามารถใช้งานใน Hyper-พารามิเตอร์) .
%set_cell_height 300
model_1.summary()
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
Model: "random_forest_model"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
=================================================================
Total params: 1
Trainable params: 0
Non-trainable params: 1
_________________________________________________________________
Type: "RANDOM_FOREST"
Task: CLASSIFICATION
Label: "__LABEL"
Input Features (7):
bill_depth_mm
bill_length_mm
body_mass_g
flipper_length_mm
island
sex
year
No weights
Variable Importance: MEAN_MIN_DEPTH:
1. "__LABEL" 3.318694 ################
2. "year" 3.297927 ###############
3. "sex" 3.267547 ###############
4. "body_mass_g" 2.658307 ##########
5. "bill_depth_mm" 2.213272 #######
6. "island" 2.153127 #######
7. "bill_length_mm" 1.515876 ##
8. "flipper_length_mm" 1.217305
Variable Importance: NUM_AS_ROOT:
1. "flipper_length_mm" 161.000000 ################
2. "bill_length_mm" 62.000000 #####
3. "bill_depth_mm" 57.000000 #####
4. "body_mass_g" 12.000000
5. "island" 8.000000
Variable Importance: NUM_NODES:
1. "bill_length_mm" 682.000000 ################
2. "bill_depth_mm" 399.000000 #########
3. "flipper_length_mm" 383.000000 ########
4. "body_mass_g" 315.000000 #######
5. "island" 298.000000 ######
6. "sex" 34.000000
7. "year" 18.000000
Variable Importance: SUM_SCORE:
1. "flipper_length_mm" 26046.340791 ################
2. "bill_length_mm" 24253.203630 ##############
3. "bill_depth_mm" 11054.011817 ######
4. "island" 10713.713617 ######
5. "body_mass_g" 4117.938353 ##
6. "sex" 290.820204
7. "year" 39.211544
Winner take all: true
Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0967387
Number of trees: 300
Total number of nodes: 4558
Number of nodes by tree:
Count: 300 Average: 15.1933 StdDev: 3.2623
Min: 9 Max: 29 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 9, 10) 6 2.00% 2.00% #
[ 10, 11) 0 0.00% 2.00%
[ 11, 12) 38 12.67% 14.67% #####
[ 12, 13) 0 0.00% 14.67%
[ 13, 14) 71 23.67% 38.33% #########
[ 14, 15) 0 0.00% 38.33%
[ 15, 16) 83 27.67% 66.00% ##########
[ 16, 17) 0 0.00% 66.00%
[ 17, 18) 52 17.33% 83.33% ######
[ 18, 19) 0 0.00% 83.33%
[ 19, 20) 27 9.00% 92.33% ###
[ 20, 21) 0 0.00% 92.33%
[ 21, 22) 12 4.00% 96.33% #
[ 22, 23) 0 0.00% 96.33%
[ 23, 24) 6 2.00% 98.33% #
[ 24, 25) 0 0.00% 98.33%
[ 25, 26) 3 1.00% 99.33%
[ 26, 27) 0 0.00% 99.33%
[ 27, 28) 1 0.33% 99.67%
[ 28, 29] 1 0.33% 100.00%
Depth by leafs:
Count: 2429 Average: 3.39234 StdDev: 1.08569
Min: 1 Max: 7 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 1, 2) 26 1.07% 1.07%
[ 2, 3) 557 22.93% 24.00% #######
[ 3, 4) 716 29.48% 53.48% #########
[ 4, 5) 767 31.58% 85.06% ##########
[ 5, 6) 300 12.35% 97.41% ####
[ 6, 7) 57 2.35% 99.75% #
[ 7, 7] 6 0.25% 100.00%
Number of training obs by leaf:
Count: 2429 Average: 31.1239 StdDev: 32.4208
Min: 5 Max: 115 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 5, 10) 1193 49.11% 49.11% ##########
[ 10, 16) 137 5.64% 54.76% #
[ 16, 21) 70 2.88% 57.64% #
[ 21, 27) 69 2.84% 60.48% #
[ 27, 32) 72 2.96% 63.44% #
[ 32, 38) 86 3.54% 66.98% #
[ 38, 43) 67 2.76% 69.74% #
[ 43, 49) 79 3.25% 72.99% #
[ 49, 54) 54 2.22% 75.22%
[ 54, 60) 43 1.77% 76.99%
[ 60, 66) 43 1.77% 78.76%
[ 66, 71) 39 1.61% 80.36%
[ 71, 77) 62 2.55% 82.91% #
[ 77, 82) 63 2.59% 85.51% #
[ 82, 88) 102 4.20% 89.71% #
[ 88, 93) 95 3.91% 93.62% #
[ 93, 99) 99 4.08% 97.69% #
[ 99, 104) 37 1.52% 99.22%
[ 104, 110) 16 0.66% 99.88%
[ 110, 115] 3 0.12% 100.00%
Attribute in nodes:
682 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
399 : bill_depth_mm [NUMERICAL]
383 : flipper_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
315 : body_mass_g [NUMERICAL]
298 : island [CATEGORICAL]
34 : sex [CATEGORICAL]
18 : year [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 0:
161 : flipper_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
62 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
57 : bill_depth_mm [NUMERICAL]
12 : body_mass_g [NUMERICAL]
8 : island [CATEGORICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 1:
236 : flipper_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
224 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
175 : bill_depth_mm [NUMERICAL]
169 : island [CATEGORICAL]
70 : body_mass_g [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 2:
401 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
319 : flipper_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
290 : bill_depth_mm [NUMERICAL]
261 : island [CATEGORICAL]
174 : body_mass_g [NUMERICAL]
14 : sex [CATEGORICAL]
6 : year [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 3:
593 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
371 : bill_depth_mm [NUMERICAL]
365 : flipper_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
290 : island [CATEGORICAL]
273 : body_mass_g [NUMERICAL]
30 : sex [CATEGORICAL]
9 : year [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 5:
681 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
399 : bill_depth_mm [NUMERICAL]
383 : flipper_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
314 : body_mass_g [NUMERICAL]
298 : island [CATEGORICAL]
33 : sex [CATEGORICAL]
18 : year [NUMERICAL]
Condition type in nodes:
1797 : HigherCondition
332 : ContainsBitmapCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 0:
292 : HigherCondition
8 : ContainsBitmapCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 1:
705 : HigherCondition
169 : ContainsBitmapCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 2:
1190 : HigherCondition
275 : ContainsBitmapCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 3:
1611 : HigherCondition
320 : ContainsBitmapCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 5:
1795 : HigherCondition
331 : ContainsBitmapCondition
Node format: NOT_SET
Training OOB:
trees: 1, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.922222 logloss:2.8034
trees: 11, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.960159 logloss:0.355553
trees: 21, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.960317 logloss:0.360011
trees: 31, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.355906
trees: 41, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.354263
trees: 51, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.980159 logloss:0.355675
trees: 61, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.354058
trees: 71, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.355711
trees: 81, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.980159 logloss:0.356747
trees: 91, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.225018
trees: 101, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.221976
trees: 111, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.223525
trees: 121, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.095911
trees: 131, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.0970941
trees: 141, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0962378
trees: 151, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0952778
trees: 161, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0953929
trees: 171, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0966406
trees: 181, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.096802
trees: 191, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0952902
trees: 201, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0926996
trees: 211, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0923645
trees: 221, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0928984
trees: 231, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.97619 logloss:0.0938896
trees: 241, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0947512
trees: 251, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0952597
trees: 261, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0948972
trees: 271, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.096022
trees: 281, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.968254 logloss:0.0950604
trees: 291, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0962781
trees: 300, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.972222 logloss:0.0967387
ข้อมูลในการ summary มีทั้งหมด programatically มีการใช้การตรวจสอบรูปแบบ:
# The input features
model_1.make_inspector().features()
["bill_depth_mm" (1; #0), "bill_length_mm" (1; #1), "body_mass_g" (1; #2), "flipper_length_mm" (1; #3), "island" (4; #4), "sex" (4; #5), "year" (1; #6)]
# The feature importances
model_1.make_inspector().variable_importances()
{'NUM_NODES': [("bill_length_mm" (1; #1), 682.0),
("bill_depth_mm" (1; #0), 399.0),
("flipper_length_mm" (1; #3), 383.0),
("body_mass_g" (1; #2), 315.0),
("island" (4; #4), 298.0),
("sex" (4; #5), 34.0),
("year" (1; #6), 18.0)],
'SUM_SCORE': [("flipper_length_mm" (1; #3), 26046.34079089854),
("bill_length_mm" (1; #1), 24253.20363048464),
("bill_depth_mm" (1; #0), 11054.011817359366),
("island" (4; #4), 10713.713617041707),
("body_mass_g" (1; #2), 4117.938353393227),
("sex" (4; #5), 290.82020355574787),
("year" (1; #6), 39.21154398471117)],
'NUM_AS_ROOT': [("flipper_length_mm" (1; #3), 161.0),
("bill_length_mm" (1; #1), 62.0),
("bill_depth_mm" (1; #0), 57.0),
("body_mass_g" (1; #2), 12.0),
("island" (4; #4), 8.0)],
'MEAN_MIN_DEPTH': [("__LABEL" (4; #7), 3.318693759943752),
("year" (1; #6), 3.2979265641765556),
("sex" (4; #5), 3.2675474155474094),
("body_mass_g" (1; #2), 2.6583072575572553),
("bill_depth_mm" (1; #0), 2.213271913271913),
("island" (4; #4), 2.153126937876938),
("bill_length_mm" (1; #1), 1.5158758371258376),
("flipper_length_mm" (1; #3), 1.2173052873052872)]}
เนื้อหาสรุปและตรวจสอบขึ้นอยู่กับขั้นตอนวิธีการเรียนรู้ ( tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel ในกรณีนี้) และ Hyper-พารามิเตอร์ (เช่น compute_oob_variable_importances=True จะเรียกคำนวณออกจากถุง importances ตัวแปรสำหรับผู้เรียนสุ่มป่า ).
แบบจำลองการประเมินตนเอง
ระหว่างการฝึกอบรมรุ่น TFDF ตนเองสามารถประเมินแม้ว่าจะไม่มีการตรวจสอบชุดข้อมูลที่มีให้กับ fit() วิธีการ ตรรกะที่แน่นอนขึ้นอยู่กับรุ่น ตัวอย่างเช่น Random Forest จะใช้การประเมิน Out-of-bag ในขณะที่ Gradient Boosted Trees จะใช้การตรวจสอบภายในรถไฟ
การประเมินผลรูปแบบตัวเองสามารถใช้ได้กับการตรวจสอบของ evaluation() :
model_1.make_inspector().evaluation()
Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09673874925762888, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)
พล็อตบันทึกการฝึกอบรม
บันทึกการฝึกแสดงคุณภาพของแบบจำลอง (เช่น การประเมินความถูกต้องเมื่อออกจากถุงหรือชุดข้อมูลการตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง) ตามจำนวนต้นไม้ในแบบจำลอง บันทึกเหล่านี้มีประโยชน์ในการศึกษาความสมดุลระหว่างขนาดโมเดลและคุณภาพของโมเดล
บันทึกมีหลายวิธี:
- แสดงในระหว่างการฝึกอบรมถ้า
fit()เป็นห่อwith sys_pipes():(ดูตัวอย่างข้างต้น) - ในตอนท้ายของการสรุปรูปแบบเช่น
model.summary()(ดูตัวอย่างข้างต้น) - โปรแกรมโดยใช้การตรวจสอบรูปแบบเช่น
model.make_inspector().training_logs() - ใช้ TensorBoard
ลองใช้ตัวเลือก 2 และ 3:
%set_cell_height 150
model_1.make_inspector().training_logs()
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object> [TrainLog(num_trees=1, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=90, accuracy=0.9222222222222223, loss=2.8033951229519314, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=11, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=251, accuracy=0.9601593625498008, loss=0.35555349201320174, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=21, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9603174603174603, loss=0.36001140491238665, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=31, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9682539682539683, loss=0.35590612713897984, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=41, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.3542631175664682, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=51, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9801587301587301, loss=0.3556750144602524, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=61, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9761904761904762, loss=0.35405768100763596, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=71, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.3557109447003948, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=81, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9801587301587301, loss=0.3567472372411026, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=91, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9761904761904762, loss=0.22501842999121263, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=101, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.22197619985256875, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=111, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.22352461745252922, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=121, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.0959110420552038, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=131, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9682539682539683, loss=0.09709411316240828, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=141, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09623779574896962, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=151, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.0952777798871495, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=161, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9761904761904762, loss=0.09539292345473928, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=171, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.0966405748567056, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=181, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9761904761904762, loss=0.09680202871280176, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=191, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09529015259994637, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=201, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09269960071625453, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=211, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9761904761904762, loss=0.09236453164605395, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=221, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9761904761904762, loss=0.09289838398791968, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=231, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9761904761904762, loss=0.09388963293491139, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=241, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09475124760028271, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=251, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09525974302197851, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=261, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09489722432391275, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=271, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9682539682539683, loss=0.09602198886152889, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=281, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9682539682539683, loss=0.09506043538613806, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=291, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09627806474750358, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None)), TrainLog(num_trees=300, evaluation=Evaluation(num_examples=252, accuracy=0.9722222222222222, loss=0.09673874925762888, rmse=None, ndcg=None, aucs=None))]
มาพล็อตกันเถอะ:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
logs = model_1.make_inspector().training_logs()
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 4))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.plot([log.num_trees for log in logs], [log.evaluation.accuracy for log in logs])
plt.xlabel("Number of trees")
plt.ylabel("Accuracy (out-of-bag)")
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.plot([log.num_trees for log in logs], [log.evaluation.loss for log in logs])
plt.xlabel("Number of trees")
plt.ylabel("Logloss (out-of-bag)")
plt.show()

ชุดข้อมูลนี้มีขนาดเล็ก คุณจะเห็นโมเดลบรรจบกันเกือบจะในทันที
มาใช้ TensorBoard กันเถอะ:
# This cell start TensorBoard that can be slow.
# Load the TensorBoard notebook extension
%load_ext tensorboard
# Google internal version
# %load_ext google3.learning.brain.tensorboard.notebook.extension
# Clear existing results (if any)rm -fr "/tmp/tensorboard_logs"
# Export the meta-data to tensorboard.
model_1.make_inspector().export_to_tensorboard("/tmp/tensorboard_logs")
# docs_infra: no_execute
# Start a tensorboard instance.
%tensorboard --logdir "/tmp/tensorboard_logs"
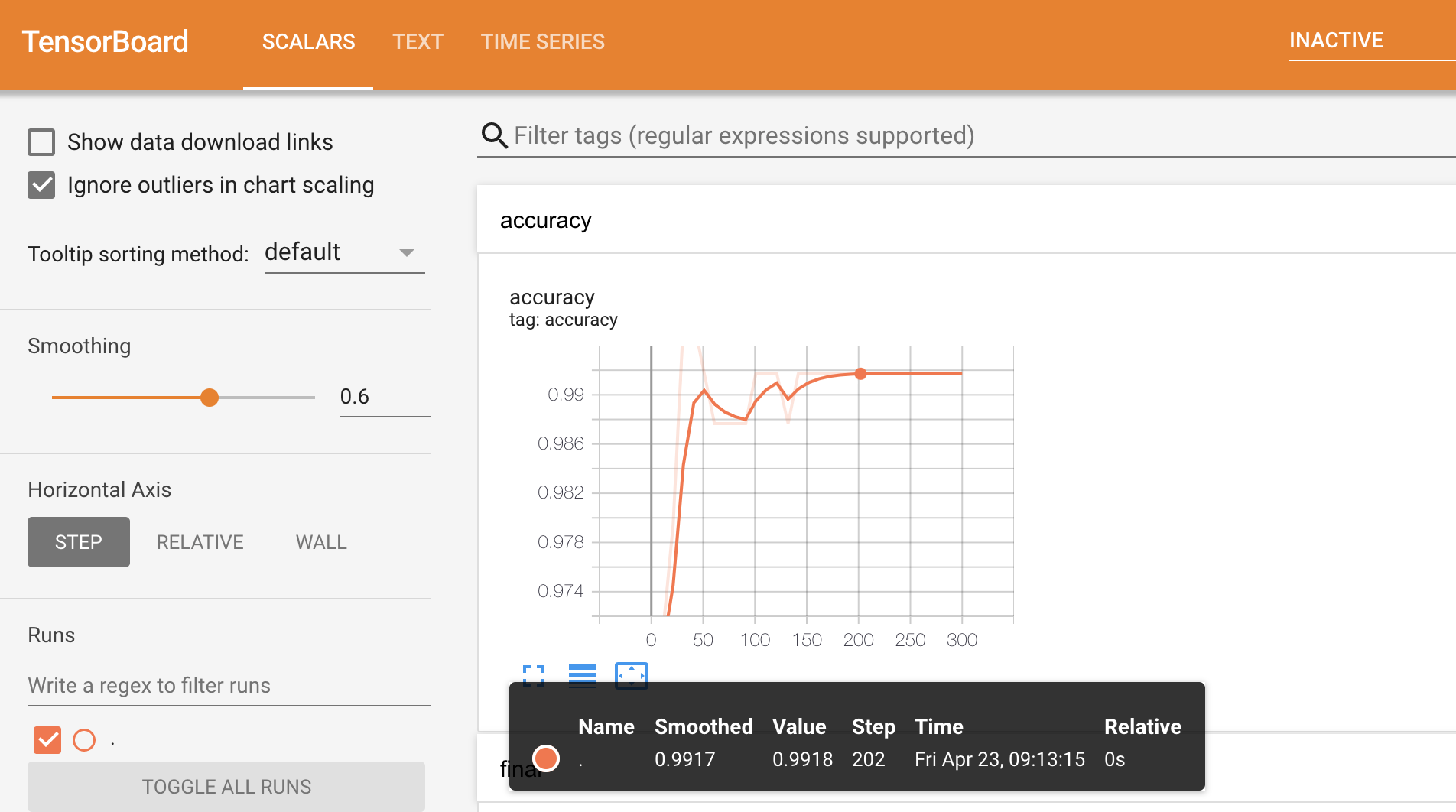
ฝึกโมเดลใหม่ด้วยอัลกอริธึมการเรียนรู้ที่แตกต่างกัน
อัลกอริทึมการเรียนรู้ถูกกำหนดโดยคลาสโมเดล ยกตัวอย่างเช่น tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel() รถไฟป่าสุ่มขณะ tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel() รถไฟลาดเพิ่มขึ้นต้นไม้ตัดสินใจ
ขั้นตอนวิธีการเรียนรู้ที่มีการระบุไว้โดยการเรียก tfdf.keras.get_all_models() หรือใน รายชื่อของผู้เรียน
tfdf.keras.get_all_models()
[tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.RandomForestModel, tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel, tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.CartModel, tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.DistributedGradientBoostedTreesModel]
รายละเอียดของขั้นตอนวิธีการเรียนรู้และ Hyper-พารามิเตอร์ของพวกเขานอกจากนี้ยังมีใน การอ้างอิง API และ builtin ความช่วยเหลือ:
# help works anywhere.
help(tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel)
# ? only works in ipython or notebooks, it usually opens on a separate panel.
tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel?
Help on class RandomForestModel in module tensorflow_decision_forests.keras:
class RandomForestModel(tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.wrappers.RandomForestModel)
| RandomForestModel(*args, **kwargs)
|
| Random Forest learning algorithm.
|
| A Random Forest (https://www.stat.berkeley.edu/~breiman/randomforest2001.pdf)
| is a collection of deep CART decision trees trained independently and without
| pruning. Each tree is trained on a random subset of the original training
| dataset (sampled with replacement).
|
| The algorithm is unique in that it is robust to overfitting, even in extreme
| cases e.g. when there is more features than training examples.
|
| It is probably the most well-known of the Decision Forest training
| algorithms.
|
| Usage example:
|
| ```python
| import tensorflow_decision_forests as tfdf
| import pandas as pd
|
| dataset = pd.read_csv("project/dataset.csv")
| tf_dataset = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(dataset, label="my_label")
|
| model = tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel()
| model.fit(tf_dataset)
|
| print(model.summary())
| ```
|
| Attributes:
| task: Task to solve (e.g. Task.CLASSIFICATION, Task.REGRESSION,
| Task.RANKING).
| features: Specify the list and semantic of the input features of the model.
| If not specified, all the available features will be used. If specified
| and if `exclude_non_specified_features=True`, only the features in
| `features` will be used by the model. If "preprocessing" is used,
| `features` corresponds to the output of the preprocessing. In this case,
| it is recommended for the preprocessing to return a dictionary of tensors.
| exclude_non_specified_features: If true, only use the features specified in
| `features`.
| preprocessing: Functional keras model or @tf.function to apply on the input
| feature before the model to train. This preprocessing model can consume
| and return tensors, list of tensors or dictionary of tensors. If
| specified, the model only "sees" the output of the preprocessing (and not
| the raw input). Can be used to prepare the features or to stack multiple
| models on top of each other. Unlike preprocessing done in the tf.dataset,
| the operation in "preprocessing" are serialized with the model.
| postprocessing: Like "preprocessing" but applied on the model output.
| ranking_group: Only for `task=Task.RANKING`. Name of a tf.string feature that
| identifies queries in a query/document ranking task. The ranking group
| is not added automatically for the set of features if
| `exclude_non_specified_features=false`.
| temp_directory: Temporary directory used to store the model Assets after the
| training, and possibly as a work directory during the training. This
| temporary directory is necessary for the model to be exported after
| training e.g. `model.save(path)`. If not specified, `temp_directory` is
| set to a temporary directory using `tempfile.TemporaryDirectory`. This
| directory is deleted when the model python object is garbage-collected.
| verbose: If true, displays information about the training.
| hyperparameter_template: Override the default value of the hyper-parameters.
| If None (default) the default parameters of the library are used. If set,
| `default_hyperparameter_template` refers to one of the following
| preconfigured hyper-parameter sets. Those sets outperforms the default
| hyper-parameters (either generally or in specific scenarios).
| You can omit the version (e.g. remove "@v5") to use the last version of
| the template. In this case, the hyper-parameter can change in between
| releases (not recommended for training in production).
| - better_default@v1: A configuration that is generally better than the
| default parameters without being more expensive. The parameters are:
| winner_take_all=True.
| - benchmark_rank1@v1: Top ranking hyper-parameters on our benchmark
| slightly modified to run in reasonable time. The parameters are:
| winner_take_all=True, categorical_algorithm="RANDOM",
| split_axis="SPARSE_OBLIQUE", sparse_oblique_normalization="MIN_MAX",
| sparse_oblique_num_projections_exponent=1.0.
|
| advanced_arguments: Advanced control of the model that most users won't need
| to use. See `AdvancedArguments` for details.
| num_threads: Number of threads used to train the model. Different learning
| algorithms use multi-threading differently and with different degree of
| efficiency. If specified, `num_threads` field of the
| `advanced_arguments.yggdrasil_deployment_config` has priority.
| name: The name of the model.
| max_vocab_count: Default maximum size of the vocabulary for CATEGORICAL and
| CATEGORICAL_SET features stored as strings. If more unique values exist,
| only the most frequent values are kept, and the remaining values are
| considered as out-of-vocabulary. The value `max_vocab_count` defined in a
| `FeatureUsage` (if any) takes precedence.
| adapt_bootstrap_size_ratio_for_maximum_training_duration: Control how the
| maximum training duration (if set) is applied. If false, the training
| stop when the time is used. If true, adapts the size of the sampled
| dataset used to train each tree such that `num_trees` will train within
| `maximum_training_duration`. Has no effect if there is no maximum
| training duration specified. Default: False.
| allow_na_conditions: If true, the tree training evaluates conditions of the
| type `X is NA` i.e. `X is missing`. Default: False.
| categorical_algorithm: How to learn splits on categorical attributes.
| - `CART`: CART algorithm. Find categorical splits of the form "value \\in
| mask". The solution is exact for binary classification, regression and
| ranking. It is approximated for multi-class classification. This is a
| good first algorithm to use. In case of overfitting (very small
| dataset, large dictionary), the "random" algorithm is a good
| alternative.
| - `ONE_HOT`: One-hot encoding. Find the optimal categorical split of the
| form "attribute == param". This method is similar (but more efficient)
| than converting converting each possible categorical value into a
| boolean feature. This method is available for comparison purpose and
| generally performs worse than other alternatives.
| - `RANDOM`: Best splits among a set of random candidate. Find the a
| categorical split of the form "value \\in mask" using a random search.
| This solution can be seen as an approximation of the CART algorithm.
| This method is a strong alternative to CART. This algorithm is inspired
| from section "5.1 Categorical Variables" of "Random Forest", 2001.
| Default: "CART".
| categorical_set_split_greedy_sampling: For categorical set splits e.g.
| texts. Probability for a categorical value to be a candidate for the
| positive set. The sampling is applied once per node (i.e. not at every
| step of the greedy optimization). Default: 0.1.
| categorical_set_split_max_num_items: For categorical set splits e.g. texts.
| Maximum number of items (prior to the sampling). If more items are
| available, the least frequent items are ignored. Changing this value is
| similar to change the "max_vocab_count" before loading the dataset, with
| the following exception: With `max_vocab_count`, all the remaining items
| are grouped in a special Out-of-vocabulary item. With `max_num_items`,
| this is not the case. Default: -1.
| categorical_set_split_min_item_frequency: For categorical set splits e.g.
| texts. Minimum number of occurrences of an item to be considered.
| Default: 1.
| compute_oob_performances: If true, compute the Out-of-bag evaluation (then
| available in the summary and model inspector). This evaluation is a cheap
| alternative to cross-validation evaluation. Default: True.
| compute_oob_variable_importances: If true, compute the Out-of-bag feature
| importance (then available in the summary and model inspector). Note that
| the OOB feature importance can be expensive to compute. Default: False.
| growing_strategy: How to grow the tree.
| - `LOCAL`: Each node is split independently of the other nodes. In other
| words, as long as a node satisfy the splits "constraints (e.g. maximum
| depth, minimum number of observations), the node will be split. This is
| the "classical" way to grow decision trees.
| - `BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL`: The node with the best loss reduction among all
| the nodes of the tree is selected for splitting. This method is also
| called "best first" or "leaf-wise growth". See "Best-first decision
| tree learning", Shi and "Additive logistic regression : A statistical
| view of boosting", Friedman for more details. Default: "LOCAL".
| in_split_min_examples_check: Whether to check the `min_examples` constraint
| in the split search (i.e. splits leading to one child having less than
| `min_examples` examples are considered invalid) or before the split
| search (i.e. a node can be derived only if it contains more than
| `min_examples` examples). If false, there can be nodes with less than
| `min_examples` training examples. Default: True.
| max_depth: Maximum depth of the tree. `max_depth=1` means that all trees
| will be roots. Negative values are ignored. Default: 16.
| max_num_nodes: Maximum number of nodes in the tree. Set to -1 to disable
| this limit. Only available for `growing_strategy=BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL`.
| Default: None.
| maximum_model_size_in_memory_in_bytes: Limit the size of the model when
| stored in ram. Different algorithms can enforce this limit differently.
| Note that when models are compiled into an inference, the size of the
| inference engine is generally much smaller than the original model.
| Default: -1.0.
| maximum_training_duration_seconds: Maximum training duration of the model
| expressed in seconds. Each learning algorithm is free to use this
| parameter at it sees fit. Enabling maximum training duration makes the
| model training non-deterministic. Default: -1.0.
| min_examples: Minimum number of examples in a node. Default: 5.
| missing_value_policy: Method used to handle missing attribute values.
| - `GLOBAL_IMPUTATION`: Missing attribute values are imputed, with the
| mean (in case of numerical attribute) or the most-frequent-item (in
| case of categorical attribute) computed on the entire dataset (i.e. the
| information contained in the data spec).
| - `LOCAL_IMPUTATION`: Missing attribute values are imputed with the mean
| (numerical attribute) or most-frequent-item (in the case of categorical
| attribute) evaluated on the training examples in the current node.
| - `RANDOM_LOCAL_IMPUTATION`: Missing attribute values are imputed from
| randomly sampled values from the training examples in the current node.
| This method was proposed by Clinic et al. in "Random Survival Forests"
| (https://projecteuclid.org/download/pdfview_1/euclid.aoas/1223908043).
| Default: "GLOBAL_IMPUTATION".
| num_candidate_attributes: Number of unique valid attributes tested for each
| node. An attribute is valid if it has at least a valid split. If
| `num_candidate_attributes=0`, the value is set to the classical default
| value for Random Forest: `sqrt(number of input attributes)` in case of
| classification and `number_of_input_attributes / 3` in case of
| regression. If `num_candidate_attributes=-1`, all the attributes are
| tested. Default: 0.
| num_candidate_attributes_ratio: Ratio of attributes tested at each node. If
| set, it is equivalent to `num_candidate_attributes =
| number_of_input_features x num_candidate_attributes_ratio`. The possible
| values are between ]0, and 1] as well as -1. If not set or equal to -1,
| the `num_candidate_attributes` is used. Default: -1.0.
| num_trees: Number of individual decision trees. Increasing the number of
| trees can increase the quality of the model at the expense of size,
| training speed, and inference latency. Default: 300.
| sorting_strategy: How are sorted the numerical features in order to find
| the splits
| - PRESORT: The features are pre-sorted at the start of the training. This
| solution is faster but consumes much more memory than IN_NODE.
| - IN_NODE: The features are sorted just before being used in the node.
| This solution is slow but consumes little amount of memory.
| . Default: "PRESORT".
| sparse_oblique_normalization: For sparse oblique splits i.e.
| `split_axis=SPARSE_OBLIQUE`. Normalization applied on the features,
| before applying the sparse oblique projections.
| - `NONE`: No normalization.
| - `STANDARD_DEVIATION`: Normalize the feature by the estimated standard
| deviation on the entire train dataset. Also known as Z-Score
| normalization.
| - `MIN_MAX`: Normalize the feature by the range (i.e. max-min) estimated
| on the entire train dataset. Default: None.
| sparse_oblique_num_projections_exponent: For sparse oblique splits i.e.
| `split_axis=SPARSE_OBLIQUE`. Controls of the number of random projections
| to test at each node as `num_features^num_projections_exponent`. Default:
| None.
| sparse_oblique_projection_density_factor: For sparse oblique splits i.e.
| `split_axis=SPARSE_OBLIQUE`. Controls of the number of random projections
| to test at each node as `num_features^num_projections_exponent`. Default:
| None.
| split_axis: What structure of split to consider for numerical features.
| - `AXIS_ALIGNED`: Axis aligned splits (i.e. one condition at a time).
| This is the "classical" way to train a tree. Default value.
| - `SPARSE_OBLIQUE`: Sparse oblique splits (i.e. splits one a small number
| of features) from "Sparse Projection Oblique Random Forests", Tomita et
| al., 2020. Default: "AXIS_ALIGNED".
| winner_take_all: Control how classification trees vote. If true, each tree
| votes for one class. If false, each tree vote for a distribution of
| classes. winner_take_all_inference=false is often preferable. Default:
| True.
|
| Method resolution order:
| RandomForestModel
| tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.wrappers.RandomForestModel
| tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.core.CoreModel
| keras.engine.training.Model
| keras.engine.base_layer.Layer
| tensorflow.python.module.module.Module
| tensorflow.python.training.tracking.tracking.AutoTrackable
| tensorflow.python.training.tracking.base.Trackable
| keras.utils.version_utils.LayerVersionSelector
| keras.utils.version_utils.ModelVersionSelector
| builtins.object
|
| Methods inherited from tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.wrappers.RandomForestModel:
|
| __init__ = wrapper(*args, **kargs)
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods inherited from tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.wrappers.RandomForestModel:
|
| capabilities() -> yggdrasil_decision_forests.learner.abstract_learner_pb2.LearnerCapabilities
| Lists the capabilities of the learning algorithm.
|
| predefined_hyperparameters() -> List[tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.core.HyperParameterTemplate]
| Returns a better than default set of hyper-parameters.
|
| They can be used directly with the `hyperparameter_template` argument of the
| model constructor.
|
| These hyper-parameters outperforms the default hyper-parameters (either
| generally or in specific scenarios). Like default hyper-parameters, existing
| pre-defined hyper-parameters cannot change.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Methods inherited from tensorflow_decision_forests.keras.core.CoreModel:
|
| call(self, inputs, training=False)
| Inference of the model.
|
| This method is used for prediction and evaluation of a trained model.
|
| Args:
| inputs: Input tensors.
| training: Is the model being trained. Always False.
|
| Returns:
| Model predictions.
|
| compile(self, metrics=None)
| Configure the model for training.
|
| Unlike for most Keras model, calling "compile" is optional before calling
| "fit".
|
| Args:
| metrics: Metrics to report during training.
|
| Raises:
| ValueError: Invalid arguments.
|
| evaluate(self, *args, **kwargs)
| Returns the loss value & metrics values for the model.
|
| See details on `keras.Model.evaluate`.
|
| Args:
| *args: Passed to `keras.Model.evaluate`.
| **kwargs: Passed to `keras.Model.evaluate`. Scalar test loss (if the
| model has a single output and no metrics) or list of scalars (if the
| model has multiple outputs and/or metrics). See details in
| `keras.Model.evaluate`.
|
| fit(self, x=None, y=None, callbacks=None, **kwargs) -> keras.callbacks.History
| Trains the model.
|
| The following dataset formats are supported:
|
| 1. "x" is a tf.data.Dataset containing a tuple "(features, labels)".
| "features" can be a dictionary a tensor, a list of tensors or a
| dictionary of tensors (recommended). "labels" is a tensor.
|
| 2. "x" is a tensor, list of tensors or dictionary of tensors containing
| the input features. "y" is a tensor.
|
| 3. "x" is a numpy-array, list of numpy-arrays or dictionary of
| numpy-arrays containing the input features. "y" is a numpy-array.
|
| Unlike classical neural networks, the learning algorithm requires to scan
| the training dataset exactly once. Therefore, the dataset should not be
| repeated. The algorithm also does not benefit from shuffling the dataset.
|
| Input features generally do not need to be normalized (numerical) or indexed
| (categorical features stored as string). Also, missing values are well
| supported (i.e. not need to replace missing values).
|
| Pandas Dataframe can be prepared with "dataframe_to_tf_dataset":
| dataset = pandas.Dataframe(...)
| model.fit(pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(dataset, label="my_label"))
|
| Some of the learning algorithm will support distributed training with the
| ParameterServerStrategy e.g.:
|
| with tf.distribute.experimental.ParameterServerStrategy(...).scope():
| model = DistributedGradientBoostedTreesModel()
| model.fit(...)
|
| Args:
| x: Training dataset (See details above for the supported formats).
| y: Label of the training dataset. Only used if "x" does not contains the
| labels.
| callbacks: Callbacks triggered during the training.
| **kwargs: Arguments passed to the core keras model's fit.
|
| Returns:
| A `History` object. Its `History.history` attribute is not yet
| implemented for decision forests algorithms, and will return empty.
| All other fields are filled as usual for `Keras.Mode.fit()`.
|
| fit_on_dataset_path(self, train_path: str, label_key: str, weight_key: Union[str, NoneType] = None, ranking_key: Union[str, NoneType] = None, valid_path: Union[str, NoneType] = None, dataset_format: Union[str, NoneType] = 'csv')
| Trains the model on a dataset stored on disk.
|
| This solution is generally more efficient and easier that loading the
| dataset with a tf.Dataset both for local and distributed training.
|
| Usage example:
|
| # Local training
| model = model = keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel()
| model.fit_on_dataset_path(
| train_path="/path/to/dataset.csv",
| label_key="label",
| dataset_format="csv")
| model.save("/model/path")
|
| # Distributed training
| with tf.distribute.experimental.ParameterServerStrategy(...).scope():
| model = model = keras.DistributedGradientBoostedTreesModel()
| model.fit_on_dataset_path(
| train_path="/path/to/dataset@10",
| label_key="label",
| dataset_format="tfrecord+tfe")
| model.save("/model/path")
|
| Args:
| train_path: Path to the training dataset. Support comma separated files,
| shard and glob notation.
| label_key: Name of the label column.
| weight_key: Name of the weighing column.
| ranking_key: Name of the ranking column.
| valid_path: Path to the validation dataset. If not provided, or if the
| learning algorithm does not support/need a validation dataset,
| `valid_path` is ignored.
| dataset_format: Format of the dataset. Should be one of the registered
| dataset format (see
| https://github.com/google/yggdrasil-decision-forests/blob/main/documentation/user_manual#dataset-path-and-format
| for more details). The format "csv" always available but it is
| generally only suited for small datasets.
|
| Returns:
| A `History` object. Its `History.history` attribute is not yet
| implemented for decision forests algorithms, and will return empty.
| All other fields are filled as usual for `Keras.Mode.fit()`.
|
| make_inspector(self) -> tensorflow_decision_forests.component.inspector.inspector.AbstractInspector
| Creates an inspector to access the internal model structure.
|
| Usage example:
|
| ```python
| inspector = model.make_inspector()
| print(inspector.num_trees())
| print(inspector.variable_importances())
| ```
|
| Returns:
| A model inspector.
|
| make_predict_function(self)
| Prediction of the model (!= evaluation).
|
| make_test_function(self)
| Predictions for evaluation.
|
| save(self, filepath: str, overwrite: Union[bool, NoneType] = True, **kwargs)
| Saves the model as a TensorFlow SavedModel.
|
| The exported SavedModel contains a standalone Yggdrasil Decision Forests
| model in the "assets" sub-directory. The Yggdrasil model can be used
| directly using the Yggdrasil API. However, this model does not contain the
| "preprocessing" layer (if any).
|
| Args:
| filepath: Path to the output model.
| overwrite: If true, override an already existing model. If false, raise an
| error if a model already exist.
| **kwargs: Arguments passed to the core keras model's save.
|
| summary(self, line_length=None, positions=None, print_fn=None)
| Shows information about the model.
|
| train_step(self, data)
| Collects training examples.
|
| yggdrasil_model_path_tensor(self) -> Union[tensorflow.python.framework.ops.Tensor, NoneType]
| Gets the path to yggdrasil model, if available.
|
| The effective path can be obtained with:
|
| ```python
| yggdrasil_model_path_tensor().numpy().decode("utf-8")
| ```
|
| Returns:
| Path to the Yggdrasil model.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Methods inherited from keras.engine.training.Model:
|
| __copy__(self)
|
| __deepcopy__(self, memo)
|
| __reduce__(self)
| Helper for pickle.
|
| __setattr__(self, name, value)
| Support self.foo = trackable syntax.
|
| build(self, input_shape)
| Builds the model based on input shapes received.
|
| This is to be used for subclassed models, which do not know at instantiation
| time what their inputs look like.
|
| This method only exists for users who want to call `model.build()` in a
| standalone way (as a substitute for calling the model on real data to
| build it). It will never be called by the framework (and thus it will
| never throw unexpected errors in an unrelated workflow).
|
| Args:
| input_shape: Single tuple, `TensorShape` instance, or list/dict of shapes,
| where shapes are tuples, integers, or `TensorShape` instances.
|
| Raises:
| ValueError:
| 1. In case of invalid user-provided data (not of type tuple,
| list, `TensorShape`, or dict).
| 2. If the model requires call arguments that are agnostic
| to the input shapes (positional or keyword arg in call signature).
| 3. If not all layers were properly built.
| 4. If float type inputs are not supported within the layers.
|
| In each of these cases, the user should build their model by calling it
| on real tensor data.
|
| evaluate_generator(self, generator, steps=None, callbacks=None, max_queue_size=10, workers=1, use_multiprocessing=False, verbose=0)
| Evaluates the model on a data generator.
|
| DEPRECATED:
| `Model.evaluate` now supports generators, so there is no longer any need
| to use this endpoint.
|
| fit_generator(self, generator, steps_per_epoch=None, epochs=1, verbose=1, callbacks=None, validation_data=None, validation_steps=None, validation_freq=1, class_weight=None, max_queue_size=10, workers=1, use_multiprocessing=False, shuffle=True, initial_epoch=0)
| Fits the model on data yielded batch-by-batch by a Python generator.
|
| DEPRECATED:
| `Model.fit` now supports generators, so there is no longer any need to use
| this endpoint.
|
| get_config(self)
| Returns the config of the layer.
|
| A layer config is a Python dictionary (serializable)
| containing the configuration of a layer.
| The same layer can be reinstantiated later
| (without its trained weights) from this configuration.
|
| The config of a layer does not include connectivity
| information, nor the layer class name. These are handled
| by `Network` (one layer of abstraction above).
|
| Note that `get_config()` does not guarantee to return a fresh copy of dict
| every time it is called. The callers should make a copy of the returned dict
| if they want to modify it.
|
| Returns:
| Python dictionary.
|
| get_layer(self, name=None, index=None)
| Retrieves a layer based on either its name (unique) or index.
|
| If `name` and `index` are both provided, `index` will take precedence.
| Indices are based on order of horizontal graph traversal (bottom-up).
|
| Args:
| name: String, name of layer.
| index: Integer, index of layer.
|
| Returns:
| A layer instance.
|
| get_weights(self)
| Retrieves the weights of the model.
|
| Returns:
| A flat list of Numpy arrays.
|
| load_weights(self, filepath, by_name=False, skip_mismatch=False, options=None)
| Loads all layer weights, either from a TensorFlow or an HDF5 weight file.
|
| If `by_name` is False weights are loaded based on the network's
| topology. This means the architecture should be the same as when the weights
| were saved. Note that layers that don't have weights are not taken into
| account in the topological ordering, so adding or removing layers is fine as
| long as they don't have weights.
|
| If `by_name` is True, weights are loaded into layers only if they share the
| same name. This is useful for fine-tuning or transfer-learning models where
| some of the layers have changed.
|
| Only topological loading (`by_name=False`) is supported when loading weights
| from the TensorFlow format. Note that topological loading differs slightly
| between TensorFlow and HDF5 formats for user-defined classes inheriting from
| `tf.keras.Model`: HDF5 loads based on a flattened list of weights, while the
| TensorFlow format loads based on the object-local names of attributes to
| which layers are assigned in the `Model`'s constructor.
|
| Args:
| filepath: String, path to the weights file to load. For weight files in
| TensorFlow format, this is the file prefix (the same as was passed
| to `save_weights`). This can also be a path to a SavedModel
| saved from `model.save`.
| by_name: Boolean, whether to load weights by name or by topological
| order. Only topological loading is supported for weight files in
| TensorFlow format.
| skip_mismatch: Boolean, whether to skip loading of layers where there is
| a mismatch in the number of weights, or a mismatch in the shape of
| the weight (only valid when `by_name=True`).
| options: Optional `tf.train.CheckpointOptions` object that specifies
| options for loading weights.
|
| Returns:
| When loading a weight file in TensorFlow format, returns the same status
| object as `tf.train.Checkpoint.restore`. When graph building, restore
| ops are run automatically as soon as the network is built (on first call
| for user-defined classes inheriting from `Model`, immediately if it is
| already built).
|
| When loading weights in HDF5 format, returns `None`.
|
| Raises:
| ImportError: If `h5py` is not available and the weight file is in HDF5
| format.
| ValueError: If `skip_mismatch` is set to `True` when `by_name` is
| `False`.
|
| make_train_function(self, force=False)
| Creates a function that executes one step of training.
|
| This method can be overridden to support custom training logic.
| This method is called by `Model.fit` and `Model.train_on_batch`.
|
| Typically, this method directly controls `tf.function` and
| `tf.distribute.Strategy` settings, and delegates the actual training
| logic to `Model.train_step`.
|
| This function is cached the first time `Model.fit` or
| `Model.train_on_batch` is called. The cache is cleared whenever
| `Model.compile` is called. You can skip the cache and generate again the
| function with `force=True`.
|
| Args:
| force: Whether to regenerate the train function and skip the cached
| function if available.
|
| Returns:
| Function. The function created by this method should accept a
| `tf.data.Iterator`, and return a `dict` containing values that will
| be passed to `tf.keras.Callbacks.on_train_batch_end`, such as
| `{'loss': 0.2, 'accuracy': 0.7}`.
|
| predict(self, x, batch_size=None, verbose=0, steps=None, callbacks=None, max_queue_size=10, workers=1, use_multiprocessing=False)
| Generates output predictions for the input samples.
|
| Computation is done in batches. This method is designed for performance in
| large scale inputs. For small amount of inputs that fit in one batch,
| directly using `__call__()` is recommended for faster execution, e.g.,
| `model(x)`, or `model(x, training=False)` if you have layers such as
| `tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization` that behaves differently during
| inference. Also, note the fact that test loss is not affected by
| regularization layers like noise and dropout.
|
| Args:
| x: Input samples. It could be:
| - A Numpy array (or array-like), or a list of arrays
| (in case the model has multiple inputs).
| - A TensorFlow tensor, or a list of tensors
| (in case the model has multiple inputs).
| - A `tf.data` dataset.
| - A generator or `keras.utils.Sequence` instance.
| A more detailed description of unpacking behavior for iterator types
| (Dataset, generator, Sequence) is given in the `Unpacking behavior
| for iterator-like inputs` section of `Model.fit`.
| batch_size: Integer or `None`.
| Number of samples per batch.
| If unspecified, `batch_size` will default to 32.
| Do not specify the `batch_size` if your data is in the
| form of dataset, generators, or `keras.utils.Sequence` instances
| (since they generate batches).
| verbose: Verbosity mode, 0 or 1.
| steps: Total number of steps (batches of samples)
| before declaring the prediction round finished.
| Ignored with the default value of `None`. If x is a `tf.data`
| dataset and `steps` is None, `predict()` will
| run until the input dataset is exhausted.
| callbacks: List of `keras.callbacks.Callback` instances.
| List of callbacks to apply during prediction.
| See [callbacks](/api_docs/python/tf/keras/callbacks).
| max_queue_size: Integer. Used for generator or `keras.utils.Sequence`
| input only. Maximum size for the generator queue.
| If unspecified, `max_queue_size` will default to 10.
| workers: Integer. Used for generator or `keras.utils.Sequence` input
| only. Maximum number of processes to spin up when using
| process-based threading. If unspecified, `workers` will default
| to 1.
| use_multiprocessing: Boolean. Used for generator or
| `keras.utils.Sequence` input only. If `True`, use process-based
| threading. If unspecified, `use_multiprocessing` will default to
| `False`. Note that because this implementation relies on
| multiprocessing, you should not pass non-picklable arguments to
| the generator as they can't be passed easily to children processes.
|
| See the discussion of `Unpacking behavior for iterator-like inputs` for
| `Model.fit`. Note that Model.predict uses the same interpretation rules as
| `Model.fit` and `Model.evaluate`, so inputs must be unambiguous for all
| three methods.
|
| Returns:
| Numpy array(s) of predictions.
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If `model.predict` is wrapped in a `tf.function`.
| ValueError: In case of mismatch between the provided
| input data and the model's expectations,
| or in case a stateful model receives a number of samples
| that is not a multiple of the batch size.
|
| predict_generator(self, generator, steps=None, callbacks=None, max_queue_size=10, workers=1, use_multiprocessing=False, verbose=0)
| Generates predictions for the input samples from a data generator.
|
| DEPRECATED:
| `Model.predict` now supports generators, so there is no longer any need
| to use this endpoint.
|
| predict_on_batch(self, x)
| Returns predictions for a single batch of samples.
|
| Args:
| x: Input data. It could be:
| - A Numpy array (or array-like), or a list of arrays (in case the
| model has multiple inputs).
| - A TensorFlow tensor, or a list of tensors (in case the model has
| multiple inputs).
|
| Returns:
| Numpy array(s) of predictions.
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If `model.predict_on_batch` is wrapped in a `tf.function`.
|
| predict_step(self, data)
| The logic for one inference step.
|
| This method can be overridden to support custom inference logic.
| This method is called by `Model.make_predict_function`.
|
| This method should contain the mathematical logic for one step of inference.
| This typically includes the forward pass.
|
| Configuration details for *how* this logic is run (e.g. `tf.function` and
| `tf.distribute.Strategy` settings), should be left to
| `Model.make_predict_function`, which can also be overridden.
|
| Args:
| data: A nested structure of `Tensor`s.
|
| Returns:
| The result of one inference step, typically the output of calling the
| `Model` on data.
|
| reset_metrics(self)
| Resets the state of all the metrics in the model.
|
| Examples:
|
| >>> inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(3,))
| >>> outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2)(inputs)
| >>> model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
| >>> model.compile(optimizer="Adam", loss="mse", metrics=["mae"])
|
| >>> x = np.random.random((2, 3))
| >>> y = np.random.randint(0, 2, (2, 2))
| >>> _ = model.fit(x, y, verbose=0)
| >>> assert all(float(m.result()) for m in model.metrics)
|
| >>> model.reset_metrics()
| >>> assert all(float(m.result()) == 0 for m in model.metrics)
|
| reset_states(self)
|
| save_spec(self, dynamic_batch=True)
| Returns the `tf.TensorSpec` of call inputs as a tuple `(args, kwargs)`.
|
| This value is automatically defined after calling the model for the first
| time. Afterwards, you can use it when exporting the model for serving:
|
| ```python
| model = tf.keras.Model(...)
|
| @tf.function
| def serve(*args, **kwargs):
| outputs = model(*args, **kwargs)
| # Apply postprocessing steps, or add additional outputs.
| ...
| return outputs
|
| # arg_specs is `[tf.TensorSpec(...), ...]`. kwarg_specs, in this example, is
| # an empty dict since functional models do not use keyword arguments.
| arg_specs, kwarg_specs = model.save_spec()
|
| model.save(path, signatures={
| 'serving_default': serve.get_concrete_function(*arg_specs, **kwarg_specs)
| })
| ```
|
| Args:
| dynamic_batch: Whether to set the batch sizes of all the returned
| `tf.TensorSpec` to `None`. (Note that when defining functional or
| Sequential models with `tf.keras.Input([...], batch_size=X)`, the
| batch size will always be preserved). Defaults to `True`.
| Returns:
| If the model inputs are defined, returns a tuple `(args, kwargs)`. All
| elements in `args` and `kwargs` are `tf.TensorSpec`.
| If the model inputs are not defined, returns `None`.
| The model inputs are automatically set when calling the model,
| `model.fit`, `model.evaluate` or `model.predict`.
|
| save_weights(self, filepath, overwrite=True, save_format=None, options=None)
| Saves all layer weights.
|
| Either saves in HDF5 or in TensorFlow format based on the `save_format`
| argument.
|
| When saving in HDF5 format, the weight file has:
| - `layer_names` (attribute), a list of strings
| (ordered names of model layers).
| - For every layer, a `group` named `layer.name`
| - For every such layer group, a group attribute `weight_names`,
| a list of strings
| (ordered names of weights tensor of the layer).
| - For every weight in the layer, a dataset
| storing the weight value, named after the weight tensor.
|
| When saving in TensorFlow format, all objects referenced by the network are
| saved in the same format as `tf.train.Checkpoint`, including any `Layer`
| instances or `Optimizer` instances assigned to object attributes. For
| networks constructed from inputs and outputs using `tf.keras.Model(inputs,
| outputs)`, `Layer` instances used by the network are tracked/saved
| automatically. For user-defined classes which inherit from `tf.keras.Model`,
| `Layer` instances must be assigned to object attributes, typically in the
| constructor. See the documentation of `tf.train.Checkpoint` and
| `tf.keras.Model` for details.
|
| While the formats are the same, do not mix `save_weights` and
| `tf.train.Checkpoint`. Checkpoints saved by `Model.save_weights` should be
| loaded using `Model.load_weights`. Checkpoints saved using
| `tf.train.Checkpoint.save` should be restored using the corresponding
| `tf.train.Checkpoint.restore`. Prefer `tf.train.Checkpoint` over
| `save_weights` for training checkpoints.
|
| The TensorFlow format matches objects and variables by starting at a root
| object, `self` for `save_weights`, and greedily matching attribute
| names. For `Model.save` this is the `Model`, and for `Checkpoint.save` this
| is the `Checkpoint` even if the `Checkpoint` has a model attached. This
| means saving a `tf.keras.Model` using `save_weights` and loading into a
| `tf.train.Checkpoint` with a `Model` attached (or vice versa) will not match
| the `Model`'s variables. See the
| [guide to training checkpoints](https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/checkpoint)
| for details on the TensorFlow format.
|
| Args:
| filepath: String or PathLike, path to the file to save the weights to.
| When saving in TensorFlow format, this is the prefix used for
| checkpoint files (multiple files are generated). Note that the '.h5'
| suffix causes weights to be saved in HDF5 format.
| overwrite: Whether to silently overwrite any existing file at the
| target location, or provide the user with a manual prompt.
| save_format: Either 'tf' or 'h5'. A `filepath` ending in '.h5' or
| '.keras' will default to HDF5 if `save_format` is `None`. Otherwise
| `None` defaults to 'tf'.
| options: Optional `tf.train.CheckpointOptions` object that specifies
| options for saving weights.
|
| Raises:
| ImportError: If `h5py` is not available when attempting to save in HDF5
| format.
|
| test_on_batch(self, x, y=None, sample_weight=None, reset_metrics=True, return_dict=False)
| Test the model on a single batch of samples.
|
| Args:
| x: Input data. It could be:
| - A Numpy array (or array-like), or a list of arrays (in case the
| model has multiple inputs).
| - A TensorFlow tensor, or a list of tensors (in case the model has
| multiple inputs).
| - A dict mapping input names to the corresponding array/tensors, if
| the model has named inputs.
| y: Target data. Like the input data `x`, it could be either Numpy
| array(s) or TensorFlow tensor(s). It should be consistent with `x`
| (you cannot have Numpy inputs and tensor targets, or inversely).
| sample_weight: Optional array of the same length as x, containing
| weights to apply to the model's loss for each sample. In the case of
| temporal data, you can pass a 2D array with shape (samples,
| sequence_length), to apply a different weight to every timestep of
| every sample.
| reset_metrics: If `True`, the metrics returned will be only for this
| batch. If `False`, the metrics will be statefully accumulated across
| batches.
| return_dict: If `True`, loss and metric results are returned as a dict,
| with each key being the name of the metric. If `False`, they are
| returned as a list.
|
| Returns:
| Scalar test loss (if the model has a single output and no metrics)
| or list of scalars (if the model has multiple outputs
| and/or metrics). The attribute `model.metrics_names` will give you
| the display labels for the scalar outputs.
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If `model.test_on_batch` is wrapped in a `tf.function`.
|
| test_step(self, data)
| The logic for one evaluation step.
|
| This method can be overridden to support custom evaluation logic.
| This method is called by `Model.make_test_function`.
|
| This function should contain the mathematical logic for one step of
| evaluation.
| This typically includes the forward pass, loss calculation, and metrics
| updates.
|
| Configuration details for *how* this logic is run (e.g. `tf.function` and
| `tf.distribute.Strategy` settings), should be left to
| `Model.make_test_function`, which can also be overridden.
|
| Args:
| data: A nested structure of `Tensor`s.
|
| Returns:
| A `dict` containing values that will be passed to
| `tf.keras.callbacks.CallbackList.on_train_batch_end`. Typically, the
| values of the `Model`'s metrics are returned.
|
| to_json(self, **kwargs)
| Returns a JSON string containing the network configuration.
|
| To load a network from a JSON save file, use
| `keras.models.model_from_json(json_string, custom_objects={})`.
|
| Args:
| **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments
| to be passed to `json.dumps()`.
|
| Returns:
| A JSON string.
|
| to_yaml(self, **kwargs)
| Returns a yaml string containing the network configuration.
|
| Note: Since TF 2.6, this method is no longer supported and will raise a
| RuntimeError.
|
| To load a network from a yaml save file, use
| `keras.models.model_from_yaml(yaml_string, custom_objects={})`.
|
| `custom_objects` should be a dictionary mapping
| the names of custom losses / layers / etc to the corresponding
| functions / classes.
|
| Args:
| **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments
| to be passed to `yaml.dump()`.
|
| Returns:
| A YAML string.
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: announces that the method poses a security risk
|
| train_on_batch(self, x, y=None, sample_weight=None, class_weight=None, reset_metrics=True, return_dict=False)
| Runs a single gradient update on a single batch of data.
|
| Args:
| x: Input data. It could be:
| - A Numpy array (or array-like), or a list of arrays
| (in case the model has multiple inputs).
| - A TensorFlow tensor, or a list of tensors
| (in case the model has multiple inputs).
| - A dict mapping input names to the corresponding array/tensors,
| if the model has named inputs.
| y: Target data. Like the input data `x`, it could be either Numpy
| array(s) or TensorFlow tensor(s). It should be consistent with `x`
| (you cannot have Numpy inputs and tensor targets, or inversely).
| sample_weight: Optional array of the same length as x, containing
| weights to apply to the model's loss for each sample. In the case of
| temporal data, you can pass a 2D array with shape (samples,
| sequence_length), to apply a different weight to every timestep of
| every sample.
| class_weight: Optional dictionary mapping class indices (integers) to a
| weight (float) to apply to the model's loss for the samples from this
| class during training. This can be useful to tell the model to "pay
| more attention" to samples from an under-represented class.
| reset_metrics: If `True`, the metrics returned will be only for this
| batch. If `False`, the metrics will be statefully accumulated across
| batches.
| return_dict: If `True`, loss and metric results are returned as a dict,
| with each key being the name of the metric. If `False`, they are
| returned as a list.
|
| Returns:
| Scalar training loss
| (if the model has a single output and no metrics)
| or list of scalars (if the model has multiple outputs
| and/or metrics). The attribute `model.metrics_names` will give you
| the display labels for the scalar outputs.
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If `model.train_on_batch` is wrapped in a `tf.function`.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods inherited from keras.engine.training.Model:
|
| from_config(config, custom_objects=None) from builtins.type
| Creates a layer from its config.
|
| This method is the reverse of `get_config`,
| capable of instantiating the same layer from the config
| dictionary. It does not handle layer connectivity
| (handled by Network), nor weights (handled by `set_weights`).
|
| Args:
| config: A Python dictionary, typically the
| output of get_config.
|
| Returns:
| A layer instance.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Static methods inherited from keras.engine.training.Model:
|
| __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs)
| Create and return a new object. See help(type) for accurate signature.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from keras.engine.training.Model:
|
| distribute_strategy
| The `tf.distribute.Strategy` this model was created under.
|
| layers
|
| metrics
| Returns the model's metrics added using `compile()`, `add_metric()` APIs.
|
| Note: Metrics passed to `compile()` are available only after a `keras.Model`
| has been trained/evaluated on actual data.
|
| Examples:
|
| >>> inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(3,))
| >>> outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2)(inputs)
| >>> model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
| >>> model.compile(optimizer="Adam", loss="mse", metrics=["mae"])
| >>> [m.name for m in model.metrics]
| []
|
| >>> x = np.random.random((2, 3))
| >>> y = np.random.randint(0, 2, (2, 2))
| >>> model.fit(x, y)
| >>> [m.name for m in model.metrics]
| ['loss', 'mae']
|
| >>> inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(3,))
| >>> d = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2, name='out')
| >>> output_1 = d(inputs)
| >>> output_2 = d(inputs)
| >>> model = tf.keras.models.Model(
| ... inputs=inputs, outputs=[output_1, output_2])
| >>> model.add_metric(
| ... tf.reduce_sum(output_2), name='mean', aggregation='mean')
| >>> model.compile(optimizer="Adam", loss="mse", metrics=["mae", "acc"])
| >>> model.fit(x, (y, y))
| >>> [m.name for m in model.metrics]
| ['loss', 'out_loss', 'out_1_loss', 'out_mae', 'out_acc', 'out_1_mae',
| 'out_1_acc', 'mean']
|
| metrics_names
| Returns the model's display labels for all outputs.
|
| Note: `metrics_names` are available only after a `keras.Model` has been
| trained/evaluated on actual data.
|
| Examples:
|
| >>> inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(3,))
| >>> outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2)(inputs)
| >>> model = tf.keras.models.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=outputs)
| >>> model.compile(optimizer="Adam", loss="mse", metrics=["mae"])
| >>> model.metrics_names
| []
|
| >>> x = np.random.random((2, 3))
| >>> y = np.random.randint(0, 2, (2, 2))
| >>> model.fit(x, y)
| >>> model.metrics_names
| ['loss', 'mae']
|
| >>> inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(3,))
| >>> d = tf.keras.layers.Dense(2, name='out')
| >>> output_1 = d(inputs)
| >>> output_2 = d(inputs)
| >>> model = tf.keras.models.Model(
| ... inputs=inputs, outputs=[output_1, output_2])
| >>> model.compile(optimizer="Adam", loss="mse", metrics=["mae", "acc"])
| >>> model.fit(x, (y, y))
| >>> model.metrics_names
| ['loss', 'out_loss', 'out_1_loss', 'out_mae', 'out_acc', 'out_1_mae',
| 'out_1_acc']
|
| non_trainable_weights
| List of all non-trainable weights tracked by this layer.
|
| Non-trainable weights are *not* updated during training. They are expected
| to be updated manually in `call()`.
|
| Returns:
| A list of non-trainable variables.
|
| run_eagerly
| Settable attribute indicating whether the model should run eagerly.
|
| Running eagerly means that your model will be run step by step,
| like Python code. Your model might run slower, but it should become easier
| for you to debug it by stepping into individual layer calls.
|
| By default, we will attempt to compile your model to a static graph to
| deliver the best execution performance.
|
| Returns:
| Boolean, whether the model should run eagerly.
|
| state_updates
| Deprecated, do NOT use!
|
| Returns the `updates` from all layers that are stateful.
|
| This is useful for separating training updates and
| state updates, e.g. when we need to update a layer's internal state
| during prediction.
|
| Returns:
| A list of update ops.
|
| trainable_weights
| List of all trainable weights tracked by this layer.
|
| Trainable weights are updated via gradient descent during training.
|
| Returns:
| A list of trainable variables.
|
| weights
| Returns the list of all layer variables/weights.
|
| Note: This will not track the weights of nested `tf.Modules` that are not
| themselves Keras layers.
|
| Returns:
| A list of variables.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Methods inherited from keras.engine.base_layer.Layer:
|
| __call__(self, *args, **kwargs)
| Wraps `call`, applying pre- and post-processing steps.
|
| Args:
| *args: Positional arguments to be passed to `self.call`.
| **kwargs: Keyword arguments to be passed to `self.call`.
|
| Returns:
| Output tensor(s).
|
| Note:
| - The following optional keyword arguments are reserved for specific uses:
| * `training`: Boolean scalar tensor of Python boolean indicating
| whether the `call` is meant for training or inference.
| * `mask`: Boolean input mask.
| - If the layer's `call` method takes a `mask` argument (as some Keras
| layers do), its default value will be set to the mask generated
| for `inputs` by the previous layer (if `input` did come from
| a layer that generated a corresponding mask, i.e. if it came from
| a Keras layer with masking support.
| - If the layer is not built, the method will call `build`.
|
| Raises:
| ValueError: if the layer's `call` method returns None (an invalid value).
| RuntimeError: if `super().__init__()` was not called in the constructor.
|
| __delattr__(self, name)
| Implement delattr(self, name).
|
| __getstate__(self)
|
| __setstate__(self, state)
|
| add_loss(self, losses, **kwargs)
| Add loss tensor(s), potentially dependent on layer inputs.
|
| Some losses (for instance, activity regularization losses) may be dependent
| on the inputs passed when calling a layer. Hence, when reusing the same
| layer on different inputs `a` and `b`, some entries in `layer.losses` may
| be dependent on `a` and some on `b`. This method automatically keeps track
| of dependencies.
|
| This method can be used inside a subclassed layer or model's `call`
| function, in which case `losses` should be a Tensor or list of Tensors.
|
| Example:
|
| ```python
| class MyLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
| def call(self, inputs):
| self.add_loss(tf.abs(tf.reduce_mean(inputs)))
| return inputs
| ```
|
| This method can also be called directly on a Functional Model during
| construction. In this case, any loss Tensors passed to this Model must
| be symbolic and be able to be traced back to the model's `Input`s. These
| losses become part of the model's topology and are tracked in `get_config`.
|
| Example:
|
| ```python
| inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
| x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(inputs)
| outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
| model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
| # Activity regularization.
| model.add_loss(tf.abs(tf.reduce_mean(x)))
| ```
|
| If this is not the case for your loss (if, for example, your loss references
| a `Variable` of one of the model's layers), you can wrap your loss in a
| zero-argument lambda. These losses are not tracked as part of the model's
| topology since they can't be serialized.
|
| Example:
|
| ```python
| inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
| d = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)
| x = d(inputs)
| outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
| model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
| # Weight regularization.
| model.add_loss(lambda: tf.reduce_mean(d.kernel))
| ```
|
| Args:
| losses: Loss tensor, or list/tuple of tensors. Rather than tensors, losses
| may also be zero-argument callables which create a loss tensor.
| **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments for backward compatibility.
| Accepted values:
| inputs - Deprecated, will be automatically inferred.
|
| add_metric(self, value, name=None, **kwargs)
| Adds metric tensor to the layer.
|
| This method can be used inside the `call()` method of a subclassed layer
| or model.
|
| ```python
| class MyMetricLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
| def __init__(self):
| super(MyMetricLayer, self).__init__(name='my_metric_layer')
| self.mean = tf.keras.metrics.Mean(name='metric_1')
|
| def call(self, inputs):
| self.add_metric(self.mean(inputs))
| self.add_metric(tf.reduce_sum(inputs), name='metric_2')
| return inputs
| ```
|
| This method can also be called directly on a Functional Model during
| construction. In this case, any tensor passed to this Model must
| be symbolic and be able to be traced back to the model's `Input`s. These
| metrics become part of the model's topology and are tracked when you
| save the model via `save()`.
|
| ```python
| inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
| x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(inputs)
| outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
| model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
| model.add_metric(math_ops.reduce_sum(x), name='metric_1')
| ```
|
| Note: Calling `add_metric()` with the result of a metric object on a
| Functional Model, as shown in the example below, is not supported. This is
| because we cannot trace the metric result tensor back to the model's inputs.
|
| ```python
| inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
| x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(inputs)
| outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
| model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
| model.add_metric(tf.keras.metrics.Mean()(x), name='metric_1')
| ```
|
| Args:
| value: Metric tensor.
| name: String metric name.
| **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments for backward compatibility.
| Accepted values:
| `aggregation` - When the `value` tensor provided is not the result of
| calling a `keras.Metric` instance, it will be aggregated by default
| using a `keras.Metric.Mean`.
|
| add_update(self, updates, inputs=None)
| Add update op(s), potentially dependent on layer inputs.
|
| Weight updates (for instance, the updates of the moving mean and variance
| in a BatchNormalization layer) may be dependent on the inputs passed
| when calling a layer. Hence, when reusing the same layer on
| different inputs `a` and `b`, some entries in `layer.updates` may be
| dependent on `a` and some on `b`. This method automatically keeps track
| of dependencies.
|
| This call is ignored when eager execution is enabled (in that case, variable
| updates are run on the fly and thus do not need to be tracked for later
| execution).
|
| Args:
| updates: Update op, or list/tuple of update ops, or zero-arg callable
| that returns an update op. A zero-arg callable should be passed in
| order to disable running the updates by setting `trainable=False`
| on this Layer, when executing in Eager mode.
| inputs: Deprecated, will be automatically inferred.
|
| add_variable(self, *args, **kwargs)
| Deprecated, do NOT use! Alias for `add_weight`.
|
| add_weight(self, name=None, shape=None, dtype=None, initializer=None, regularizer=None, trainable=None, constraint=None, use_resource=None, synchronization=<VariableSynchronization.AUTO: 0>, aggregation=<VariableAggregationV2.NONE: 0>, **kwargs)
| Adds a new variable to the layer.
|
| Args:
| name: Variable name.
| shape: Variable shape. Defaults to scalar if unspecified.
| dtype: The type of the variable. Defaults to `self.dtype`.
| initializer: Initializer instance (callable).
| regularizer: Regularizer instance (callable).
| trainable: Boolean, whether the variable should be part of the layer's
| "trainable_variables" (e.g. variables, biases)
| or "non_trainable_variables" (e.g. BatchNorm mean and variance).
| Note that `trainable` cannot be `True` if `synchronization`
| is set to `ON_READ`.
| constraint: Constraint instance (callable).
| use_resource: Whether to use `ResourceVariable`.
| synchronization: Indicates when a distributed a variable will be
| aggregated. Accepted values are constants defined in the class
| `tf.VariableSynchronization`. By default the synchronization is set to
| `AUTO` and the current `DistributionStrategy` chooses
| when to synchronize. If `synchronization` is set to `ON_READ`,
| `trainable` must not be set to `True`.
| aggregation: Indicates how a distributed variable will be aggregated.
| Accepted values are constants defined in the class
| `tf.VariableAggregation`.
| **kwargs: Additional keyword arguments. Accepted values are `getter`,
| `collections`, `experimental_autocast` and `caching_device`.
|
| Returns:
| The variable created.
|
| Raises:
| ValueError: When giving unsupported dtype and no initializer or when
| trainable has been set to True with synchronization set as `ON_READ`.
|
| apply(self, inputs, *args, **kwargs)
| Deprecated, do NOT use!
|
| This is an alias of `self.__call__`.
|
| Args:
| inputs: Input tensor(s).
| *args: additional positional arguments to be passed to `self.call`.
| **kwargs: additional keyword arguments to be passed to `self.call`.
|
| Returns:
| Output tensor(s).
|
| compute_mask(self, inputs, mask=None)
| Computes an output mask tensor.
|
| Args:
| inputs: Tensor or list of tensors.
| mask: Tensor or list of tensors.
|
| Returns:
| None or a tensor (or list of tensors,
| one per output tensor of the layer).
|
| compute_output_shape(self, input_shape)
| Computes the output shape of the layer.
|
| If the layer has not been built, this method will call `build` on the
| layer. This assumes that the layer will later be used with inputs that
| match the input shape provided here.
|
| Args:
| input_shape: Shape tuple (tuple of integers)
| or list of shape tuples (one per output tensor of the layer).
| Shape tuples can include None for free dimensions,
| instead of an integer.
|
| Returns:
| An input shape tuple.
|
| compute_output_signature(self, input_signature)
| Compute the output tensor signature of the layer based on the inputs.
|
| Unlike a TensorShape object, a TensorSpec object contains both shape
| and dtype information for a tensor. This method allows layers to provide
| output dtype information if it is different from the input dtype.
| For any layer that doesn't implement this function,
| the framework will fall back to use `compute_output_shape`, and will
| assume that the output dtype matches the input dtype.
|
| Args:
| input_signature: Single TensorSpec or nested structure of TensorSpec
| objects, describing a candidate input for the layer.
|
| Returns:
| Single TensorSpec or nested structure of TensorSpec objects, describing
| how the layer would transform the provided input.
|
| Raises:
| TypeError: If input_signature contains a non-TensorSpec object.
|
| count_params(self)
| Count the total number of scalars composing the weights.
|
| Returns:
| An integer count.
|
| Raises:
| ValueError: if the layer isn't yet built
| (in which case its weights aren't yet defined).
|
| finalize_state(self)
| Finalizes the layers state after updating layer weights.
|
| This function can be subclassed in a layer and will be called after updating
| a layer weights. It can be overridden to finalize any additional layer state
| after a weight update.
|
| get_input_at(self, node_index)
| Retrieves the input tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
|
| Args:
| node_index: Integer, index of the node
| from which to retrieve the attribute.
| E.g. `node_index=0` will correspond to the
| first input node of the layer.
|
| Returns:
| A tensor (or list of tensors if the layer has multiple inputs).
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If called in Eager mode.
|
| get_input_mask_at(self, node_index)
| Retrieves the input mask tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
|
| Args:
| node_index: Integer, index of the node
| from which to retrieve the attribute.
| E.g. `node_index=0` will correspond to the
| first time the layer was called.
|
| Returns:
| A mask tensor
| (or list of tensors if the layer has multiple inputs).
|
| get_input_shape_at(self, node_index)
| Retrieves the input shape(s) of a layer at a given node.
|
| Args:
| node_index: Integer, index of the node
| from which to retrieve the attribute.
| E.g. `node_index=0` will correspond to the
| first time the layer was called.
|
| Returns:
| A shape tuple
| (or list of shape tuples if the layer has multiple inputs).
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If called in Eager mode.
|
| get_losses_for(self, inputs)
| Deprecated, do NOT use!
|
| Retrieves losses relevant to a specific set of inputs.
|
| Args:
| inputs: Input tensor or list/tuple of input tensors.
|
| Returns:
| List of loss tensors of the layer that depend on `inputs`.
|
| get_output_at(self, node_index)
| Retrieves the output tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
|
| Args:
| node_index: Integer, index of the node
| from which to retrieve the attribute.
| E.g. `node_index=0` will correspond to the
| first output node of the layer.
|
| Returns:
| A tensor (or list of tensors if the layer has multiple outputs).
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If called in Eager mode.
|
| get_output_mask_at(self, node_index)
| Retrieves the output mask tensor(s) of a layer at a given node.
|
| Args:
| node_index: Integer, index of the node
| from which to retrieve the attribute.
| E.g. `node_index=0` will correspond to the
| first time the layer was called.
|
| Returns:
| A mask tensor
| (or list of tensors if the layer has multiple outputs).
|
| get_output_shape_at(self, node_index)
| Retrieves the output shape(s) of a layer at a given node.
|
| Args:
| node_index: Integer, index of the node
| from which to retrieve the attribute.
| E.g. `node_index=0` will correspond to the
| first time the layer was called.
|
| Returns:
| A shape tuple
| (or list of shape tuples if the layer has multiple outputs).
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If called in Eager mode.
|
| get_updates_for(self, inputs)
| Deprecated, do NOT use!
|
| Retrieves updates relevant to a specific set of inputs.
|
| Args:
| inputs: Input tensor or list/tuple of input tensors.
|
| Returns:
| List of update ops of the layer that depend on `inputs`.
|
| set_weights(self, weights)
| Sets the weights of the layer, from NumPy arrays.
|
| The weights of a layer represent the state of the layer. This function
| sets the weight values from numpy arrays. The weight values should be
| passed in the order they are created by the layer. Note that the layer's
| weights must be instantiated before calling this function, by calling
| the layer.
|
| For example, a `Dense` layer returns a list of two values: the kernel matrix
| and the bias vector. These can be used to set the weights of another
| `Dense` layer:
|
| >>> layer_a = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1,
| ... kernel_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1.))
| >>> a_out = layer_a(tf.convert_to_tensor([[1., 2., 3.]]))
| >>> layer_a.get_weights()
| [array([[1.],
| [1.],
| [1.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)]
| >>> layer_b = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1,
| ... kernel_initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2.))
| >>> b_out = layer_b(tf.convert_to_tensor([[10., 20., 30.]]))
| >>> layer_b.get_weights()
| [array([[2.],
| [2.],
| [2.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)]
| >>> layer_b.set_weights(layer_a.get_weights())
| >>> layer_b.get_weights()
| [array([[1.],
| [1.],
| [1.]], dtype=float32), array([0.], dtype=float32)]
|
| Args:
| weights: a list of NumPy arrays. The number
| of arrays and their shape must match
| number of the dimensions of the weights
| of the layer (i.e. it should match the
| output of `get_weights`).
|
| Raises:
| ValueError: If the provided weights list does not match the
| layer's specifications.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from keras.engine.base_layer.Layer:
|
| activity_regularizer
| Optional regularizer function for the output of this layer.
|
| compute_dtype
| The dtype of the layer's computations.
|
| This is equivalent to `Layer.dtype_policy.compute_dtype`. Unless
| mixed precision is used, this is the same as `Layer.dtype`, the dtype of
| the weights.
|
| Layers automatically cast their inputs to the compute dtype, which causes
| computations and the output to be in the compute dtype as well. This is done
| by the base Layer class in `Layer.__call__`, so you do not have to insert
| these casts if implementing your own layer.
|
| Layers often perform certain internal computations in higher precision when
| `compute_dtype` is float16 or bfloat16 for numeric stability. The output
| will still typically be float16 or bfloat16 in such cases.
|
| Returns:
| The layer's compute dtype.
|
| dtype
| The dtype of the layer weights.
|
| This is equivalent to `Layer.dtype_policy.variable_dtype`. Unless
| mixed precision is used, this is the same as `Layer.compute_dtype`, the
| dtype of the layer's computations.
|
| dtype_policy
| The dtype policy associated with this layer.
|
| This is an instance of a `tf.keras.mixed_precision.Policy`.
|
| dynamic
| Whether the layer is dynamic (eager-only); set in the constructor.
|
| inbound_nodes
| Deprecated, do NOT use! Only for compatibility with external Keras.
|
| input
| Retrieves the input tensor(s) of a layer.
|
| Only applicable if the layer has exactly one input,
| i.e. if it is connected to one incoming layer.
|
| Returns:
| Input tensor or list of input tensors.
|
| Raises:
| RuntimeError: If called in Eager mode.
| AttributeError: If no inbound nodes are found.
|
| input_mask
| Retrieves the input mask tensor(s) of a layer.
|
| Only applicable if the layer has exactly one inbound node,
| i.e. if it is connected to one incoming layer.
|
| Returns:
| Input mask tensor (potentially None) or list of input
| mask tensors.
|
| Raises:
| AttributeError: if the layer is connected to
| more than one incoming layers.
|
| input_shape
| Retrieves the input shape(s) of a layer.
|
| Only applicable if the layer has exactly one input,
| i.e. if it is connected to one incoming layer, or if all inputs
| have the same shape.
|
| Returns:
| Input shape, as an integer shape tuple
| (or list of shape tuples, one tuple per input tensor).
|
| Raises:
| AttributeError: if the layer has no defined input_shape.
| RuntimeError: if called in Eager mode.
|
| input_spec
| `InputSpec` instance(s) describing the input format for this layer.
|
| When you create a layer subclass, you can set `self.input_spec` to enable
| the layer to run input compatibility checks when it is called.
| Consider a `Conv2D` layer: it can only be called on a single input tensor
| of rank 4. As such, you can set, in `__init__()`:
|
| ```python
| self.input_spec = tf.keras.layers.InputSpec(ndim=4)
| ```
|
| Now, if you try to call the layer on an input that isn't rank 4
| (for instance, an input of shape `(2,)`, it will raise a nicely-formatted
| error:
|
| ```
| ValueError: Input 0 of layer conv2d is incompatible with the layer:
| expected ndim=4, found ndim=1. Full shape received: [2]
| ```
|
| Input checks that can be specified via `input_spec` include:
| - Structure (e.g. a single input, a list of 2 inputs, etc)
| - Shape
| - Rank (ndim)
| - Dtype
|
| For more information, see `tf.keras.layers.InputSpec`.
|
| Returns:
| A `tf.keras.layers.InputSpec` instance, or nested structure thereof.
|
| losses
| List of losses added using the `add_loss()` API.
|
| Variable regularization tensors are created when this property is accessed,
| so it is eager safe: accessing `losses` under a `tf.GradientTape` will
| propagate gradients back to the corresponding variables.
|
| Examples:
|
| >>> class MyLayer(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
| ... def call(self, inputs):
| ... self.add_loss(tf.abs(tf.reduce_mean(inputs)))
| ... return inputs
| >>> l = MyLayer()
| >>> l(np.ones((10, 1)))
| >>> l.losses
| [1.0]
|
| >>> inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
| >>> x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)(inputs)
| >>> outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
| >>> model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
| >>> # Activity regularization.
| >>> len(model.losses)
| 0
| >>> model.add_loss(tf.abs(tf.reduce_mean(x)))
| >>> len(model.losses)
| 1
|
| >>> inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(10,))
| >>> d = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, kernel_initializer='ones')
| >>> x = d(inputs)
| >>> outputs = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
| >>> model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
| >>> # Weight regularization.
| >>> model.add_loss(lambda: tf.reduce_mean(d.kernel))
| >>> model.losses
| [<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=1.0>]
|
| Returns:
| A list of tensors.
|
| name
| Name of the layer (string), set in the constructor.
|
| non_trainable_variables
| Sequence of non-trainable variables owned by this module and its submodules.
|
| Note: this method uses reflection to find variables on the current instance
| and submodules. For performance reasons you may wish to cache the result
| of calling this method if you don't expect the return value to change.
|
| Returns:
| A sequence of variables for the current module (sorted by attribute
| name) followed by variables from all submodules recursively (breadth
| first).
|
| outbound_nodes
| Deprecated, do NOT use! Only for compatibility with external Keras.
|
| output
| Retrieves the output tensor(s) of a layer.
|
| Only applicable if the layer has exactly one output,
| i.e. if it is connected to one incoming layer.
|
| Returns:
| Output tensor or list of output tensors.
|
| Raises:
| AttributeError: if the layer is connected to more than one incoming
| layers.
| RuntimeError: if called in Eager mode.
|
| output_mask
| Retrieves the output mask tensor(s) of a layer.
|
| Only applicable if the layer has exactly one inbound node,
| i.e. if it is connected to one incoming layer.
|
| Returns:
| Output mask tensor (potentially None) or list of output
| mask tensors.
|
| Raises:
| AttributeError: if the layer is connected to
| more than one incoming layers.
|
| output_shape
| Retrieves the output shape(s) of a layer.
|
| Only applicable if the layer has one output,
| or if all outputs have the same shape.
|
| Returns:
| Output shape, as an integer shape tuple
| (or list of shape tuples, one tuple per output tensor).
|
| Raises:
| AttributeError: if the layer has no defined output shape.
| RuntimeError: if called in Eager mode.
|
| stateful
|
| supports_masking
| Whether this layer supports computing a mask using `compute_mask`.
|
| trainable
|
| trainable_variables
| Sequence of trainable variables owned by this module and its submodules.
|
| Note: this method uses reflection to find variables on the current instance
| and submodules. For performance reasons you may wish to cache the result
| of calling this method if you don't expect the return value to change.
|
| Returns:
| A sequence of variables for the current module (sorted by attribute
| name) followed by variables from all submodules recursively (breadth
| first).
|
| updates
|
| variable_dtype
| Alias of `Layer.dtype`, the dtype of the weights.
|
| variables
| Returns the list of all layer variables/weights.
|
| Alias of `self.weights`.
|
| Note: This will not track the weights of nested `tf.Modules` that are not
| themselves Keras layers.
|
| Returns:
| A list of variables.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Class methods inherited from tensorflow.python.module.module.Module:
|
| with_name_scope(method) from builtins.type
| Decorator to automatically enter the module name scope.
|
| >>> class MyModule(tf.Module):
| ... @tf.Module.with_name_scope
| ... def __call__(self, x):
| ... if not hasattr(self, 'w'):
| ... self.w = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([x.shape[1], 3]))
| ... return tf.matmul(x, self.w)
|
| Using the above module would produce `tf.Variable`s and `tf.Tensor`s whose
| names included the module name:
|
| >>> mod = MyModule()
| >>> mod(tf.ones([1, 2]))
| <tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32, numpy=..., dtype=float32)>
| >>> mod.w
| <tf.Variable 'my_module/Variable:0' shape=(2, 3) dtype=float32,
| numpy=..., dtype=float32)>
|
| Args:
| method: The method to wrap.
|
| Returns:
| The original method wrapped such that it enters the module's name scope.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from tensorflow.python.module.module.Module:
|
| name_scope
| Returns a `tf.name_scope` instance for this class.
|
| submodules
| Sequence of all sub-modules.
|
| Submodules are modules which are properties of this module, or found as
| properties of modules which are properties of this module (and so on).
|
| >>> a = tf.Module()
| >>> b = tf.Module()
| >>> c = tf.Module()
| >>> a.b = b
| >>> b.c = c
| >>> list(a.submodules) == [b, c]
| True
| >>> list(b.submodules) == [c]
| True
| >>> list(c.submodules) == []
| True
|
| Returns:
| A sequence of all submodules.
|
| ----------------------------------------------------------------------
| Data descriptors inherited from tensorflow.python.training.tracking.base.Trackable:
|
| __dict__
| dictionary for instance variables (if defined)
|
| __weakref__
| list of weak references to the object (if defined)
การใช้ชุดย่อยของคุณสมบัติ
ตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ไม่ได้ระบุคุณสมบัติ ดังนั้นคอลัมน์ทั้งหมดจึงถูกใช้เป็นคุณสมบัติอินพุต (ยกเว้นป้ายกำกับ) ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้แสดงวิธีการระบุคุณสมบัติอินพุต
feature_1 = tfdf.keras.FeatureUsage(name="bill_length_mm")
feature_2 = tfdf.keras.FeatureUsage(name="island")
all_features = [feature_1, feature_2]
# Note: This model is only trained with two features. It will not be as good as
# the one trained on all features.
model_2 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(
features=all_features, exclude_non_specified_features=True)
model_2.compile(metrics=["accuracy"])
model_2.fit(x=train_ds, validation_data=test_ds)
print(model_2.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True))
1/4 [======>.......................] - ETA: 0s
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 3
Number of columns by type:
CATEGORICAL: 2 (66.6667%)
NUMERICAL: 1 (33.3333%)
Columns:
CATEGORICAL: 2 (66.6667%)
1: "island" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:4 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Biscoe" 126 (50%)
2: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
NUMERICAL: 1 (33.3333%)
0: "bill_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1643] Subsample hyperparameter given but sampling method does not match.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1656] GOSS alpha hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1665] GOSS beta hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1677] SelGB ratio hyperparameter given but SelGB is disabled.
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
features: "bill_length_mm"
features: "island"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.gradient_boosted_trees.proto.gradient_boosted_trees_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 6
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
shrinkage: 0.1
validation_set_ratio: 0.1
early_stopping: VALIDATION_LOSS_INCREASE
early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead: 30
l2_regularization: 0
lambda_loss: 1
mart {
}
adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration: false
l1_regularization: 0
use_hessian_gain: false
l2_regularization_categorical: 1
apply_link_function: true
compute_permutation_variable_importance: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:404] Default loss set to MULTINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1001] Training gradient boosted tree on 252 example(s) and 2 feature(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1044] 223 examples used for training and 29 examples used for validation
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1426] num-trees:1 train-loss:0.933984 train-accuracy:0.977578 valid-loss:0.948754 valid-accuracy:0.931035
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1428] num-trees:2 train-loss:0.792019 train-accuracy:0.973094 valid-loss:0.830319 valid-accuracy:0.896552
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:2740] Early stop of the training because the validation loss does not decrease anymore. Best valid-loss: 0.2425
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:229] Truncates the model to 78 tree(s) i.e. 26 iteration(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:263] Final model num-trees:26 valid-loss:0.242500 valid-accuracy:0.931035
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmpzdx1sewe
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 78 root(s), 2752 node(s), and 2 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 92ms/step - val_loss: 0.0000e+00 - val_accuracy: 0.9674
2/2 [==============================] - 0s 3ms/step - loss: 0.0000e+00 - accuracy: 0.9674
{'loss': 0.0, 'accuracy': 0.967391312122345}
TF-DF ยึดติดความหมายให้แต่ละคุณลักษณะ ความหมายนี้ควบคุมวิธีที่โมเดลใช้คุณลักษณะนี้ ปัจจุบันรองรับความหมายต่อไปนี้:
- ตัวเลข: โดยทั่วไปสำหรับปริมาณหรือนับกับการสั่งซื้ออย่างเต็มรูปแบบ เช่น อายุของบุคคล หรือจำนวนสิ่งของในกระเป๋า สามารถเป็นทุ่นหรือจำนวนเต็ม ค่าที่หายไปจะแสดงด้วย float(Nan) หรือค่า sparse tensor ที่ว่างเปล่า
- หมวดหมู่: โดยทั่วไปสำหรับประเภท A / ชั้นในชุด จำกัด ของค่าที่เป็นไปได้โดยไม่ต้องสั่งซื้อ ตัวอย่างเช่น สีแดงในชุด {RED, BLUE, GREEN} อาจเป็นสตริงหรือจำนวนเต็มก็ได้ ค่าที่หายไปจะแสดงเป็น "" (ต่อยที่ว่างเปล่า) ค่า -2 หรือด้วยเทนเซอร์เบาบางที่ว่างเปล่า
- เด็ดขาด-Set: ชุดของค่าเด็ดขาด เหมาะสำหรับการแสดงข้อความโทเค็น อาจเป็นสตริงหรือจำนวนเต็มในเมตริกซ์กระจัดกระจายหรือเทนเซอร์ขาด (แนะนำ) ลำดับ/ดัชนีของแต่ละรายการไม่สำคัญ
หากไม่ได้ระบุไว้ ความหมายจะถูกอนุมานจากประเภทการแสดงและแสดงในบันทึกการฝึก:
- int, float (หนาแน่นหรือเบาบาง) → ความหมายเชิงตัวเลข
- str (หนาแน่นหรือเบาบาง) → ความหมายเชิงหมวดหมู่
- int, str (มอมแมม) → ความหมายชุดตามหมวดหมู่
ในบางกรณี ความหมายที่อนุมานไม่ถูกต้อง ตัวอย่างเช่น Enum ที่จัดเก็บเป็นจำนวนเต็มจะถูกจัดหมวดหมู่ตามความหมาย แต่จะถูกตรวจพบเป็นตัวเลข ในกรณีนี้ คุณควรระบุอาร์กิวเมนต์เชิงความหมายในอินพุต education_num เขตของชุดข้อมูลที่ผู้ใหญ่เป็นตัวอย่างคลาสสิก
ชุดข้อมูลนี้ไม่มีคุณลักษณะดังกล่าว อย่างไรก็ตามสำหรับการสาธิตเราจะทำให้การรักษารูปแบบ year เป็นคุณลักษณะเด็ดขาด:
%set_cell_height 300
feature_1 = tfdf.keras.FeatureUsage(name="year", semantic=tfdf.keras.FeatureSemantic.CATEGORICAL)
feature_2 = tfdf.keras.FeatureUsage(name="bill_length_mm")
feature_3 = tfdf.keras.FeatureUsage(name="sex")
all_features = [feature_1, feature_2, feature_3]
model_3 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(features=all_features, exclude_non_specified_features=True)
model_3.compile( metrics=["accuracy"])
with sys_pipes():
model_3.fit(x=train_ds, validation_data=test_ds)
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
1/4 [======>.......................] - ETA: 0s
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 4
Number of columns by type:
CATEGORICAL: 3 (75%)
NUMERICAL: 1 (25%)
Columns:
CATEGORICAL: 3 (75%)
1: "sex" CATEGORICAL num-nas:7 (2.77778%) has-dict vocab-size:3 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"male" 124 (50.6122%)
2: "year" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:2011 no-ood-item
3: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
NUMERICAL: 1 (25%)
0: "bill_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1643] Subsample hyperparameter given but sampling method does not match.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1656] GOSS alpha hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1665] GOSS beta hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1677] SelGB ratio hyperparameter given but SelGB is disabled.
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
features: "bill_length_mm"
features: "sex"
features: "year"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.gradient_boosted_trees.proto.gradient_boosted_trees_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 6
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
shrinkage: 0.1
validation_set_ratio: 0.1
early_stopping: VALIDATION_LOSS_INCREASE
early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead: 30
l2_regularization: 0
lambda_loss: 1
mart {
}
adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration: false
l1_regularization: 0
use_hessian_gain: false
l2_regularization_categorical: 1
apply_link_function: true
compute_permutation_variable_importance: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:404] Default loss set to MULTINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1001] Training gradient boosted tree on 252 example(s) and 3 feature(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1044] 223 examples used for training and 29 examples used for validation
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1426] num-trees:1 train-loss:0.967301 train-accuracy:0.865471 valid-loss:1.017016 valid-accuracy:0.655172
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:2740] Early stop of the training because the validation loss does not decrease anymore. Best valid-loss: 0.761793
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:229] Truncates the model to 45 tree(s) i.e. 15 iteration(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:263] Final model num-trees:15 valid-loss:0.761793 valid-accuracy:0.586207
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmpetvbj79i
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 45 root(s), 1933 node(s), and 3 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 97ms/step - val_loss: 0.0000e+00 - val_accuracy: 0.7935
โปรดทราบว่า year อยู่ในรายการของคุณลักษณะเด็ดขาด (ที่แตกต่างจากการทำงานครั้งแรก)
ไฮเปอร์พารามิเตอร์
Hyper-พารามิเตอร์พารามิเตอร์ของขั้นตอนวิธีการฝึกอบรมที่ส่งผลกระทบต่อคุณภาพของรูปแบบสุดท้าย มีการระบุไว้ในตัวสร้างคลาสโมเดล รายการ Hyper-พารามิเตอร์ที่สามารถมองเห็นได้ด้วยคำสั่ง Colab เครื่องหมายคำถาม (เช่น ?tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel )
หรือคุณสามารถพบพวกเขาใน TensorFlow ตัดสินใจป่า Github หรือ เอกสารประกอบการตัดสินใจป่า Yggdrasil
พารามิเตอร์ไฮเปอร์เริ่มต้นของแต่ละอัลกอริทึมจะตรงกับกระดาษสิ่งพิมพ์เริ่มต้นโดยประมาณ เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่ามีความสอดคล้องกัน คุณลักษณะใหม่และไฮเปอร์พารามิเตอร์ที่ตรงกันจะถูกปิดใช้งานตามค่าเริ่มต้นเสมอ จึงเป็นความคิดที่ดีที่จะปรับแต่งไฮเปอร์พารามิเตอร์ของคุณ
# A classical but slighly more complex model.
model_6 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(
num_trees=500, growing_strategy="BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL", max_depth=8)
model_6.fit(x=train_ds)
1/4 [======>.......................] - ETA: 0s
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 8
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
0: "bill_depth_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:17.1936 min:13.2 max:21.5 sd:1.96763
1: "bill_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
2: "body_mass_g" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:4221 min:2700 max:6300 sd:811.125
3: "flipper_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:201.264 min:172 max:231 sd:14.0793
6: "year" NUMERICAL mean:2008.05 min:2007 max:2009 sd:0.817297
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
4: "island" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:4 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Biscoe" 126 (50%)
5: "sex" CATEGORICAL num-nas:7 (2.77778%) has-dict vocab-size:3 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"male" 124 (50.6122%)
7: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1643] Subsample hyperparameter given but sampling method does not match.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1656] GOSS alpha hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1665] GOSS beta hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1677] SelGB ratio hyperparameter given but SelGB is disabled.
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
features: "bill_depth_mm"
features: "bill_length_mm"
features: "body_mass_g"
features: "flipper_length_mm"
features: "island"
features: "sex"
features: "year"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.gradient_boosted_trees.proto.gradient_boosted_trees_config] {
num_trees: 500
decision_tree {
max_depth: 8
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_best_first_global {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
shrinkage: 0.1
validation_set_ratio: 0.1
early_stopping: VALIDATION_LOSS_INCREASE
early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead: 30
l2_regularization: 0
lambda_loss: 1
mart {
}
adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration: false
l1_regularization: 0
use_hessian_gain: false
l2_regularization_categorical: 1
apply_link_function: true
compute_permutation_variable_importance: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:404] Default loss set to MULTINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1001] Training gradient boosted tree on 252 example(s) and 7 feature(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1044] 223 examples used for training and 29 examples used for validation
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1426] num-trees:1 train-loss:0.917037 train-accuracy:0.991031 valid-loss:0.926836 valid-accuracy:0.965517
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 119ms/step
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:2740] Early stop of the training because the validation loss does not decrease anymore. Best valid-loss: 0.15912
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:229] Truncates the model to 87 tree(s) i.e. 29 iteration(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:263] Final model num-trees:29 valid-loss:0.159120 valid-accuracy:0.965517
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmp0acspar2
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 87 root(s), 4853 node(s), and 7 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f9f80122590>
# A more complex, but possibly, more accurate model.
model_7 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(
num_trees=500,
growing_strategy="BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL",
max_depth=8,
split_axis="SPARSE_OBLIQUE",
categorical_algorithm="RANDOM",
)
model_7.fit(x=train_ds)
1/4 [======>.......................] - ETA: 0s
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 8
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
0: "bill_depth_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:17.1936 min:13.2 max:21.5 sd:1.96763
1: "bill_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
2: "body_mass_g" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:4221 min:2700 max:6300 sd:811.125
3: "flipper_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:201.264 min:172 max:231 sd:14.0793
6: "year" NUMERICAL mean:2008.05 min:2007 max:2009 sd:0.817297
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
4: "island" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:4 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Biscoe" 126 (50%)
5: "sex" CATEGORICAL num-nas:7 (2.77778%) has-dict vocab-size:3 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"male" 124 (50.6122%)
7: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1643] Subsample hyperparameter given but sampling method does not match.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1656] GOSS alpha hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1665] GOSS beta hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1677] SelGB ratio hyperparameter given but SelGB is disabled.
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
features: "bill_depth_mm"
features: "bill_length_mm"
features: "body_mass_g"
features: "flipper_length_mm"
features: "island"
features: "sex"
features: "year"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.gradient_boosted_trees.proto.gradient_boosted_trees_config] {
num_trees: 500
decision_tree {
max_depth: 8
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_best_first_global {
}
categorical {
random {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
sparse_oblique_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
shrinkage: 0.1
validation_set_ratio: 0.1
early_stopping: VALIDATION_LOSS_INCREASE
early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead: 30
l2_regularization: 0
lambda_loss: 1
mart {
}
adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration: false
l1_regularization: 0
use_hessian_gain: false
l2_regularization_categorical: 1
apply_link_function: true
compute_permutation_variable_importance: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:404] Default loss set to MULTINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1001] Training gradient boosted tree on 252 example(s) and 7 feature(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1044] 223 examples used for training and 29 examples used for validation
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1426] num-trees:1 train-loss:0.916409 train-accuracy:0.986547 valid-loss:0.937726 valid-accuracy:0.896552
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 82ms/step
WARNING:tensorflow:5 out of the last 5 calls to <function CoreModel.make_predict_function.<locals>.predict_function_trained at 0x7f9f8009f7a0> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has experimental_relax_shapes=True option that relaxes argument shapes that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:2740] Early stop of the training because the validation loss does not decrease anymore. Best valid-loss: 0.166186
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:229] Truncates the model to 78 tree(s) i.e. 26 iteration(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:263] Final model num-trees:26 valid-loss:0.166186 valid-accuracy:0.965517
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmpv6yz6pmp
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 78 root(s), 3770 node(s), and 7 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
WARNING:tensorflow:5 out of the last 5 calls to <function CoreModel.make_predict_function.<locals>.predict_function_trained at 0x7f9f8009f7a0> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has experimental_relax_shapes=True option that relaxes argument shapes that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f9f80095750>
เมื่อมีการเผยแพร่และนำวิธีการฝึกอบรมใหม่มาใช้ การรวมพารามิเตอร์หลายตัวเข้าด้วยกันสามารถแสดงผลได้ดีหรือดีกว่าพารามิเตอร์เริ่มต้นเกือบตลอดเวลา เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการเปลี่ยนค่าพารามิเตอร์ไฮเปอร์ดีฟอลต์ ชุดค่าผสมที่ดีเหล่านี้จะได้รับการจัดทำดัชนีและพร้อมใช้งานเป็นเทมเพลตไฮเปอร์พารามิเตอร์
ยกตัวอย่างเช่น benchmark_rank1 แม่แบบเป็น combinaison ที่ดีที่สุดเกี่ยวกับการวัดภายในของเรา แม่แบบเหล่านี้จะ versioned ที่จะอนุญาตให้มีเสถียรภาพการกำหนดค่าการฝึกอบรมเช่น benchmark_rank1@v1
# A good template of hyper-parameters.
model_8 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(hyperparameter_template="benchmark_rank1")
model_8.fit(x=train_ds)
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 38ms/step
WARNING:tensorflow:6 out of the last 6 calls to <function CoreModel.make_predict_function.<locals>.predict_function_trained at 0x7f9f607f3ef0> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has experimental_relax_shapes=True option that relaxes argument shapes that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 8
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 5 (62.5%)
0: "bill_depth_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:17.1936 min:13.2 max:21.5 sd:1.96763
1: "bill_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
2: "body_mass_g" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:4221 min:2700 max:6300 sd:811.125
3: "flipper_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:201.264 min:172 max:231 sd:14.0793
6: "year" NUMERICAL mean:2008.05 min:2007 max:2009 sd:0.817297
CATEGORICAL: 3 (37.5%)
4: "island" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:4 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"Biscoe" 126 (50%)
5: "sex" CATEGORICAL num-nas:7 (2.77778%) has-dict vocab-size:3 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"male" 124 (50.6122%)
7: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1643] Subsample hyperparameter given but sampling method does not match.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1656] GOSS alpha hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1665] GOSS beta hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1677] SelGB ratio hyperparameter given but SelGB is disabled.
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
features: "bill_depth_mm"
features: "bill_length_mm"
features: "body_mass_g"
features: "flipper_length_mm"
features: "island"
features: "sex"
features: "year"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.gradient_boosted_trees.proto.gradient_boosted_trees_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 6
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_best_first_global {
}
categorical {
random {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
sparse_oblique_split {
num_projections_exponent: 1
normalization: MIN_MAX
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
shrinkage: 0.1
validation_set_ratio: 0.1
early_stopping: VALIDATION_LOSS_INCREASE
early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead: 30
l2_regularization: 0
lambda_loss: 1
mart {
}
adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration: false
l1_regularization: 0
use_hessian_gain: false
l2_regularization_categorical: 1
apply_link_function: true
compute_permutation_variable_importance: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:404] Default loss set to MULTINOMIAL_LOG_LIKELIHOOD
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1001] Training gradient boosted tree on 252 example(s) and 7 feature(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1044] 223 examples used for training and 29 examples used for validation
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1426] num-trees:1 train-loss:0.916678 train-accuracy:0.991031 valid-loss:0.935327 valid-accuracy:0.896552
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:2740] Early stop of the training because the validation loss does not decrease anymore. Best valid-loss: 0.0875364
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:229] Truncates the model to 135 tree(s) i.e. 45 iteration(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:263] Final model num-trees:45 valid-loss:0.087536 valid-accuracy:0.965517
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmp_ta7z9ad
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 135 root(s), 5145 node(s), and 7 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
WARNING:tensorflow:6 out of the last 6 calls to <function CoreModel.make_predict_function.<locals>.predict_function_trained at 0x7f9f607f3ef0> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has experimental_relax_shapes=True option that relaxes argument shapes that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f9f607de590>
tempaltes ที่มีอยู่สามารถใช้ได้กับ predefined_hyperparameters โปรดทราบว่าอัลกอริธึมการเรียนรู้ที่แตกต่างกันมีเทมเพลตที่แตกต่างกัน แม้ว่าชื่อจะคล้ายกันก็ตาม
# The hyper-parameter templates of the Gradient Boosted Tree model.
print(tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel.predefined_hyperparameters())
[HyperParameterTemplate(name='better_default', version=1, parameters={'growing_strategy': 'BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL'}, description='A configuration that is generally better than the default parameters without being more expensive.'), HyperParameterTemplate(name='benchmark_rank1', version=1, parameters={'growing_strategy': 'BEST_FIRST_GLOBAL', 'categorical_algorithm': 'RANDOM', 'split_axis': 'SPARSE_OBLIQUE', 'sparse_oblique_normalization': 'MIN_MAX', 'sparse_oblique_num_projections_exponent': 1.0}, description='Top ranking hyper-parameters on our benchmark slightly modified to run in reasonable time.')]
การประมวลผลคุณสมบัติล่วงหน้า
ในบางครั้ง ฟีเจอร์ก่อนการประมวลผลอาจจำเป็นในการใช้สัญญาณที่มีโครงสร้างที่ซับซ้อน เพื่อทำให้โมเดลเป็นปกติหรือใช้การเรียนรู้การถ่ายโอน การประมวลผลล่วงหน้าสามารถทำได้หนึ่งในสามวิธี:
การประมวลผลล่วงหน้าบนดาต้าเฟรมของ Pandas โซลูชันนี้ใช้งานง่ายและโดยทั่วไปเหมาะสำหรับการทดลอง แต่ตรรกะก่อนการประมวลผลจะไม่ถูกส่งออกในรูปแบบโดย
model.save()Keras กระบวนการเตรียมการผลิต : ในขณะที่มีความซับซ้อนมากกว่าการแก้ปัญหาก่อนหน้านี้ Keras กระบวนการเตรียมการผลิตเป็นที่บรรจุในรูปแบบ
TensorFlow คอลัมน์คุณสมบัติ : API นี้เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของห้องสมุด TF ประมาณการ (= Keras!) และการวางแผนสำหรับการเลิกใช้ โซลูชันนี้น่าสนใจเมื่อใช้โค้ดประมวลผลล่วงหน้าที่มีอยู่
ในตัวอย่างต่อไปก่อนประมวลผล body_mass_g คุณลักษณะเข้า body_mass_kg = body_mass_g / 1000 bill_length_mm มีการบริโภคโดยไม่ต้องก่อนการประมวลผล โปรดทราบว่าการเปลี่ยนแปลงแบบโมโนโทนิกดังกล่าวโดยทั่วไปไม่มีผลกระทบต่อแบบจำลองการตัดสินใจของฟอเรสต์
%set_cell_height 300
body_mass_g = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(1,), name="body_mass_g")
body_mass_kg = body_mass_g / 1000.0
bill_length_mm = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=(1,), name="bill_length_mm")
raw_inputs = {"body_mass_g": body_mass_g, "bill_length_mm": bill_length_mm}
processed_inputs = {"body_mass_kg": body_mass_kg, "bill_length_mm": bill_length_mm}
# "preprocessor" contains the preprocessing logic.
preprocessor = tf.keras.Model(inputs=raw_inputs, outputs=processed_inputs)
# "model_4" contains both the pre-processing logic and the decision forest.
model_4 = tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel(preprocessing=preprocessor)
model_4.fit(x=train_ds)
model_4.summary()
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/keras/engine/functional.py:559: UserWarning: Input dict contained keys ['island', 'bill_depth_mm', 'flipper_length_mm', 'sex', 'year'] which did not match any model input. They will be ignored by the model.
inputs = self._flatten_to_reference_inputs(inputs)
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 16ms/step
Model: "random_forest_model_1"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
model (Functional) {'body_mass_kg': (None, 0
1),
'bill_length_mm': (None
, 1)}
=================================================================
Total params: 1
Trainable params: 0
Non-trainable params: 1
_________________________________________________________________
Type: "RANDOM_FOREST"
Task: CLASSIFICATION
Label: "__LABEL"
Input Features (2):
bill_length_mm
body_mass_kg
No weights
Variable Importance: MEAN_MIN_DEPTH:
1. "__LABEL" 3.902486 ################
2. "body_mass_kg" 1.189670 ####
3. "bill_length_mm" 0.085316
Variable Importance: NUM_AS_ROOT:
1. "bill_length_mm" 277.000000 ################
2. "body_mass_kg" 23.000000
Variable Importance: NUM_NODES:
1. "bill_length_mm" 1662.000000 ################
2. "body_mass_kg" 1254.000000
Variable Importance: SUM_SCORE:
1. "bill_length_mm" 44153.014873 ################
2. "body_mass_kg" 29047.432848
Winner take all: true
Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870757
Number of trees: 300
Total number of nodes: 6132
Number of nodes by tree:
Count: 300 Average: 20.44 StdDev: 3.36745
Min: 11 Max: 27 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 11, 12) 2 0.67% 0.67%
[ 12, 13) 0 0.00% 0.67%
[ 13, 14) 6 2.00% 2.67% #
[ 14, 15) 0 0.00% 2.67%
[ 15, 16) 19 6.33% 9.00% ###
[ 16, 17) 0 0.00% 9.00%
[ 17, 18) 49 16.33% 25.33% #######
[ 18, 19) 0 0.00% 25.33%
[ 19, 20) 56 18.67% 44.00% ########
[ 20, 21) 0 0.00% 44.00%
[ 21, 22) 67 22.33% 66.33% ##########
[ 22, 23) 0 0.00% 66.33%
[ 23, 24) 53 17.67% 84.00% ########
[ 24, 25) 0 0.00% 84.00%
[ 25, 26) 36 12.00% 96.00% #####
[ 26, 27) 0 0.00% 96.00%
[ 27, 27] 12 4.00% 100.00% ##
Depth by leafs:
Count: 3216 Average: 3.94092 StdDev: 1.28045
Min: 1 Max: 8 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 1, 2) 51 1.59% 1.59% #
[ 2, 3) 317 9.86% 11.44% ###
[ 3, 4) 879 27.33% 38.77% #########
[ 4, 5) 978 30.41% 69.19% ##########
[ 5, 6) 610 18.97% 88.15% ######
[ 6, 7) 289 8.99% 97.14% ###
[ 7, 8) 80 2.49% 99.63% #
[ 8, 8] 12 0.37% 100.00%
Number of training obs by leaf:
Count: 3216 Average: 23.5075 StdDev: 28.8461
Min: 5 Max: 117 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 5, 10) 2106 65.49% 65.49% ##########
[ 10, 16) 180 5.60% 71.08% #
[ 16, 21) 17 0.53% 71.61%
[ 21, 27) 12 0.37% 71.98%
[ 27, 33) 23 0.72% 72.70%
[ 33, 38) 59 1.83% 74.53%
[ 38, 44) 106 3.30% 77.83% #
[ 44, 50) 81 2.52% 80.35%
[ 50, 55) 36 1.12% 81.47%
[ 55, 61) 31 0.96% 82.43%
[ 61, 67) 61 1.90% 84.33%
[ 67, 72) 78 2.43% 86.75%
[ 72, 78) 103 3.20% 89.96%
[ 78, 84) 120 3.73% 93.69% #
[ 84, 89) 79 2.46% 96.14%
[ 89, 95) 65 2.02% 98.17%
[ 95, 101) 34 1.06% 99.22%
[ 101, 106) 15 0.47% 99.69%
[ 106, 112) 9 0.28% 99.97%
[ 112, 117] 1 0.03% 100.00%
Attribute in nodes:
1662 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
1254 : body_mass_kg [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 0:
277 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
23 : body_mass_kg [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 1:
509 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
340 : body_mass_kg [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 2:
829 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
801 : body_mass_kg [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 3:
1287 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
1026 : body_mass_kg [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 5:
1636 : bill_length_mm [NUMERICAL]
1231 : body_mass_kg [NUMERICAL]
Condition type in nodes:
2916 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 0:
300 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 1:
849 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 2:
1630 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 3:
2313 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 5:
2867 : HigherCondition
Node format: NOT_SET
Training OOB:
trees: 1, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.917647 logloss:2.9683
trees: 11, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912351 logloss:1.92845
trees: 21, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.11427
trees: 31, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.12232
trees: 41, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.12847
trees: 51, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.990838
trees: 62, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.994012
trees: 72, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.994701
trees: 82, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.995821
trees: 92, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998233
trees: 102, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998181
trees: 112, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998903
trees: 122, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998643
trees: 132, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.99731
trees: 142, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996077
trees: 152, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996836
trees: 162, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996395
trees: 172, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996696
trees: 182, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998245
trees: 192, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.997358
trees: 202, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.999001
trees: 213, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998658
trees: 223, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.00071
trees: 233, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.00151
trees: 243, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.874558
trees: 253, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.872911
trees: 263, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.871938
trees: 273, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.871203
trees: 283, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.86921
trees: 293, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870217
trees: 300, Out-of-bag evaluation: accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870757
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 3
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 2 (66.6667%)
CATEGORICAL: 1 (33.3333%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 2 (66.6667%)
0: "bill_length_mm" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
1: "body_mass_kg" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:4.221 min:2.7 max:6.3 sd:0.811125
CATEGORICAL: 1 (33.3333%)
2: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "RANDOM_FOREST"
features: "bill_length_mm"
features: "body_mass_kg"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.random_forest.proto.random_forest_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 16
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
winner_take_all_inference: true
compute_oob_performances: true
compute_oob_variable_importances: false
adapt_bootstrap_size_ratio_for_maximum_training_duration: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO random_forest.cc:315] Training random forest on 252 example(s) and 2 feature(s).
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 1/300 (tree index:1) done accuracy:0.917647 logloss:2.9683
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 11/300 (tree index:12) done accuracy:0.912351 logloss:1.92845
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 21/300 (tree index:22) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.11427
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 31/300 (tree index:30) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.12232
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 41/300 (tree index:40) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.12847
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 51/300 (tree index:50) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.990838
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 62/300 (tree index:61) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.994012
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 72/300 (tree index:71) done accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.994701
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 82/300 (tree index:81) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.995821
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 92/300 (tree index:91) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998233
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 102/300 (tree index:100) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998181
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 112/300 (tree index:111) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998903
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 122/300 (tree index:121) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998643
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 132/300 (tree index:132) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.99731
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 142/300 (tree index:141) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996077
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 152/300 (tree index:152) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996836
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 162/300 (tree index:159) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996395
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 172/300 (tree index:171) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996696
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 182/300 (tree index:181) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998245
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 192/300 (tree index:191) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.997358
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 202/300 (tree index:201) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.999001
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 213/300 (tree index:211) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998658
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 223/300 (tree index:222) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.00071
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 233/300 (tree index:232) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.00151
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 243/300 (tree index:242) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.874558
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 253/300 (tree index:252) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.872911
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 263/300 (tree index:261) done accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.871938
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 273/300 (tree index:272) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.871203
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 283/300 (tree index:283) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.86921
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 293/300 (tree index:292) done accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870217
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 300/300 (tree index:299) done accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870757
[INFO random_forest.cc:696] Final OOB metrics: accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870757
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmp7wtb85on
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 300 root(s), 6132 node(s), and 2 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้นำตรรกะเดิมไปใช้ใหม่โดยใช้คอลัมน์คุณลักษณะ TensorFlow
def g_to_kg(x):
return x / 1000
feature_columns = [
tf.feature_column.numeric_column("body_mass_g", normalizer_fn=g_to_kg),
tf.feature_column.numeric_column("bill_length_mm"),
]
preprocessing = tf.keras.layers.DenseFeatures(feature_columns)
model_5 = tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel(preprocessing=preprocessing)
model_5.compile(metrics=["accuracy"])
model_5.fit(x=train_ds)
4/4 [==============================] - 0s 16ms/step
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 4
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 252
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 252
Number of columns: 3
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 2 (66.6667%)
CATEGORICAL: 1 (33.3333%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 2 (66.6667%)
0: "dense_features/concat:0.0" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:44.1884 min:33.1 max:59.6 sd:5.36528
1: "dense_features/concat:0.1" NUMERICAL num-nas:2 (0.793651%) mean:4.221 min:2.7 max:6.3 sd:0.811125
CATEGORICAL: 1 (33.3333%)
2: "__LABEL" CATEGORICAL integerized vocab-size:4 no-ood-item
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "RANDOM_FOREST"
features: "dense_features/concat:0\\.0"
features: "dense_features/concat:0\\.1"
label: "__LABEL"
task: CLASSIFICATION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.random_forest.proto.random_forest_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 16
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
winner_take_all_inference: true
compute_oob_performances: true
compute_oob_variable_importances: false
adapt_bootstrap_size_ratio_for_maximum_training_duration: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO random_forest.cc:315] Training random forest on 252 example(s) and 2 feature(s).
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 1/300 (tree index:0) done accuracy:0.877778 logloss:4.40534
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 11/300 (tree index:9) done accuracy:0.912351 logloss:1.92845
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 21/300 (tree index:20) done accuracy:0.904762 logloss:1.1152
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 31/300 (tree index:30) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:1.12252
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 41/300 (tree index:40) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.12847
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 51/300 (tree index:50) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.990838
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 61/300 (tree index:60) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.992791
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 71/300 (tree index:70) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.993973
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 81/300 (tree index:80) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.995832
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 91/300 (tree index:90) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.997874
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 101/300 (tree index:99) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998375
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 111/300 (tree index:110) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998195
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 121/300 (tree index:120) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.998617
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 131/300 (tree index:132) done accuracy:0.90873 logloss:0.997612
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 141/300 (tree index:142) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.995196
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 151/300 (tree index:152) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996306
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 161/300 (tree index:159) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.995389
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 171/300 (tree index:169) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.996696
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 181/300 (tree index:182) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998122
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 191/300 (tree index:191) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.997473
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 201/300 (tree index:201) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998968
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 211/300 (tree index:211) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.998485
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 221/300 (tree index:221) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.00061
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 231/300 (tree index:230) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:1.00203
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 241/300 (tree index:238) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.874645
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 251/300 (tree index:248) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.872291
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 261/300 (tree index:261) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.873186
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 272/300 (tree index:271) done accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.871294
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 282/300 (tree index:280) done accuracy:0.912698 logloss:0.86903
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 292/300 (tree index:291) done accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870345
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 300/300 (tree index:299) done accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870757
[INFO random_forest.cc:696] Final OOB metrics: accuracy:0.916667 logloss:0.870757
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmp8zmkaeqx
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 300 root(s), 6132 node(s), and 2 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
<keras.callbacks.History at 0x7f9f8040f390>
ฝึกแบบจำลองการถดถอย
ตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ฝึกโมเดลการจัดประเภท (TF-DF ไม่แยกความแตกต่างระหว่างการจัดประเภทไบนารีและการจัดประเภทหลายคลาส) ในตัวอย่างต่อไปการฝึกอบรมรูปแบบการถดถอยใน ชุดข้อมูลที่หอยเป๋าฮื้อ วัตถุประสงค์ของชุดข้อมูลนี้คือเพื่อทำนายจำนวนวงแหวนของหอยเป๋าฮื้อ

# Download the dataset.
!wget -q https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/data/abalone_raw.csv -O /tmp/abalone.csv
dataset_df = pd.read_csv("/tmp/abalone.csv")
print(dataset_df.head(3))
Type LongestShell Diameter Height WholeWeight ShuckedWeight \ 0 M 0.455 0.365 0.095 0.5140 0.2245 1 M 0.350 0.265 0.090 0.2255 0.0995 2 F 0.530 0.420 0.135 0.6770 0.2565 VisceraWeight ShellWeight Rings 0 0.1010 0.15 15 1 0.0485 0.07 7 2 0.1415 0.21 9
# Split the dataset into a training and testing dataset.
train_ds_pd, test_ds_pd = split_dataset(dataset_df)
print("{} examples in training, {} examples for testing.".format(
len(train_ds_pd), len(test_ds_pd)))
# Name of the label column.
label = "Rings"
train_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_ds_pd, label=label, task=tfdf.keras.Task.REGRESSION)
test_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_ds_pd, label=label, task=tfdf.keras.Task.REGRESSION)
2896 examples in training, 1281 examples for testing. /tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow_decision_forests/keras/core.py:1612: FutureWarning: In a future version of pandas all arguments of DataFrame.drop except for the argument 'labels' will be keyword-only features_dataframe = dataframe.drop(label, 1)
%set_cell_height 300
# Configure the model.
model_7 = tfdf.keras.RandomForestModel(task = tfdf.keras.Task.REGRESSION)
# Optional.
model_7.compile(metrics=["mse"])
# Train the model.
with sys_pipes():
model_7.fit(x=train_ds)
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
25/46 [===============>..............] - ETA: 0s
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 46
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 2896
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 2896
Number of columns: 9
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 8 (88.8889%)
CATEGORICAL: 1 (11.1111%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 8 (88.8889%)
0: "Diameter" NUMERICAL mean:0.40852 min:0.055 max:0.63 sd:0.0990864
1: "Height" NUMERICAL mean:0.140059 min:0 max:1.13 sd:0.04324
2: "LongestShell" NUMERICAL mean:0.525167 min:0.075 max:0.8 sd:0.120085
3: "ShellWeight" NUMERICAL mean:0.240438 min:0.0015 max:1.005 sd:0.139656
4: "ShuckedWeight" NUMERICAL mean:0.362275 min:0.001 max:1.488 sd:0.222695
6: "VisceraWeight" NUMERICAL mean:0.18221 min:0.0005 max:0.76 sd:0.110215
7: "WholeWeight" NUMERICAL mean:0.835914 min:0.002 max:2.8255 sd:0.493095
8: "__LABEL" NUMERICAL mean:9.89572 min:1 max:29 sd:3.19208
CATEGORICAL: 1 (11.1111%)
5: "Type" CATEGORICAL has-dict vocab-size:4 zero-ood-items most-frequent:"M" 1057 (36.4986%)
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "RANDOM_FOREST"
features: "Diameter"
features: "Height"
features: "LongestShell"
features: "ShellWeight"
features: "ShuckedWeight"
features: "Type"
features: "VisceraWeight"
features: "WholeWeight"
label: "__LABEL"
task: REGRESSION
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.random_forest.proto.random_forest_config] {
num_trees: 300
decision_tree {
max_depth: 16
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
winner_take_all_inference: true
compute_oob_performances: true
compute_oob_variable_importances: false
adapt_bootstrap_size_ratio_for_maximum_training_duration: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO random_forest.cc:315] Training random forest on 2896 example(s) and 8 feature(s).
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 1/300 (tree index:4) done rmse:2.65458
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 11/300 (tree index:9) done rmse:2.23049
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 21/300 (tree index:20) done rmse:2.16349
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 31/300 (tree index:28) done rmse:2.14447
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 41/300 (tree index:40) done rmse:2.1277
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 51/300 (tree index:50) done rmse:2.1135
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 61/300 (tree index:59) done rmse:2.10612
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 71/300 (tree index:69) done rmse:2.11104
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 81/300 (tree index:80) done rmse:2.11052
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 91/300 (tree index:92) done rmse:2.10818
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 101/300 (tree index:101) done rmse:2.10873
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 111/300 (tree index:108) done rmse:2.10696
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 121/300 (tree index:120) done rmse:2.10652
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 131/300 (tree index:129) done rmse:2.10811
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 141/300 (tree index:138) done rmse:2.10587
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 151/300 (tree index:153) done rmse:2.10578
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 161/300 (tree index:159) done rmse:2.10376
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 171/300 (tree index:169) done rmse:2.10388
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 181/300 (tree index:179) done rmse:2.1034
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 191/300 (tree index:189) done rmse:2.10272
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 201/300 (tree index:202) done rmse:2.10077
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 211/300 (tree index:211) done rmse:2.10126
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 221/300 (tree index:219) done rmse:2.10128
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 231/300 (tree index:229) done rmse:2.10058
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 241/300 (tree index:242) done rmse:2.10035
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 251/300 (tree index:250) done rmse:2.0999
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 261/300 (tree index:259) done rmse:2.10021
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 271/300 (tree index:269) done rmse:2.1001
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 281/300 (tree index:282) done rmse:2.09985
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 291/300 (tree index:292) done rmse:2.09927
[INFO random_forest.cc:628] Training of tree 300/300 (tree index:298) done rmse:2.09961
[INFO random_forest.cc:696] Final OOB metrics: rmse:2.09961
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmpceztfba5
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
[INFO decision_forest.cc:590] Model loaded with 300 root(s), 259840 node(s), and 8 input feature(s).
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
46/46 [==============================] - 2s 36ms/step
# Evaluate the model on the test dataset.
evaluation = model_7.evaluate(test_ds, return_dict=True)
print(evaluation)
print()
print(f"MSE: {evaluation['mse']}")
print(f"RMSE: {math.sqrt(evaluation['mse'])}")
WARNING:tensorflow:5 out of the last 9 calls to <function CoreModel.make_test_function.<locals>.test_function at 0x7fa09077c290> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has experimental_relax_shapes=True option that relaxes argument shapes that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
WARNING:tensorflow:5 out of the last 9 calls to <function CoreModel.make_test_function.<locals>.test_function at 0x7fa09077c290> triggered tf.function retracing. Tracing is expensive and the excessive number of tracings could be due to (1) creating @tf.function repeatedly in a loop, (2) passing tensors with different shapes, (3) passing Python objects instead of tensors. For (1), please define your @tf.function outside of the loop. For (2), @tf.function has experimental_relax_shapes=True option that relaxes argument shapes that can avoid unnecessary retracing. For (3), please refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/function#controlling_retracing and https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/function for more details.
46/46 [==============================] - 0s 5ms/step - loss: 0.0000e+00 - mse: 1.8496
{'loss': 0.0, 'mse': 1.8496248722076416}
MSE: 1.8496248722076416
RMSE: 1.3600091441632447
การฝึกอบรมรูปแบบการจัดอันดับ
Finaly หลังจากที่ได้รับการฝึกอบรมการจัดหมวดหมู่และแบบจำลองการถดถอยการฝึกอบรม การจัดอันดับ รุ่น
เป้าหมายของการจัดอันดับคือการรับรายการสั่งซื้อสินค้าตามความสำคัญ "คุณค่า" ของความเกี่ยวข้องไม่สำคัญโดยตรง การจัดอันดับชุดของเอกสารเกี่ยวกับการค้นหาของผู้ใช้ที่มีเป็นตัวอย่างของปัญหาการจัดอันดับ: มันเป็นสิ่งสำคัญเท่านั้นที่จะได้รับการสั่งซื้อที่เหมาะสมที่เอกสารด้านบนมีความสำคัญมากขึ้น
TF-DF คาดว่าชุดข้อมูลการจัดอันดับจะถูกนำเสนอในรูปแบบ "แบน" ชุดข้อมูลเอกสาร+คิวรีอาจมีลักษณะดังนี้:
| แบบสอบถาม | document_id | คุณลักษณะ_1 | คุณลักษณะ_2 | ความเกี่ยวข้อง/ฉลาก |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| แมว | 1 | 0.1 | สีฟ้า | 4 |
| แมว | 2 | 0.5 | เขียว | 1 |
| แมว | 3 | 0.2 | สีแดง | 2 |
| สุนัข | 4 | NA | สีแดง | 0 |
| สุนัข | 5 | 0.2 | สีแดง | 1 |
| สุนัข | 6 | 0.6 | เขียว | 1 |
ความเกี่ยวข้อง / ฉลากเป็นจุดลอยค่าตัวเลขระหว่าง 0 และ 5 (โดยทั่วไประหว่าง 0 และ 4) โดยที่ 0 หมายถึง "ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง" 4 หมายถึง "ความเกี่ยวข้องมาก" และ 5 หมายถึง "เช่นเดียวกับการค้นหา"
ที่น่าสนใจคือ ป่าเพื่อการตัดสินใจมักเป็นตัวกำหนดที่ดี และแบบจำลองการจัดอันดับที่ล้ำสมัยหลายแบบก็คือป่าเพื่อการตัดสินใจ
ในตัวอย่างนี้ใช้ตัวอย่างของการ LETOR3 ชุด แม่นยำมากขึ้นเราต้องการที่จะดาวน์โหลด OHSUMED.zip จาก ซื้อคืนภาค LETOR3 ชุดข้อมูลนี้จัดเก็บในรูปแบบ libsvm ดังนั้น เราจะต้องแปลงเป็น csv
%set_cell_height 200
archive_path = tf.keras.utils.get_file("letor.zip",
"https://download.microsoft.com/download/E/7/E/E7EABEF1-4C7B-4E31-ACE5-73927950ED5E/Letor.zip",
extract=True)
# Path to the train and test dataset using libsvm format.
raw_dataset_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(archive_path),"OHSUMED/Data/All/OHSUMED.txt")
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object> Downloading data from https://download.microsoft.com/download/E/7/E/E7EABEF1-4C7B-4E31-ACE5-73927950ED5E/Letor.zip 61825024/61824018 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step 61833216/61824018 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step
ชุดข้อมูลถูกจัดเก็บเป็นไฟล์ .txt ในรูปแบบเฉพาะ ดังนั้นก่อนอื่นให้แปลงเป็นไฟล์ csv
def convert_libsvm_to_csv(src_path, dst_path):
"""Converts a libsvm ranking dataset into a flat csv file.
Note: This code is specific to the LETOR3 dataset.
"""
dst_handle = open(dst_path, "w")
first_line = True
for src_line in open(src_path,"r"):
# Note: The last 3 items are comments.
items = src_line.split(" ")[:-3]
relevance = items[0]
group = items[1].split(":")[1]
features = [ item.split(":") for item in items[2:]]
if first_line:
# Csv header
dst_handle.write("relevance,group," + ",".join(["f_" + feature[0] for feature in features]) + "\n")
first_line = False
dst_handle.write(relevance + ",g_" + group + "," + (",".join([feature[1] for feature in features])) + "\n")
dst_handle.close()
# Convert the dataset.
csv_dataset_path="/tmp/ohsumed.csv"
convert_libsvm_to_csv(raw_dataset_path, csv_dataset_path)
# Load a dataset into a Pandas Dataframe.
dataset_df = pd.read_csv(csv_dataset_path)
# Display the first 3 examples.
dataset_df.head(3)
train_ds_pd, test_ds_pd = split_dataset(dataset_df)
print("{} examples in training, {} examples for testing.".format(
len(train_ds_pd), len(test_ds_pd)))
# Display the first 3 examples of the training dataset.
train_ds_pd.head(3)
11319 examples in training, 4821 examples for testing.
ในชุดนี้ relevance กำหนดตำแหน่งบนพื้นโลกความจริงในหมู่แถวเดียวกัน group
# Name of the relevance and grouping columns.
relevance = "relevance"
ranking_train_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_ds_pd, label=relevance, task=tfdf.keras.Task.RANKING)
ranking_test_ds = tfdf.keras.pd_dataframe_to_tf_dataset(train_ds_pd, label=relevance, task=tfdf.keras.Task.RANKING)
/tmpfs/src/tf_docs_env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/tensorflow_decision_forests/keras/core.py:1612: FutureWarning: In a future version of pandas all arguments of DataFrame.drop except for the argument 'labels' will be keyword-only features_dataframe = dataframe.drop(label, 1)
%set_cell_height 400
model_8 = tfdf.keras.GradientBoostedTreesModel(
task=tfdf.keras.Task.RANKING,
ranking_group="group",
num_trees=50)
with sys_pipes():
model_8.fit(x=ranking_train_ds)
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
171/177 [===========================>..] - ETA: 0s
[INFO kernel.cc:736] Start Yggdrasil model training
[INFO kernel.cc:737] Collect training examples
[INFO kernel.cc:392] Number of batches: 177
[INFO kernel.cc:393] Number of examples: 11319
[INFO kernel.cc:759] Dataset:
Number of records: 11319
Number of columns: 27
Number of columns by type:
NUMERICAL: 26 (96.2963%)
HASH: 1 (3.7037%)
Columns:
NUMERICAL: 26 (96.2963%)
1: "f_1" NUMERICAL mean:1.18217 min:0 max:9 sd:1.11541
2: "f_10" NUMERICAL mean:3.99046 min:0 max:20.6046 sd:3.73218
3: "f_11" NUMERICAL mean:4.60756 min:0 max:59 sd:4.77462
4: "f_12" NUMERICAL mean:2.03091 min:0 max:9.75731 sd:1.64511
5: "f_13" NUMERICAL mean:0.0487304 min:0 max:0.357143 sd:0.0479245
6: "f_14" NUMERICAL mean:0.0476729 min:0 max:0.336056 sd:0.0463874
7: "f_15" NUMERICAL mean:21.7471 min:7.51456 max:40.0616 sd:7.02527
8: "f_16" NUMERICAL mean:6.91506 min:2.01684 max:13.5772 sd:2.23384
9: "f_17" NUMERICAL mean:19.7598 min:9.0472 max:40.1808 sd:6.57407
10: "f_18" NUMERICAL mean:0.202416 min:0 max:1.51088 sd:0.18941
11: "f_19" NUMERICAL mean:20.8352 min:0 max:178.097 sd:20.9669
12: "f_2" NUMERICAL mean:0.805272 min:0 max:4.56435 sd:0.746546
13: "f_20" NUMERICAL mean:1.83596 min:0 max:13.4423 sd:1.70616
14: "f_21" NUMERICAL mean:12.2662 min:3.18098 max:45.0501 sd:6.85595
15: "f_22" NUMERICAL mean:2.31463 min:1.15719 max:3.80778 sd:0.669815
16: "f_23" NUMERICAL mean:-6.10301 min:-9.49097 max:-1.85651 sd:2.20217
17: "f_24" NUMERICAL mean:-5.79457 min:-9.22971 max:-0.691579 sd:1.99232
18: "f_25" NUMERICAL mean:-5.9689 min:-9.60073 max:-0.691579 sd:2.20707
19: "f_3" NUMERICAL mean:0.159851 min:0 max:1 sd:0.164307
20: "f_4" NUMERICAL mean:0.147621 min:0 max:0.892574 sd:0.147925
21: "f_5" NUMERICAL mean:27.1798 min:6.3511 max:55.3932 sd:9.38075
22: "f_6" NUMERICAL mean:8.14849 min:2.03154 max:16.8986 sd:2.74133
23: "f_7" NUMERICAL mean:27.6599 min:14.2035 max:55.1926 sd:9.4262
24: "f_8" NUMERICAL mean:0.626537 min:0 max:3.80599 sd:0.599143
25: "f_9" NUMERICAL mean:6.5037 min:0 max:47.7046 sd:6.04042
26: "__LABEL" NUMERICAL mean:0.439968 min:0 max:2 sd:0.725817
HASH: 1 (3.7037%)
0: "__RANK_GROUP" HASH
Terminology:
nas: Number of non-available (i.e. missing) values.
ood: Out of dictionary.
manually-defined: Attribute which type is manually defined by the user i.e. the type was not automatically inferred.
tokenized: The attribute value is obtained through tokenization.
has-dict: The attribute is attached to a string dictionary e.g. a categorical attribute stored as a string.
vocab-size: Number of unique values.
[INFO kernel.cc:762] Configure learner
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1643] Subsample hyperparameter given but sampling method does not match.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1656] GOSS alpha hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1665] GOSS beta hyperparameter given but GOSS is disabled.
[WARNING gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1677] SelGB ratio hyperparameter given but SelGB is disabled.
[INFO kernel.cc:787] Training config:
learner: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
features: "__RANK_GROUP"
features: "f_1"
features: "f_10"
features: "f_11"
features: "f_12"
features: "f_13"
features: "f_14"
features: "f_15"
features: "f_16"
features: "f_17"
features: "f_18"
features: "f_19"
features: "f_2"
features: "f_20"
features: "f_21"
features: "f_22"
features: "f_23"
features: "f_24"
features: "f_25"
features: "f_3"
features: "f_4"
features: "f_5"
features: "f_6"
features: "f_7"
features: "f_8"
features: "f_9"
label: "__LABEL"
task: RANKING
ranking_group: "__RANK_GROUP"
[yggdrasil_decision_forests.model.gradient_boosted_trees.proto.gradient_boosted_trees_config] {
num_trees: 50
decision_tree {
max_depth: 6
min_examples: 5
in_split_min_examples_check: true
missing_value_policy: GLOBAL_IMPUTATION
allow_na_conditions: false
categorical_set_greedy_forward {
sampling: 0.1
max_num_items: -1
min_item_frequency: 1
}
growing_strategy_local {
}
categorical {
cart {
}
}
num_candidate_attributes_ratio: -1
axis_aligned_split {
}
internal {
sorting_strategy: PRESORTED
}
}
shrinkage: 0.1
validation_set_ratio: 0.1
early_stopping: VALIDATION_LOSS_INCREASE
early_stopping_num_trees_look_ahead: 30
l2_regularization: 0
lambda_loss: 1
mart {
}
adapt_subsample_for_maximum_training_duration: false
l1_regularization: 0
use_hessian_gain: false
l2_regularization_categorical: 1
apply_link_function: true
compute_permutation_variable_importance: false
}
[INFO kernel.cc:790] Deployment config:
num_threads: 6
[INFO kernel.cc:817] Train model
[INFO abstract_learner.cc:126] The ranking_group "__RANK_GROUP" was removed from the input feature set.
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:404] Default loss set to LAMBDA_MART_NDCG5
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1001] Training gradient boosted tree on 11319 example(s) and 25 feature(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:2306] Split training/validation dataset by "__RANK_GROUP". 106 groups found in 11319 examples i.e. 106.783 examples/groups.
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1044] 10276 examples used for training and 1043 examples used for validation
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees_loss.cc:1547] Found 97 groups in 10276 examples.
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees_loss.cc:1547] Found 9 groups in 1043 examples.
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1426] num-trees:1 train-loss:-0.348863 train-NDCG@5:0.348863 valid-loss:-0.271541 valid-NDCG@5:0.271541
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:1426] num-trees:50 train-loss:-0.607105 train-NDCG@5:0.607105 valid-loss:-0.404367 valid-NDCG@5:0.404367
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:229] Truncates the model to 21 tree(s) i.e. 21 iteration(s).
[INFO gradient_boosted_trees.cc:263] Final model num-trees:21 valid-loss:-0.459177 valid-NDCG@5:0.459177
[INFO kernel.cc:828] Export model in log directory: /tmp/tmpo_9lrcak
[INFO kernel.cc:836] Save model in resources
[INFO kernel.cc:988] Loading model from path
177/177 [==============================] - 2s 11ms/step
[INFO abstract_model.cc:993] Engine "GradientBoostedTreesQuickScorerExtended" built
[INFO kernel.cc:848] Use fast generic engine
ณ จุดนี้ keras ไม่ได้เสนอเมตริกการจัดอันดับใดๆ การฝึกอบรมและการตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง (GBDT ใช้ชุดข้อมูลการตรวจสอบความถูกต้อง) จะแสดงในบันทึกการฝึกอบรมแทน ในกรณีนี้การสูญเสีย LAMBDA_MART_NDCG5 และสุดท้าย (เช่นในตอนท้ายของการฝึกอบรม) NDCG (ปกติลดกำไรสะสม) คือ 0.510136 (ดูบรรทัด Final model valid-loss: -0.510136 )
โปรดทราบว่า NDCG เป็นค่าระหว่าง 0 ถึง 1 ยิ่ง NDCG มีขนาดใหญ่เท่าใด โมเดลก็จะยิ่งดีขึ้นเท่านั้น ด้วยเหตุนี้จึงขาดทุนเป็น -NDCG
ก่อนหน้านี้สามารถวิเคราะห์แบบจำลองได้:
%set_cell_height 400
model_8.summary()
<IPython.core.display.Javascript object>
Model: "gradient_boosted_trees_model_5"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
=================================================================
Total params: 1
Trainable params: 0
Non-trainable params: 1
_________________________________________________________________
Type: "GRADIENT_BOOSTED_TREES"
Task: RANKING
Label: "__LABEL"
Rank group: "__RANK_GROUP"
Input Features (25):
f_1
f_10
f_11
f_12
f_13
f_14
f_15
f_16
f_17
f_18
f_19
f_2
f_20
f_21
f_22
f_23
f_24
f_25
f_3
f_4
f_5
f_6
f_7
f_8
f_9
No weights
Variable Importance: MEAN_MIN_DEPTH:
1. "__RANK_GROUP" 4.580857 ################
2. "__LABEL" 4.580857 ################
3. "f_1" 4.571903 ###############
4. "f_2" 4.546650 ###############
5. "f_18" 4.538126 ###############
6. "f_14" 4.484272 ###############
7. "f_11" 4.446549 ###############
8. "f_7" 4.434940 ###############
9. "f_13" 4.431744 ###############
10. "f_15" 4.428829 ###############
11. "f_19" 4.413141 ##############
12. "f_16" 4.395927 ##############
13. "f_20" 4.325392 ##############
14. "f_5" 4.306650 ##############
15. "f_6" 4.304228 ##############
16. "f_23" 4.222661 #############
17. "f_17" 4.152362 #############
18. "f_9" 4.115222 #############
19. "f_25" 3.999537 ############
20. "f_21" 3.980909 ############
21. "f_22" 3.851452 ###########
22. "f_12" 3.820965 ###########
23. "f_10" 3.816843 ###########
24. "f_24" 3.751312 ##########
25. "f_3" 3.556091 #########
26. "f_8" 3.286981 ########
27. "f_4" 1.971756
Variable Importance: NUM_AS_ROOT:
1. "f_4" 10.000000 ################
2. "f_3" 3.000000 ###
3. "f_8" 3.000000 ###
4. "f_24" 2.000000 #
5. "f_10" 1.000000
6. "f_22" 1.000000
7. "f_9" 1.000000
Variable Importance: NUM_NODES:
1. "f_8" 34.000000 ################
2. "f_4" 28.000000 #############
3. "f_22" 27.000000 ############
4. "f_10" 25.000000 ###########
5. "f_21" 23.000000 ##########
6. "f_17" 21.000000 #########
7. "f_23" 21.000000 #########
8. "f_9" 20.000000 #########
9. "f_24" 19.000000 ########
10. "f_12" 18.000000 ########
11. "f_16" 18.000000 ########
12. "f_3" 18.000000 ########
13. "f_6" 17.000000 #######
14. "f_20" 16.000000 #######
15. "f_19" 14.000000 ######
16. "f_15" 13.000000 #####
17. "f_25" 13.000000 #####
18. "f_5" 12.000000 #####
19. "f_7" 10.000000 ####
20. "f_13" 9.000000 ###
21. "f_14" 8.000000 ###
22. "f_11" 7.000000 ##
23. "f_18" 6.000000 ##
24. "f_2" 3.000000
25. "f_1" 2.000000
Variable Importance: SUM_SCORE:
1. "f_4" 2980.573819 ################
2. "f_24" 2158.482164 ###########
3. "f_8" 2084.795939 ###########
4. "f_3" 1550.118161 ########
5. "f_17" 1463.975795 #######
6. "f_10" 1394.182907 #######
7. "f_21" 1294.251099 ######
8. "f_23" 1205.467035 ######
9. "f_22" 927.605266 ####
10. "f_25" 920.474810 ####
11. "f_12" 828.448676 ####
12. "f_9" 808.014761 ####
13. "f_16" 698.778111 ###
14. "f_7" 599.805417 ###
15. "f_5" 543.782969 ##
16. "f_15" 500.776397 ##
17. "f_19" 475.478397 ##
18. "f_6" 446.515160 ##
19. "f_20" 416.825290 ##
20. "f_11" 304.808988 #
21. "f_14" 263.830200 #
22. "f_13" 185.897133
23. "f_1" 109.890124
24. "f_18" 75.664346
25. "f_2" 29.043191
Loss: LAMBDA_MART_NDCG5
Validation loss value: -0.459177
Number of trees per iteration: 1
Node format: NOT_SET
Number of trees: 21
Total number of nodes: 825
Number of nodes by tree:
Count: 21 Average: 39.2857 StdDev: 6.82532
Min: 23 Max: 51 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 23, 24) 1 4.76% 4.76% ##
[ 24, 25) 0 0.00% 4.76%
[ 25, 27) 0 0.00% 4.76%
[ 27, 28) 0 0.00% 4.76%
[ 28, 30) 0 0.00% 4.76%
[ 30, 31) 0 0.00% 4.76%
[ 31, 33) 1 4.76% 9.52% ##
[ 33, 34) 1 4.76% 14.29% ##
[ 34, 36) 6 28.57% 42.86% ##########
[ 36, 37) 0 0.00% 42.86%
[ 37, 38) 1 4.76% 47.62% ##
[ 38, 40) 1 4.76% 52.38% ##
[ 40, 41) 0 0.00% 52.38%
[ 41, 43) 2 9.52% 61.90% ###
[ 43, 44) 4 19.05% 80.95% #######
[ 44, 46) 0 0.00% 80.95%
[ 46, 47) 0 0.00% 80.95%
[ 47, 49) 1 4.76% 85.71% ##
[ 49, 50) 1 4.76% 90.48% ##
[ 50, 51] 2 9.52% 100.00% ###
Depth by leafs:
Count: 423 Average: 4.60284 StdDev: 0.748958
Min: 1 Max: 5 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 1, 2) 1 0.24% 0.24%
[ 2, 3) 8 1.89% 2.13%
[ 3, 4) 38 8.98% 11.11% #
[ 4, 5) 64 15.13% 26.24% ##
[ 5, 5] 312 73.76% 100.00% ##########
Number of training obs by leaf:
Count: 423 Average: 510.156 StdDev: 1820.92
Min: 5 Max: 9742 Ignored: 0
----------------------------------------------
[ 5, 491) 380 89.83% 89.83% ##########
[ 491, 978) 11 2.60% 92.43%
[ 978, 1465) 6 1.42% 93.85%
[ 1465, 1952) 1 0.24% 94.09%
[ 1952, 2439) 1 0.24% 94.33%
[ 2439, 2926) 2 0.47% 94.80%
[ 2926, 3413) 0 0.00% 94.80%
[ 3413, 3900) 1 0.24% 95.04%
[ 3900, 4387) 1 0.24% 95.27%
[ 4387, 4874) 1 0.24% 95.51%
[ 4874, 5360) 1 0.24% 95.74%
[ 5360, 5847) 0 0.00% 95.74%
[ 5847, 6334) 0 0.00% 95.74%
[ 6334, 6821) 2 0.47% 96.22%
[ 6821, 7308) 0 0.00% 96.22%
[ 7308, 7795) 0 0.00% 96.22%
[ 7795, 8282) 1 0.24% 96.45%
[ 8282, 8769) 2 0.47% 96.93%
[ 8769, 9256) 9 2.13% 99.05%
[ 9256, 9742] 4 0.95% 100.00%
Attribute in nodes:
34 : f_8 [NUMERICAL]
28 : f_4 [NUMERICAL]
27 : f_22 [NUMERICAL]
25 : f_10 [NUMERICAL]
23 : f_21 [NUMERICAL]
21 : f_23 [NUMERICAL]
21 : f_17 [NUMERICAL]
20 : f_9 [NUMERICAL]
19 : f_24 [NUMERICAL]
18 : f_3 [NUMERICAL]
18 : f_16 [NUMERICAL]
18 : f_12 [NUMERICAL]
17 : f_6 [NUMERICAL]
16 : f_20 [NUMERICAL]
14 : f_19 [NUMERICAL]
13 : f_25 [NUMERICAL]
13 : f_15 [NUMERICAL]
12 : f_5 [NUMERICAL]
10 : f_7 [NUMERICAL]
9 : f_13 [NUMERICAL]
8 : f_14 [NUMERICAL]
7 : f_11 [NUMERICAL]
6 : f_18 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_2 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_1 [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 0:
10 : f_4 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_8 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_3 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_24 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_9 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_22 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_10 [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 1:
14 : f_4 [NUMERICAL]
7 : f_12 [NUMERICAL]
6 : f_8 [NUMERICAL]
5 : f_22 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_3 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_25 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_24 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_21 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_17 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_10 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_5 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_23 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_9 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_7 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_15 [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 2:
17 : f_4 [NUMERICAL]
12 : f_3 [NUMERICAL]
11 : f_21 [NUMERICAL]
11 : f_12 [NUMERICAL]
10 : f_8 [NUMERICAL]
9 : f_22 [NUMERICAL]
8 : f_24 [NUMERICAL]
8 : f_17 [NUMERICAL]
8 : f_10 [NUMERICAL]
6 : f_25 [NUMERICAL]
5 : f_11 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_6 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_23 [NUMERICAL]
4 : f_20 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_9 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_7 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_19 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_13 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_5 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_15 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_16 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_14 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_1 [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 3:
23 : f_8 [NUMERICAL]
21 : f_4 [NUMERICAL]
18 : f_22 [NUMERICAL]
17 : f_21 [NUMERICAL]
16 : f_3 [NUMERICAL]
14 : f_17 [NUMERICAL]
14 : f_12 [NUMERICAL]
12 : f_24 [NUMERICAL]
11 : f_23 [NUMERICAL]
11 : f_20 [NUMERICAL]
11 : f_10 [NUMERICAL]
10 : f_6 [NUMERICAL]
10 : f_19 [NUMERICAL]
9 : f_9 [NUMERICAL]
9 : f_25 [NUMERICAL]
8 : f_5 [NUMERICAL]
7 : f_7 [NUMERICAL]
5 : f_16 [NUMERICAL]
5 : f_13 [NUMERICAL]
5 : f_11 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_18 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_15 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_2 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_14 [NUMERICAL]
1 : f_1 [NUMERICAL]
Attribute in nodes with depth <= 5:
34 : f_8 [NUMERICAL]
28 : f_4 [NUMERICAL]
27 : f_22 [NUMERICAL]
25 : f_10 [NUMERICAL]
23 : f_21 [NUMERICAL]
21 : f_23 [NUMERICAL]
21 : f_17 [NUMERICAL]
20 : f_9 [NUMERICAL]
19 : f_24 [NUMERICAL]
18 : f_3 [NUMERICAL]
18 : f_16 [NUMERICAL]
18 : f_12 [NUMERICAL]
17 : f_6 [NUMERICAL]
16 : f_20 [NUMERICAL]
14 : f_19 [NUMERICAL]
13 : f_25 [NUMERICAL]
13 : f_15 [NUMERICAL]
12 : f_5 [NUMERICAL]
10 : f_7 [NUMERICAL]
9 : f_13 [NUMERICAL]
8 : f_14 [NUMERICAL]
7 : f_11 [NUMERICAL]
6 : f_18 [NUMERICAL]
3 : f_2 [NUMERICAL]
2 : f_1 [NUMERICAL]
Condition type in nodes:
402 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 0:
21 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 1:
62 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 2:
136 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 3:
246 : HigherCondition
Condition type in nodes with depth <= 5:
402 : HigherCondition
